Abstract
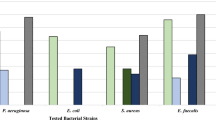
This study aimed to evaluate the antibacterial properties of nine lactic acid bacterial strains. The agar diffusion method (Oxford cup method) was used to assess the antimicrobial activity against pathogenic bacteria in aquaculture. The results showed that all selected strains inhibited the growth of Photobacterium damsel, Vibrio alginolyticus, Listonella anguillarum, Edwardsiella ictaluri, Aeromonas hydrophila, V. arahaemolyticus, Edwardsiella tarda and V. harveyi, but did not inhibit the growth of Metschnikowia bicuspidata. Among these strains of lactic acid bacteria, r1 was selected for its obvious antibacterial activity against eight kinds of pathogenic bacteria by 96-well plate method. Its inhibitory rate reached 96%, and it could inhibit the growth of six pathogenic bacteria at 121 ℃, 20 min and pH 3.5–4.0. It was identified as Lactiplantibacillus plantarum by morphological observation and 16S rRNA sequencing analysis. Because strain r1 was isolated from culture ponds and exerted strong inhibitory effects on pathogenic bacteria, it holds potential as an agent to prevent and control infectious diseases in aquaculture. This study provides a foundation for the development and utilization of probiotics in aquaculture.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abdel-Latif HMR, Soliman AA, Sewilam H, Almeer R, Van Doan H, Alagawany M, MaO D (2020) The influence of raffinose on the growth performance, oxidative status, and immunity in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture Rep. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2020.100457
Ahmed AI, El Moghazy GM, Elsayed TR, HaL G, Khalafalla GM (2021) Molecular identification and in vitro evaluation of probiotic functional properties of some Egyptian lactic acid bacteria and yeasts. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 19(1):114. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43141-021-00212-4
Ahmmed F, Ahmmed MK, Shah MS, Banu GR (2018) Use of indigenous beneficial bacteria (Lactobacillus spp.) as probiotics in shrimp (Penaeus monodon) aquaculture. Research in Agriculture Livestock and Fisheries 5(1): 127–135. https://doi.org/10.3329/ralf.v5i1.36561
Arena MP, Silvain A, Normanno G, Grieco F, Drider D, Spano G, Fiocco D (2016) Use of lactobacillus plantarum strains as a bio-control strategy against food-borne pathogenic microorganisms. Front Microbiol 7:464. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00464
Arig N, Suzer C, Gokvardar A, Basaran F, Coban D, Yildirim S, Kamaci HO, Firat K, Saka S (2013) Effects of Probiotic (Bacillus sp.) Supplementation during Larval Development of Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata, L.). Turkish Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 13(3): 407–414. https://doi.org/10.4194/1303-2712-v13_3_03
Arulmoorthy MP, Anandajothi E, Vasudevan S, Suresh E (2020) Major viral diseases in culturable penaeid shrimps: a review. Aquacult Int 28(5):1939–1967. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-020-00568-3
Bagci U, Ozmen Togay S, Temiz A, Ay M (2019) Probiotic characteristics of bacteriocin-producing Enterococcus faecium strains isolated from human milk and colostrum. Folia Microbiol (praha) 64(6):735–750. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-019-00687-2
Bao J, Jiang H, Shen H, Xing Y, Feng C, Li X, Chen Q (2021) First description of milky disease in the Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis caused by the yeast Metschnikowia bicuspidata. Aquaculture. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735984
