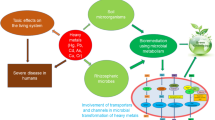
Abstract
The most contemporary ecological issues are the dumping of unprocessed factories’ effluent. As a result, there is an increasing demand for creative, practical, environmentally acceptable, and inexpensive methodologies to remediate inorganic metals (Hg, Cr, Pb, and Cd) liquidated into the atmosphere, protecting ecosystems. Latest innovations in biological metals have driven natural treatment as a viable substitute for traditional approaches in this area. To eliminate pesticide remains from soil/water sites, technologies such as oxidation, burning, adsorption, and microbial degradation have been established. Bioremediation is a more cost-effective and ecologically responsible means of removing heavy metals than conventional alternatives. As a result, microorganisms have emerged as a necessary component of methyl breakdown and detoxification via metabolic reactions and hereditary characteristics. The utmost operative variant for confiscating substantial metals commencing contaminated soil was A. niger, which had a maximum bioaccumulation efficiency of 98% (Cd) and 43% (Cr). Biosensor bacteria are both environmentally sustainable and cost-effective. As a result, microbes have a range of metal absorption processes that allow them to have higher metal biosorption capabilities. Additionally, the biosorption potential of bacterium, fungus, biofilm, and algae, inherently handled microorganisms that immobilized microbial cells for the elimination of heavy metals, was reviewed in this study. Furthermore, we discuss some of the challenges and opportunities associated with producing effective heavy metal removal techniques, such as those that employ different types of nanoparticles.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas SH et al (2014) Biosorption of heavy metals: a review. J Chem Sci Technol 3(4):74–102
Abinandan S et al (2019) Acid-tolerant microalgae can withstand higher concentrations of invasive cadmium and produce sustainable biomass and biodiesel at pH 3.5. Bioresour Technol 281:469–473
Ahemad M (2019) Remediation of metalliferous soils through the heavy metal resistant plant growth promoting bacteria: paradigms and prospects. Arab J Chem 12(7):1365–1377
Ahirwar NK et al (2016) Isolation, identification and characterization of heavy metal resistant bacteria from industrial affected soil in central India. Int J Pure Appl Biosci 4(6):88–93
Aken BV, Tehrani R, Schnoor JL (2011) Endophyte-assisted phytoremediation of explosives in poplar trees by Methylobacterium populi BJ001 T. Endophytes of forest trees. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 217–234
Aksu Z, İşoğlu İA (2005) Removal of copper (II) ions from aqueous solution by biosorption onto agricultural waste sugar beet pulp. Process Biochem 40(9):3031–3044
Al Hasin A et al (2010) Remediation of chromium (VI) by a methane-oxidizing bacterium. Environ Sci Technol 44(1):400–405
Ali AM, Emanuelsson EA, Patterson DA (2010) Photocatalysis with nanostructured zinc oxide thin films: the relationship between morphology and photocatalytic activity under oxygen limited and oxygen rich conditions and evidence for a Mars Van Krevelen mechanism. Appl Catal B 97(1–2):168–181
Alvarez A et al (2017) Actinobacteria: current research and perspectives for bioremediation of pesticides and heavy metals. Chemosphere 166:41–62
An J et al (2019) A novel electro-coagulation-fenton for energy efficient cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins removal without chemical addition. J Hazard Mater 365:650–658
Asemoloye MD, Jonathan SG, Ahmad R (2019) Synergistic plant-microbes interactions in the rhizosphere: a potential headway for the remediation of hydrocarbon polluted soils. Int J Phytorem 21(2):71–83
Avalos M et al (2020) Production of ammonia as a low-cost and long-distance antibiotic strategy by Streptomyces species. ISME J 14(2):569–583
Aydin S et al (2017) Aerobic and anaerobic fungal metabolism and omics insights for increasing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons biodegradation. Fungal Biol Rev 31(2):61–72
Azimi A et al (2017) Removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewaters: a review. ChemBioEng Rev 4(1):37–59
