Abstract
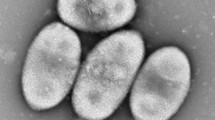
A rod-shaped, Gram-negative staining strain, FBM22T, was isolated from a microbial fermentation bed substrate from a pig farm. Its colonies appeared yellow and were 0.5–1.2 mm in diameter. Cells were 0.3–0.5 μm wide, 0.5–0.83 μm long. Optimal growth occurred at 30 °C and pH 7.0–8.0; NaCl was not required for growth. The strain performed denitrification and nitrate reduction functions. And it could produce catalase. FBM22-1T utilized the following organic substrates for growth: tyrosine, glutamic acid, d-glucose, and galactose. The novel isolate could degrade 2-nitropropane as carbon and nitrogen source. The dominant respiratory quinone was Q-10. The major polar lipids were diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine. C18:1 ω7c, C16:1 ω7c and/ or C16:1 ω6c, and C14:0 2-OH were the major (≥ 8%) fatty acids. The G+C content was 56.8 mol%. FBM22T was found to be a member of the genus Sphingopyxis in the family Sphingomonadaceae of the class Alphaproteobacteria. It had the highest sequence similarity with the type strains Sphingopyxis terrae subsp. ummariensis UI2T (96.47%) and Sphingopyxis terrae subsp. terrae NBRC 15098T (96.40%). Furthermore, FBM22T had 18.7% and 18.4% relatedness (based on digital DNA–DNA hybridization) with its two relatives (S. terrae subsp. ummariensis UI2T and S. terrae subsp. terrae NBRC 15098T). The morphological, physiological, and genotypic differences identified in this study support the classification of FBM22T as a novel species within the genus Sphingopyxis, for which the name Sphingopyxis yananensis sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is FBM22T (= KCTC 82290T = CCTC AB2020286T).

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANI:
-
Average nucleotide identity
- dDDH:
-
Digital DNA–DNA hybridization
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- TLC:
-
Thin-layer chromatography
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscope
- NJ:
-
Neighbor-joining
- ML:
-
Maximum-likelihood
- MP:
-
Maximum-parsimony
- GL:
-
Glycolipid
- PL:
-
Unknown phospholipids
- DPG:
-
Diphosphatidylglycerol
- PC:
-
Phosphatidylcholine
- PE:
-
Phosphatidylethanolamine
References
Alias-Villegas C, Jurado V, Laiz L, Saiz-Jimenez C (2013) Sphingopyxis italica sp. nov., isolated from Roman catacombs. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:2565–2569. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.046573-0
Chen L, Chen WF, Xu ZL, Li W, Zhang XY et al (2018) Sphingorhabdus buctiana sp. nov., isolated from fresh water, and reclassification of Sphingopyxis contaminans as Sphingorhabdus contaminans comb. nov. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 111:323–331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0954-z
Choi JH, Kim MS, Jung MJ, Roh SW, Shin KS et al (2010) Sphingopyxis soli sp. nov., isolated from landfill soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:1682–1686. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.013128-0
Collins MD, Goodfellow M, Minnikin DE (1979) Isoprenoid quinones in the classification of coryneform and related bacteria. J Gen Microbiol 110:127–136. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-110-1-127
Feng GD, Wang DD, Yang SZ, Li HP, Zhu HH (2017) Genome-based reclassification of Sphingopyxis ummariensis as a later heterotypic synonym of Sphingopyxis terrae, with the descriptions of Sphingopyxis terrae subsp. terrae subsp. nov. and Sphingopyxis terrae subsp. ummariensis subsp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:5279–5283. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002465
Godoy F, Vancanneyt M, Martinez M, Steinbüchel A, Swings J et al (2003) Sphingopyxis chilensis sp. nov., a chlorophenol-degrading bacterium that accumulates polyhydroxyalkanoate, and transfer of Sphingomonas alaskensis to Sphingopyxis alaskensis comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:473–477. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.02375-0
Jindal S, Dua A, Lal R (2013) Sphingopyxis indica sp. nov., isolated from a high dose point hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH)-contaminated dumpsite. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:2186–2191. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.040840-0
Jogler M, Chen H, Simon J, Rohde M, Busse HJ et al (2013) Description of Sphingorhabdus planktonica gen. nov., sp. nov. and reclassification of three related members of the genus Sphingopyxis in the genus Sphingorhabdus gen. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:1342–1349. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.043133-0