Buzdar MA, Chi Z, Wang Q, Hua MX, Chi ZM (2011) Production, purification, and characterization of a novel killer toxin from Kluyveromyces siamensis against a pathogenic yeast in crab. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91(6):1571–1579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3220-8
Chen SC, Chen TH, Wang PC, Chen YC, Liaw LL (2003) Metschnikowia bicuspidata and Enterococcus faecium co-infection in the giant freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Dis Aquat Org 55(2):161. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao055161
Chen L, Yuan S, Liu Q, Mai G, Yang J, Deng D, Zhang B, Liu C, Ma Y (2018) In Vitro design and evaluation of phage cocktails against Aeromonas salmonicida. Front Microbiol 9:1476. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01476
Chika F, Nnadozie, Oghenekaro, Nelson, Pollution OJE (2019) Freshwater environments as reservoirs of antibiotic resistant bacteria and their role in the dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes - ScienceDirect. Environ Pollut 254(Part B): 113067–113067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113067
Cleveland J, Montville TJ, Nes IF, Chikindas ML (2001) Bacteriocins: safe, natural antimicrobials for food preservation. Int J Food Microbiol 71(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-1605(01)00560-8
Cortes-Zavaleta O, Lopez-Malo A, Hernandez-Mendoza A, Garcia HS (2014) Antifungal activity of lactobacilli and its relationship with 3-phenyllactic acid production. Int J Food Microbiol 173:30–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2013.12.016
Dincer E, Kivanc M (2021) In vitro evaluation of probiotic potential of Enterococcus faecium strains isolated from Turkish pastirma. Arch Microbiol 203(6):2831–2841. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02273-y
Fao (2020) The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020. Sustainability in action. Rome, Italy. https://doi.org/10.4060/ca9229en
Fečkaninová A, Koščová J, Mudroňová D, Popelka P, Toropilová J (2017) The use of probiotic bacteria against Aeromonas infections in salmonid aquaculture. Aquaculture 469:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.11.042
Flegel TW (2012) Historic emergence, impact and current status of shrimp pathogens in Asia. J Invertebr Pathol 110(2):166–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jip.2012.03.004
Fooks LJ, Gibson GR (2002) Probiotics as modulators of the gut flora. Br J Nutr 88 Suppl 1(S1): S39–49. https://doi.org/10.1079/BJN2002628
Gaudana SB, Dhanani AS, Bagchi T (2010) Probiotic attributes of Lactobacillus strains isolated from food and of human origin. Br J Nutr 103(11):1620–1628. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114509993643
Gonçalves LMD, Ramos A, Almeida JS, Xavier AMRB, Carrondo MJT (1997) Elucidation of the mechanism of lactic acid growth inhibition and production in batch cultures of Lactobacillus rhamnosus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 48(3):346–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051060
Gou XL, Su YQ, Shi R, Gu JR, Luo GQ, Wang L (2015) Inhibition of Aquatic Pathogenic Bacteria by Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Fish. Fisheries Science 34(9): 575–579. https://doi.org/10.16378/j.cnki.1003-1111.2015.09.008
Govindaraj K, Samayanpaulraj V, Narayanadoss V, Uthandakalaipandian R (2021) Isolation of lactic acid bacteria from intestine of freshwater fishes and elucidation of probiotic potential for aquaculture application. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 13(6):1598–1610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-021-09811-6
Hodar AR, Vasava R, Mahavadiya D, Joshi NH, Solanki H (2021) Herbs and herbal medicines: A prominent source for sustainable aquaculture. J. Exp. Zool. India 5(1): 719–732.