Azubuike CC, Chikere CB, Okpokwasili GC (2016) Bioremediation techniques–classification based on site of application: principles, advantages, limitations and prospects. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 32(11):1–18
Bagchi S, Behera M (2020) Assessment of heavy metal removal in different bioelectrochemical systems: a review. J Hazard Toxic Radioact Waste 24(3):04020010
Balaji S et al (2016) Characterization of sorption sites and differential stress response of microalgae isolates against tannery effluents from Ranipet industrial area—an application towards phycoremediation. Int J Phytorem 18(8):747–753
Balcázar JL, Subirats J, Borrego CM (2015) The role of biofilms as environmental reservoirs of antibiotic resistance. Front Microbiol 6:1216
Balzano S et al (2020) Microalgal metallothioneins and phytochelatins and their potential use in bioremediation. Front Microbiol 11:517
Bansod B et al (2017) A review on various electrochemical techniques for heavy metal ions detection with different sensing platforms. Biosens Bioelectron 94:443–455
Bhatt P (2018) Insilico tools to study the bioremediation in microorganisms. Handbook of research on microbial tools for environmental waste management. IGI Global, Pennsylvania, pp 389–395
Bhatt P, Barh A (2018) Bioinformatic tools to study the soil microorganisms: an in silico approach for sustainable agriculture. In silico approach for sustainable agriculture. Springer, Singapore, pp 169–182
Birungi Z, Chirwa E (2015) The adsorption potential and recovery of thallium using green micro-algae from eutrophic water sources. J Hazard Mater 299:67–77
Bodzek M (2015) Membrane technologies for the removal of micropollutants in water treatment. Advances in membrane technologies for water treatment. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 465–517
Bordjiba O et al (2001) Removal of herbicides from liquid media by fungi isolated from a contaminated soil. J Environ Qual 30(2):418–426
Bressuire-Isoard C, Broussolle V, Carlin F (2018) Sporulation environment influences spore properties in Bacillus: evidence and insights on underlying molecular and physiological mechanisms. FEMS Microbiol Rev 42(5):614–626
Brim H et al (2003) Engineering Deinococcus geothermalis for bioremediation of high-temperature radioactive waste environments. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(8):4575–4582
Brim H et al (2006) Deinococcus radiodurans engineered for complete toluene degradation facilitates Cr (VI) reduction. Microbiology 152(8):2469–2477
Buermans H, Den Dunnen J (2014) Next generation sequencing technology: advances and applications. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842:1932–1941
Burgos-Castillo R et al (2018) Removal of metals and phosphorus recovery from urban anaerobically digested sludge by electro-fenton treatment. Sci Total Environ 644:173–182
Cabral Pinto M et al (2019) Links between cognitive status and trace element levels in hair for an environmentally exposed population: a case study in the surroundings of the estarreja industrial area. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(22):4560
Cameron H, Mata MT, Riquelme C (2018) The effect of heavy metals on the viability of Tetraselmis marina AC16-MESO and an evaluation of the potential use of this microalga in bioremediation. PeerJ 6:e5295
Castro D et al (2021) Chemical modification of agro-industrial waste-based bioadsorbents for enhanced removal of Zn (Ii) ions from aqueous solutions. Materials 14(9):2134
Chabukdhara M, Gupta SK, Gogoi M (2017) Phycoremediation of heavy metals coupled with generation of bioenergy. Algal biofuels. Springer, Cham, pp 163–188
Chakrabarty A (1986) Genetic engineering and problems of environmental pollution. Bio/technology 8:515–530
Chang J-H, Yang T-J, Tung C-H (2009) Performance of nano-and nonnano-catalytic electrodes for decontaminating municipal wastewater. J Hazard Mater 163(1):152–157
Chettri D, Sharma B, Verma AK (2022) Advancement in microbial bioremediation. Development in wastewater treatment research and processes. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 243–262
Chiang H-C, Lo J-C, Yeh K-C (2006) Genes associated with heavy metal tolerance and accumulation in Zn/Cd hyperaccumulator Arabidopsis halleri: a genomic survey with cDNA microarray. Environ Sci Technol 40(21):6792–6798