Kämpfer P (2002) Sphingopyxis witflariensis sp. nov., isolated from activated sludge. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:2029–2034. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.02217-0
Konstantinos TK, Tiedje JM (2005) Towards a genome-based taxonomy for prokaryotes. J Bacteriol 187:6258–6264. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.187.18.6258-6264.2005
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.187.18.6258-6264.2005
Lakshmi KVNS, Sasikala Ch, Ramana VV, Ramaprasad EVV, Ramana CV (2011) Rhodovulum phaeolacus sp. nov. a phototrophic alphaproteobacterium isolated from a brown pond. J Gen Appl Microbiol 57:145–151. https://doi.org/10.2323/jgam.57.145
Lapage SP, Sneath PHA, Lessel EF, Skerman VBD, Seeliger HPR (1992) International code of nomenclature of bacteria bacteriological code, 1990 revision. FEMS Microbiol Lett 94:i–i. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb05316.x
Li RX, Hua RM, Tang XY, Wang YL, Zhang J et al (2011) Isolation, identification and degradation characteristics of a novel chlorpyrifos degrading strain Sphingopyxis terrae R17. Chin J Laser Biol 20(02):261–268
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinformatics 14:60. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-60
Michael R, Rosselló-Móra R (2009) Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Pro Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:19126–19131. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0906412106
Minnikin DE, O’Donnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M et al (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-7012(84)90018-6
Raj PS, Ramaprasad EVV, Vaseef S, Sasikala C, Ramana CV (2013) Rhodobacter viridis sp. nov., a phototrophic bacterium isolated from mud of a stream. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:181–186. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.038471-0
Richter M, Rossello-Mora R, Oliver Glöckner FO, Peplies J (2016) JSpeciesWS: a web server for prokaryotic species circumscription based on pairwise genome comparison. Bioinformatics 32:929–931. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv681
Takeuchi M, Hamana K, Hiraishi A (2001) Proposal of the genus Sphingomonas sensu stricto and three new genera, Sphingobium, Novosphingobium and Sphingopyxis, on the basis of phylogenetic and chemotaxonomic analyses. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1405–1417. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-51-4-1405
Verma H, Rani P, Singh AK, Kumar R, Dwivedi V et al (2015) Sphingopyxis flava sp. nov., isolated from a hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH)-contaminated soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.040840-0
Yabuuchi E, Yano I, Oyaizu H, Hashimoto Y, Ezaki T et al (1990) Proposals of Sphingomonas paucimobilis gen. nov. and comb. nov., Sphingomonas parapaucimobilis sp. nov., Sphingomonas yanoikuyae sp. nov., Sphingomonas adhaesiva sp. nov., Sphingomonas capsulata comb. nov., and two genospecies of the genus Sphingomonas. Microbiol Immunol 34:99–119. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1348-0421.1990.tb00996.x
Yang X, Jiang Z, Zhang J, Zhou X, Zhang X et al (2020) Mesorhizobium alexandrii sp. nov., isolated from phycosphere microbiota of PSTs-producing marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum amtk4. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 113:907–917. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-020-01400-x
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y et al (2017) Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613–1617. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001755
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 32160003), Doctor Support Project of Yan’an University (No. YDBK2019-44), Key Science and Technology Program at County Level of Shaanxi Province (2018XY-14), Graduate Education Innovation Plan of Yan’an University in 2021 (YCX2021083) and Yan’an Science and Technology Bureau Park and County Characteristic Economic Innovation Chain Project in 2019 (No. 2019ZDQY-035).
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China, 32160003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZD: designed the experiments; YJ and CZ: performed the experiments; TY, JL and JA: analyzed the data; ML: provided the material; XL and ZD: drafted and revised the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Cc., Jiang, Yy., Yu, Tf. et al. Sphingopyxis yananensis sp. nov., a novel 2-nitropropane degrading bacterium isolated from a microbial fermentation bed substrate. Arch Microbiol 204, 529 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-03132-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-03132-0