Irene B, Dominic T, Gerardo GR, Julio A, Celia L, Garcia BC, Phelps N, Britta W, Johnson TJ, Qian Z (2019) Antibiotic resistance genes in freshwater trout farms in a watershed in Chile. J Environ Qual 48(5):1462–1471. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2018.12.0431
Jack RW, Tagg JR, Ray B (1995) Bacteriocins of gram-positive bacteria. Microbiol Rev 59(2):171–200. https://doi.org/10.1128/mr.59.2.171-200.1995
James G, Das BC, Jose S, V.J RK, (2021) Bacillus as an aquaculture friendly microbe. Aquacult Int 29(1):323–353. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-020-00630-0
Kabwe M, Brown T, Speirs L, Ku H, Leach M, Chan HT, Petrovski S, Lock P, Tucci J (2020) Novel bacteriophages capable of disrupting biofilms from clinical strains of Aeromonas hydrophila. Front Microbiol 11:194. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.00194
Katharios P, Varvarigos P, Keklikoglou K, Ruetten M, Sojan J, Akter M, Cascarano MC, Tsertou MI, Kokkari C (2020) Native parasite affecting an introduced host in aquaculture: cardiac henneguyosis in the red seabream Pagrus major Temminck & Schlegel (Perciformes: Sparidae) caused by Henneguya aegea n. sp. (Myxosporea: Myxobolidae). Parasit Vectors 13(1): 27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-020-3888-7
Khouadja S, Haddaji N, Hanchi M, Bakhrouf A (2017) Selection of lactic acid bacteria as candidate probiotics forVibrio parahaemolyticusdepuration in pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas). Aquac Res 48(4):1885–1894. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.13026
Kumar V, Roy S, Meena DK, Sarkar UK (2016) Application of probiotics in shrimp aquaculture: importance, mechanisms of action, and methods of administration. Rev Fisheries Sci Aquacult 24(4):342–368. https://doi.org/10.1080/23308249.2016.1193841
Le B, Yang SH (2018) Probiotic potential of novel Lactobacillus strains isolated from salted-fermented shrimp as antagonists for Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Microbiol 56(2):138–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-018-7407-x
Li M, Wei D, Huang S, Huang L, Xu F, Yu Q, Liu M, Li P (2022) Medicinal herbs and phytochemicals to combat pathogens in aquaculture. Aquacult Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-022-00841-7
Li B, Wang YG, Liao MJ, Zhang YG, Rong XJ, Wang JJ, Yu YX, Zhang Z, Ning LG (2021) Isolation and biological characterization of Lactobacillus paracasei isolated from a sea cucumber pond culture system. Progress in Fishery Sciences 42(3): 100–107. https://doi.org/10.19663/j.issn2095-9869.20201216003
Liang X, Zeng J, Wang A, Jianmin YE, Feng J, Liao S (2019) The Inhibition of Pathogenic Vibrios with Lactobacillus Paracasei S-4. Journal of South China Normal University(Natural Science Edition) 51(5): 66–74. https://doi.org/10.6054/j.jscnun.2019067
Lin W, Yue L, Chi Z, Wang X (2008) Marine killer yeasts active against a yeast strain pathogenic to crab Portunus trituberculatus. Dis Aquat Org 80(3):211–218. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao01943
Liu F, Wang F, Du L, Zhao T, Doyle MP, Wang D, Zhang X, Sun Z, Xu W (2018) Antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of phenyllactic acid against Enterobacter cloacae. Food Control 84:442–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.09.004
Liu Z, Xu C, Tian R, Wang W, Ma J, Gu L, Liu F, Jiang Z, Hou J (2021) Screening beneficial bacteriostatic lactic acid bacteria in the intestine and studies of bacteriostatic substances. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 22(7):533–547. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000602
Mayrhofer S, Domig KJ, Mair C, Zitz U, Huys G, Kneifel W (2008) Comparison of broth microdilution, Etest, and agar disk diffusion methods for antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Lactobacillus acidophilus group members. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(12):3745–3748. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02849-07
Miyasaka H, Koga A, Tani Y, Ozaki K-I, Maki T, Hayashi S, Yamamoto S (2021) The effects of a marine photosynthetic bacteria Rhodovulum sulfidophilum on the growth and survival rate of Marsupenaeus japonicus (kuruma shrimp). SDRP Journal of Aquaculture, Fisheries & Fish Science 3(2): 245–249. https://doi.org/10.25177/jaffs.3.2.Ra.10713