Chowdhury S et al (2016) Heavy metals in drinking water: occurrences, implications, and future needs in developing countries. Sci Total Environ 569:476–488
Crini G et al (2019) Conventional and non-conventional adsorbents for wastewater treatment. Environ Chem Lett 17(1):195–213
Cybulski Z et al (2003) The influence of emulsifiers on hydrocarbon biodegradation by Pseudomonadacea and Bacillacea strains. Spill Sci Technol Bull 8(5–6):503–507
Daccò C et al (2020) Key fungal degradation patterns, enzymes and their applications for the removal of aliphatic hydrocarbons in polluted soils: a review. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 147:104866
Danwittayakul S, Jaisai M, Dutta J (2015) Efficient solar photocatalytic degradation of textile wastewater using ZnO/ZTO composites. Appl Catal B 163:1–8
Dean-Ross D, Moody J, Cerniglia C (2002) Utilization of mixtures of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by bacteria isolated from contaminated sediment. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 41(1):1–7
Delgado-González CR, Madariaga-Navarrete A, Fernández-Cortés JM, Islas-Pelcastre M, Oza G, Iqbal H, Sharma A (2021) Advances and applications of water phytoremediation: a potential biotechnological approach for the treatment of heavy metals from contaminated water. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(10):5215
Devi P, Kumar P (2020) Concept and application of phytoremediation in the fight of heavy metal toxicity. J Pharm Sci Res 12(6):795–804
Díaz-López M et al (2021) Combined ozonation and solarization for the removal of pesticides from soil: effects on soil microbial communities. Sci Total Environ 758:143950
Diep P, Mahadevan R, Yakunin AF (2018) Heavy metal removal by bioaccumulation using genetically engineered microorganisms. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 6:157
Divya B, Deepak M, Kumar (2011) Plant–microbe interaction with enhanced bioremediation. Res J Biotechnol 6:4
Dixit R et al (2015) Bioremediation of heavy metals from soil and aquatic environment: an overview of principles and criteria of fundamental processes. Sustainability 7(2):2189–2212
Donkadokula NY et al (2020) A review on advanced physico-chemical and biological textile dye wastewater treatment techniques. Rev Environ Bio/technol 19(3):543–560
Dow N et al (2013) Outcomes of the Australian ozone/ceramic membrane trial on secondary effluent. Water J Aust Water Assoc 40:45–51
Durairaj P et al (2015) Fungal cytochrome P450 monooxygenases of Fusarium oxysporum for the synthesis of ω-hydroxy fatty acids in engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb Cell Fact 14(1):1–16
Edwards SJ, Kjellerup BV (2013) Applications of biofilms in bioremediation and biotransformation of persistent organic pollutants, pharmaceuticals/personal care products, and heavy metals. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(23):9909–9921
Elamin N, Elsanousi A (2013) Synthesis of ZnO nanostructures and their photocatalytic activity. J Appl Ind Sci 1(1):32–35
Essa A, Macaskie L, Brown N (2002) Mechanisms of mercury bioremediation. Biochem Soc Trans 30:672–674
Frederick TM et al (2013) Chromate reduction is expedited by bacteria engineered to produce the compatible solute trehalose. Biotechnol Lett 35(8):1291–1296
Fu F, Wang Q (2011) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. J Environ Manage 92(3):407–418
Fuhrer J et al (2016) Current and future ozone risks to global terrestrial biodiversity and ecosystem processes. Ecol Evol 6(24):8785–8799
Fuller E et al (2021) Using molecular methods to identify and monitor xenobiotic-degrading genes for bioremediation. Biodegradation pollutants and bioremediation principles. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 65–90
Gangola S et al (2018) Presence of esterase and laccase in Bacillus subtilis facilitates biodegradation and detoxification of cypermethrin. Sci Rep 8(1):1–11
Gangola S et al (2018) Bioremediation of industrial waste using microbial metabolic diversity, in microbial biotechnology in environmental monitoring and cleanup. IGI Global, Pennsylvania