Moore MM, Strom MS (2003) Infection and mortality by the yeast Metschnikowia bicuspidata var. bicuspidata in chinook salmon fed live adult brine shrimp ( Artemia franciscana). Aquaculture 220(1–4): 43–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(02)00271-5
Naiel MAE, Farag MR, Gewida AGA, Elnakeeb MA, Amer MS, Alagawany M (2020) Using lactic acid bacteria as an immunostimulants in cultured shrimp with special reference to Lactobacillus spp. Aquacult Int 29(1):219–231. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-020-00620-2
Ng ZJ, Zarin MA, Lee CK, Phapugrangkul P, Tan JS (2020) Isolation and characterization of Enterococcus faecium DSM 20477 with ability to secrete antimicrobial substance for the inhibition of oral pathogen Streptococcus mutans UKMCC 1019. Arch Oral Biol 110:104617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2019.104617
Pereira C, Moreirinha C, Lewicka M, Almeida P, Clemente C, Cunha N, Delgadillo I, Romalde JL, Nunes ML, Almeida AJVR (2016) Bacteriophages with potential to inactivate Salmonella Typhimurium: Use of single phage suspensions and phage cocktails. Virus Res 220:179–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2016.04.020
Piazentin ACM, Mendonca CMN, Vallejo M, Mussatto SI, De Souza Oliveira RP (2022) Bacteriocin-like inhibitory substances production by Enterococcus faecium 135 in co-culture with Ligilactobacillus salivarius and Limosilactobacillus reuteri. Braz J Microbiol 53(1):131–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-021-00661-6
Pooljun C, Daorueang S, Weerachatyanukul W, Direkbusarakom S, Jariyapong P (2020) Enhancement of shrimp health and immunity with diets supplemented with combined probiotics: application to Vibrio parahaemolyticus infections. Dis Aquat Organ 140:37–46. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao03491
Rajme-Manzur D, Gollas-Galvan T, Vargas-Albores F, Martinez-Porchas M, Hernandez-Onate MA, Hernandez-Lopez J (2021) Granulomatous bacterial diseases in fish: An overview of the host’s immune response. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 261:111058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2021.111058
Reverter M, Sarter S, Caruso D, Avarre JC, Combe M, Pepey E, Pouyaud L, Vega-Heredia S, De Verdal H, Gozlan RE (2020) Aquaculture at the crossroads of global warming and antimicrobial resistance. Nat Commun 11(1):1870. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15735-6
Ringoe E, Doan HV, Lee SH, Soltani M, Song S (2020) R 32. Ringo et al. (2020) JAM 129, 116–136. jam.14628.pdf.
Saha M, Sarkar A, Bandyopadhyay B (2021) Water quality assessment of East Kolkata Wetland with a special focus on bioremediation by nitrifying bacteria. Water Sci Technol 84(10–11):2718–2736. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2021.223
Sequeiros C, Garcés ME, Fernández M, Marcos M, Castaños C, Moris M, Olivera NL (2022) Zebrafish intestinal colonization by three lactic acid bacteria isolated from Patagonian fish provides evidence for their possible application as candidate probiotic in aquaculture. Aquacult Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-022-00864-0
Sha Y, Wang L, Liu M, Jiang K, Xin F, Wang B (2016) Effects of lactic acid bacteria and the corresponding supernatant on the survival, growth performance, immune response and disease resistance of Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 452:28–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.10.014
Tan C, Wang L, Xue Y, Lin S, Yu G, Yang S (2018) Purification and molecular characterization of a Metschnikowia saccharicola killer toxin lethal to a crab pathogenic yeast. FEMS Microbiol Lett 365(10). https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fny038
Wang X, Chi Z, Yue L, Jing L, Li M, Wu L (2007) A marine killer yeast against the pathogenic yeast strain in crab (Portunus trituberculatus) and an optimization of the toxin production. Microbiol Res 162(1):77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2006.09.002
Wang H, Zhu L, Yang N, Tl. W, Zhang Z, Gao G, Shi Q (2018) Study on Antibacterial Effects of Common Chinese Herbs Against Aquatic Animal Pathogens in vitro. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine 45(5): 1357–1366. https://doi.org/10.16431/j.cnki.1671-7236.2018.05.029