Gautam RK et al (2014) Chapter 1 contamination of heavy metals in aquatic media: transport, toxicity and technologies for remediation. Heavy metals in water: presence, removal and safety. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge
Ghahrchi M, Rezaee A (2020) Electro-catalytic ozonation for improving the biodegradability of mature landfill leachate. J Environ Manage 254:109811
Ghosal D et al (2016) Current state of knowledge in microbial degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): a review. Front Microbiol 7:1369
Goi A, Trapido M (2004) Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil: the fenton reagent versus ozonation. Environ Technol 25(2):155–164
Goswami RK et al (2021) Bioremediation of heavy metals from wastewater: a current perspective on microalgae-based future. Lett Appl Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.13564
Gupta P, Diwan B (2017) Bacterial exopolysaccharide mediated heavy metal removal: a review on biosynthesis, mechanism and remediation strategies. Biotechnol Rep 13:58–71
Gupta A et al (2016) Microbes as potential tool for remediation of heavy metals: a review. J Microb Biochem Technol 8(4):364–372
Gusain R et al (2019) Efficient removal of Pb (II) and Cd (II) from industrial mine water by a hierarchical MoS2/SH-MWCNT nanocomposite. ACS Omega 4(9):13922–13935
Haldar S, Ghosh A (2020) Microbial and plant-assisted heavy metal remediation in aquatic ecosystems: a comprehensive review. 3 Biotech 10:1–13
Haritash A, Kaushik C (2009) Biodegradation aspects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): a review. J Hazard Mater 169(1–3):1–15
Harris PA et al (2019) The REDCap consortium: building an international community of software platform partners. J Biomed Inform 95:103208
He K et al (2018) Advancement of Ag–graphene based nanocomposites: an overview of synthesis and its applications. Small 14(32):1800871
Hegazi H (2013) Removal of heavy metals from wastewater using agricultural and industrial wastes as adsorbents. HBRC J 9:276–282
Ibuot A et al (2017) Metal bioremediation by CrMTP4 over-expressing Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in comparison to natural wastewater-tolerant microalgae strains. Algal Res 24:89–96
Iram S et al (2013) Heavy metal tolerance of fungus isolated from soil contaminated with sewage and industrial wastewater. Polish J Environ Stud 22:691–697
Jaafari J, Yaghmaeian K (2019) Optimization of heavy metal biosorption onto freshwater algae (Chlorella coloniales) using response surface methodology (RSM). Chemosphere 217:447–455
Jan AT et al (2014) Prospects for exploiting bacteria for bioremediation of metal pollution. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 44(5):519–560
Javaid A et al (2021) Nanohybrids-assisted photocatalytic removal of pharmaceutical pollutants to abate their toxicological effects–a review. Chemosphere 2021:133056
Jiménez-Díaz V et al (2022) Synthetic biology: a new era in hydrocarbon bioremediation. Processes 10(4):712
Joseph L et al (2019) Removal of heavy metals from water sources in the developing world using low-cost materials: a review. Chemosphere 229:142–159
Kang SH et al (2007) Bacteria metabolically engineered for enhanced phytochelatin production and cadmium accumulation. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(19):6317–6320
Kang C-H, Kwon Y-J, So J-S (2016) Bioremediation of heavy metals by using bacterial mixtures. Ecol Eng 89:64–69
Kapley A et al (1999) Osmotolerance and hydrocarbon degradation by a genetically engineered microbial consortium. Biores Technol 67(3):241–245
Khalid S et al (2017) A comparison of technologies for remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils. J Geochem Explor 182:247–268
Khan A (2020) Promises and potential of in situ nano-phytoremediation strategy to mycorrhizo-remediate heavy metal contaminated soils using non-food bioenergy crops (Vetiver zizinoides & Cannabis sativa). Int J Phytorem 22(9):900–915
Khan I et al (2019) Mycoremediation of heavy metal (Cd and Cr)–polluted soil through indigenous metallotolerant fungal isolates. Environ Monit Assess 191(9):1–11
Kiyono M, Pan-Hou H (2006) Genetic engineering of bacteria for environmental remediation of mercury. J Health Sci 52(3):199–204
Kostal J et al (2004) Enhanced arsenic accumulation in engineered bacterial cells expressing ArsR. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(8):4582–4587
Kuhad RC, Kapoor M, Rustagi R (2004) Enhanced production of an alkaline pectinase from Streptomyces sp. RCK-SC by whole-cell immobilization and solid-state cultivation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 20(3):257–263
Kumar D, Pannu R (2018) Perspectives of lindane (γ-hexachlorocyclohexane) biodegradation from the environment: a review. Bioresour Bioprocess 5(1):1–18
Kumar KS et al (2015) Microalgae–a promising tool for heavy metal remediation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 113:329–352
Kumar V et al (2019) Global evaluation of heavy metal content in surface water bodies: a meta-analysis using heavy metal pollution indices and multivariate statistical analyses. Chemosphere 236:124364
Liang R et al (2019) Photo-degradation dynamics of five neonicotinoids: bamboo vinegar as a synergistic agent for improved functional duration. PLoS ONE 14(10):e0223708
Lovley DR (2003) Cleaning up with genomics: applying molecular biology to bioremediation. Nat Rev Microbiol 1(1):35–44
Luo S et al (2019) Soil microbial communities under film mulching and N fertilization in semiarid farmland. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 114(2):157–170
Lutzu GA et al (2021) Latest developments in wastewater treatment and biopolymer production by microalgae. J Environ Chem Eng 9(1):104926
Mateos LM et al (2017) The arsenic detoxification system in corynebacteria: basis and application for bioremediation and redox control. Adv Appl Microbiol 99:103–137
Medfu Tarekegn M, Zewdu Salilih F, Ishetu AI (2020) Microbes used as a tool for bioremediation of heavy metal from the environment. Cogent Food Agric 6(1):1783174
Mehwish HM et al (2021) Green synthesis of a silver nanoparticle using Moringa oleifera seed and its applications for antimicrobial and sun-light mediated photocatalytic water detoxification. J Environ Chem Eng 9(4):105290
Mitsugi F et al (2014) Properties of soil treated with ozone generated by surface discharge. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 42(12):3706–3711
Murtaza I, Dutt A, Ali A (2002) Biomolecular engineering of Escherichia coli organo-mercurial lyase gene and its expression. Indian J Biotechnol 1:117–120
Nehra V, Choudhary M (2015) A review on plant growth promoting rhizobacteria acting as bioinoculants and their biological approach towards the production of sustainable agriculture. J Appl Nat Sci 7(1):540–556
Ng SP et al (2009) A Tn 5051-like mer-containing transposon identified in a heavy metal tolerant strain Achromobacter sp. AO22. BMC Res Notes 2:1–7
Nguyen T et al (2013) Applicability of agricultural waste and by-products for adsorptive removal of heavy metals from wastewater. Bioresour Technol 148:574–585
Ojuederie OB, Babalola OO (2017) Microbial and plant-assisted bioremediation of heavy metal polluted environments: a review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14(12):1504
Osman AI et al (2018) Physicochemical characterization of miscanthus and its application in heavy metals removal from wastewaters. Environ Prog Sustainable Energy 37(3):1058–1067
Penny C, Vuilleumier S, Bringel F (2010) Microbial degradation of tetrachloromethane: mechanisms and perspectives for bioremediation. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 74(2):257–275
Prenafeta-Boldú FX, De Hoog GS, Summerbell RC (2018) Fungal communities in hydrocarbon degradation. In: McGenity TJ (ed) Microbial communities utilizing hydrocarbons and lipids: members, metagenomics and ecophysiology. Springer, Cham
Qadri H et al (2020) Fresh water pollution dynamics and remediation. Springer, Singapore
Rai PK (2018) Heavy metal phyto-technologies from Ramsar wetland plants: green approach. Chem Ecol 34(8):786–796
Rojas LA et al (2011) Characterization of the metabolically modified heavy metal-resistant Cupriavidus metallidurans strain MSR33 generated for mercury bioremediation. PLoS One 6(3):e17555
Roy T (2020) Bioremediation of heavy metal by microorganism. Eur J Mol Clin Med 7(07):2020
Ryle MJ, Hausinger RP (2002) Non-heme iron oxygenases. Curr Opin Chem Biol 6(2):193–201