Wang N, Li H, Dai LL, Sun XY, Jin Y, Zhao LH (2020) Screening and Identification of Bacteriocin-producing Lactic Acid Bacteria. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology 20(12): 248–255. https://doi.org/10.16429/j.1009-7848.2020.12.030
Watts JEM, Schreier HJ, Lanska L, Hale MS (2017) The Rising Tide of Antimicrobial Resistance in Aquaculture: Sources, Sinks and Solutions. Mar Drugs 15(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/md15060158
Wu D, Cheng M, Zhao S, Peng N, Hu R, Hu J, Liang Y (2020) Algal Growth Enhances Light-Mediated Limitation of Bacterial Nitrification in an Aquaculture System. Water Air Soil Pollut 231(2):73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-4436-y
Xu F, Peng L, Cai T, Hu L, Zhou Z, Zhu S (2016) Research progress of the antimicrobial effects of Chinese herbal medicines to aquatic animal pathogens. J Aquac 37(10):48–52. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-2091.2016.10.009
Xu X, Luo Z, Zhong W, Hao J, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Geng X (2021) Studies on pathogen and its pathogenesis causing milky disease of Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis. Periodical of Ocean University of China 51(12): 23–32. https://doi.org/10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20210025
Yca B, Sl A, Di WA, Jz A, Lx A, Hl A, Tl A, Zm B (2019) Genomic characterization of a novel virulent phage infecting the Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from rainbow trout ( Oncorhynchus mykiss ). Virus Res 273:197764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2019.197764
Zacharof MP, Lovitt RW (2012) Bacteriocins Produced by lactic acid bacteria a review article. APCBEE Proc 2:50–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcbee.2012.06.010
Zhang XD, Jin YF, Chen Y (2008) Influence of photosynthetic bacteria on pathogenic bacteria isolated from two freshwater fish. Chin J Eco-Agric 16(3):659–663. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1011.2008.00659
Zhang HQ, Chi Z, Liu GL, Zhang M, Hu Z, Chi ZM (2021a) Metschnikowia bicuspidate associated with a milky disease in Eriocheir sinensis and its effectitve treatment by Massoia lactone. Microbiol Res 242:126641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2020.126641
Zhang M, Luo Q, Wei J, Liu Q, Luo F (2021b) Screening for and identification for bacteriocin-producing Enterococcus faecium and its antibacterial properties. Food Science 42(6):171–177. https://doi.org/10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191213-147
Zheng J, Wittouck S, Salvetti E, Franz C, Harris HMB, Mattarelli P, O'toole PW, Pot B, Vandamme P, Walter J, Watanabe K, Wuyts S, Felis GE, Ganzle MG, Lebeer S (2020) A taxonomic note on the genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 novel genera, emended description of the genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70(4): 2782-2858. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004107
Zhou HP, Jia LZ, Yang YY, Chen YQ (2006) Antagonistic action of Lactobacillaceae on pathogen Vibrio sp. J Oceanography Taiwan Strait 25(3):388–395. https://doi.org/10.1360/aps050066
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Doctor Xu Xiaoli of The Institute of Tianjin Fisheries Research for providing the pathogenic bacteria in aquaculture, for conducting this study.
Funding
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Demonstration Project of Major Special Projects and Engineering Projects (17ZXYENC00070).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FZ analyzed the formal data and wrote original draft. KZ performed the investigation and methodology. FX designed the experiment, reviewed and edited the manuscript. QZ conducted supervision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Human and animal ethics
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, F., Zhou, K., Xie, F. et al. Screening and identification of lactic acid bacteria with antimicrobial abilities for aquaculture pathogens in vitro. Arch Microbiol 204, 689 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-03285-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-03285-y