Sánchez-Castro I et al (2020) High-efficient microbial immobilization of solved U (VI) by the Stenotrophomonas strain Br 8. Water Res 183:116110
Sánchez-Castro I et al (2021) Uranium removal from complex mining waters by alginate beads doped with cells of Stenotrophomonas sp. Br8: novel perspectives for metal bioremediation. J Environ Manag 296:113411
Saravanan A et al (2020) Rhizoremediation–a promising tool for the removal of soil contaminants: a review. J Environ Chem Eng 8(2):103543
Sarma H, Sonowal S, Prasad M (2019) Plant-microbiome assisted and biochar-amended remediation of heavy metals and polyaromatic compounds─a microcosmic study. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 176:288–299
Sauge-Merle S et al (2012) Heavy metal accumulation by recombinant mammalian metallothionein within Escherichia coli protects against elevated metal exposure. Chemosphere 88(8):918–924
Schück M, Greger M (2020) Plant traits related to the heavy metal removal capacities of wetland plants. Int J Phytorem 22(4):427–435
Selatnia A et al (2004) Biosorption of lead (II) from aqueous solution by a bacterial dead Streptomyces rimosus biomass. Biochem Eng J 19(2):127–135
Sharma P et al (2021) Critical review on microbial community during in-situ bioremediation of heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Environ Technol Innov 24:101826
Shukla SK et al (2017) 19-bacterial biofilms and genetic regulation for metal detoxification. Handbook of metal–microbe interactions and bioremediation. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Shukla SK, Hariharan S, Rao TS (2020) Uranium bioremediation by acid phosphatase activity of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms: can a foe turn a friend? J Hazard Mater 384:121316
Singh B. 2011a Emerging and genomic approaches in bioremediation. In: proceedings of the 4th international contaminated site remediation conference, Adelaide, Australia.
Singh A (2011b) Navigation Bar. J Polym Sci Part b: Polym Phys 49:1563–1568
Singh R et al (2011a) Heavy metals and living systems: An overview. Indian Journal of Pharmacology 43(3):246
Singh JS et al (2011b) Genetically engineered bacteria: an emerging tool for environmental remediation and future research perspectives. Gene 480(1–2):1–9
Sone Y et al (2013) Mercurial-resistance determinants in Pseudomonas strain K-62 plasmid pMR68. AMB Express 3(1):1–7
Sparks TC et al (2019) The new age of insecticide discovery-the crop protection industry and the impact of natural products. Pestic Biochem Physiol 161:12–22
Sriprang R et al (2003) Enhanced accumulation of Cd2+ by a Mesorhizobium sp. transformed with a gene from Arabidopsis thaliana coding for phytochelatin synthase. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(3):1791–1796
Srivastava S, Dwivedi AK (2015) Biological wastes the tool for biosorption of arsenic. J Biorem Biodegrad 7:323
Sud D, Mahajan G, Kaur MP (2008) Agricultural waste material as potential adsorbent for sequestering heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions–a review. Bioresour Technol 99:6017–6027
Tak HI, Ahmad F, Babalola OO (2013) Advances in the application of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria in phytoremediation of heavy metals. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 223:33–52
Tariq M et al (2017) Antagonistic features displayed by plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): a review. J Plant Sci Phytopathol 1(1):038–043
Upadhyay A et al (2016) Augmentation of arsenic enhances lipid yield and defense responses in alga Nannochloropsis sp. Bioresour Technol 221:430–437
Valls M, De Lorenzo V (2002) Exploiting the genetic and biochemical capacities of bacteria for the remediation of heavy metal pollution. FEMS Microbiol Rev 26(4):327–338
Valls M et al (2000) Engineering a mouse metallothionein on the cell surface of Ralstonia eutropha CH34 for immobilization of heavy metals in soil. Nat Biotechnol 18(6):661–665
Van Nostrand JD, He Z, Zhou J (2012) Use of functional gene arrays for elucidating in situ biodegradation. Front Microbiol 3:339
Vardhan KH, Kumar PS, Panda RC (2019) A review on heavy metal pollution, toxicity and remedial measures: current trends and future perspectives. J Mol Liq 290:111197
Vareda JP, Valente AJ, Durães L (2019) Assessment of heavy metal pollution from anthropogenic activities and remediation strategies: a review. J Environ Manage 246:101–118
Varol M, Sünbül MR (2018) Biomonitoring of trace metals in the Keban Dam Reservoir (Turkey) using mussels (Unio elongatulus eucirrus) and crayfish (Astacus leptodactylus). Biol Trace Elem Res 185(1):216–224
Varshney P et al (2015) Extremophilic micro-algae and their potential contribution in biotechnology. Bioresour Technol 184:363–372
Vélez-Pérez L et al (2020) Industrial acid mine drainage and municipal wastewater co-treatment by dual-chamber microbial fuel cells. Int J Hydrogen Energy 45(26):13757–13766
Verma S, Kuila A (2019) Bioremediation of heavy metals by microbial process. Environ Technol Innov 14:100369
Verma RK et al (2021) Phytoremediation of heavy metals extracted soil and aquatic environments: current advances as well as emerging trends. Biointerface Res Appl Chem 12:5486–5509
Verma S et al (2021) Microbial technologies for heavy metal remediation: effect of process conditions and current practices. Clean Technol Environ Policy. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-021-02029-8
Vidali M (2001) Bioremediation an overview. Pure Appl Chem 73(7):1163–1172
Vinopal S, Ruml T, Kotrba P (2007) Biosorption of Cd2+ and Zn2+ by cell surface-engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 60(2):96–102
Wang J, Chen C (2009) Biosorbents for heavy metals removal and their future. Biotechnol Adv 27(2):195–226
Wu X et al (2020) Positive effects of concomitant heavy metals and their reduzates on hexavalent chromium removal in microbial fuel cells. RSC Adv 10(26):15107–15115
Wu C et al (2021) Genetically engineered microbial remediation of soils co-contaminated by heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: advances and ecological risk assessment. J Environ Manage 296:113185
Yijing C, Jue W (2019) The dilemma and solution of water pollution control from the perspective of environmental regulation. E3S Web Conf 136:06007
Yoshida H, Yazawa Y, Hattori T (2003) Effects of support and additive on oxidation state and activity of Pt catalyst in propane combustion. Catal Today 87(1–4):19–28
Yousefi Z et al (2018) Effect of cadmium on morphometric traits, antioxidant enzyme activity and phytochelatin synthase gene expression (SoPCS) of Saccharum officinarum var. cp48–103 in vitro. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 157:472–481
Zamora-Ledezma C et al (2021) Heavy metal water pollution: a fresh look about hazards, novel and conventional remediation methods. Environ Technol Innov 22:101504
Zhang W, Jiang F, Ou J (2011) Global pesticide consumption and pollution: with China as a focus. Proc Int Acad Ecol Environ Sci 1(2):125
Zhao X et al (2005) Simultaneous mercury bioaccumulation and cell propagation by genetically engineered Escherichia coli. Process Biochem 40(5):1611–1616
Zhou H, Luo J, Chen Y (2020) Nitrogen moieties-dominated Co–N-doped nanoparticle-modified cathodes in heterogeneous-electro-fenton-like system for catalytic decontamination of EDTA-Ni (II). Chemosphere 239:124743
Zhu Y et al (2021) A critical review on metal complexes removal from water using methods based on fenton-like reactions: analysis and comparison of methods and mechanisms. J Hazard Mater 414:125517
Acknowledgements
Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACyT) Mexico is thankfully acknowledged for partially supporting this work under Sistema Nacional de Investigadores (SNI) program awarded to Hafiz M.N. Iqbal (CVU: 735340).
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QM, NH and MB conceptualized the review theme. QM, NH, MM, MB and HMNI wrote the main manuscript text. QM prepared the Tables. NH and HMNI prepared figures. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declare no conflicting interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maqsood, Q., Hussain, N., Mumtaz, M. et al. Novel strategies and advancement in reducing heavy metals from the contaminated environment. Arch Microbiol 204, 478 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-03087-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-03087-2