Abstract
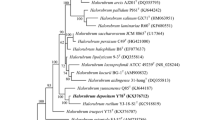
Two extremely halophilic strains, designated SYSU A558-1T and SYSU A121-1, were isolated from a saline sediment sample collected from Aiding salt-lake, China. Cells of strains SYSU A558-1T and SYSU A121-1 were Gram-stain-negative, coccoid, and non-motile. The strains were aerobic and grew at NaCl concentration of 10–30% (optimum, 20–22%), at 20–55 °C (optimum, 37–42 °C) and at pH 6.5–8.5 (optimum, 7.0–8.0). Cells lysed in distilled water. The polar lipids were phosphatidyl choline, phosphatidylglycerol phosphate methyl ester, disulfated diglycosyl diether-1 and unidentified glycolipid. Phylogenetic analysis based on the 16S rRNA gene sequence revealed that the two strains SYSU A558-1T and SYSU A121-1 were closely related to the membranes of the genus Haloterrigena. Phylogenetic and phylogenomic trees of strains SYSU A558-1T and SYSU A121-1 demonstrated a robust clade with Haloterrigena turkmenica, Haloterrigena salifodinae and Haloterrigena salina. The genomic DNA G + C content of strains SYSU A558-1T and SYSU A121-1 were 65.8 and 65.0%, respectively. Phenotypic, phylogenetic, chemotaxonomic and genome analysis suggested that the two strains SYSU A558-1T and SYSU A121-1 represent a novel species of the genus Haloterrigena, for which the name Haloterrigena gelatinilytica sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is SYSU A558-1T (= KCTC 4259T = CGMCC 1.15953T).



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The draft genome sequences of isolates SYSU A558-1T and SYSU A121-1 are available at the NCBI genome database under the accessions JABUQZ000000000 and JABURA000000000, respectively. The three copies of 16S rRNA gene sequences of the isolate SYSU A558-1T are available under the accessions MT809061 (rrnA), MT809062 (rrnB) and MT809063 (rrnC), and that of isolate SYSU A121-1 under the accessions MT808217 (rrnA), MT808218 (rrnB) and MT808219 (rrnC). The rpoB' gene sequences of isolates SYSU A558-1T and SYSU A121-1 have been deposited in GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ under the accession numbers MT572483 and MT572484, respectively.
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z et al (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.17.3389
Asem MD, Salam N, Idris H, Zhang XT, Bull AT et al (2020) Nocardiopsis deserti sp. nov., isolated from a high altitude Atacama Desert soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70:3210–3218. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004158
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H et al (2000) Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet 25:25–29. https://doi.org/10.1038/75556
Aziz RK, Bartels D, Best AA, DeJongh M, Disz T et al (2008) The RAST Server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genomics 9:75. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-9-75
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M et al (2012) SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19:455–477. https://doi.org/10.1089/cmb.2012.0021
Bland C, Ramsey TL, Sabree F, Lowe M, Brown K et al (2007) CRISPR recognition tool (CRT): a tool for automatic detection of clustered regularly interspaced palindromic repeats. BMC Bioinform 8:209. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-8-209
Cantarel BL, Coutinho PM, Rancurel C, Bernard T, Lombard V et al (2009) The Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes database (CAZy): an expert resource for Glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D233-238. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn663
Chen L, Yang J, Yu J, Yao Z, Sun L et al (2005) VFDB: a reference database for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res 33:D325-328. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gki008
Chen S, Xu Y, Sun S, Chen F (2019) Haloterrigena salifodinae sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from a subterranean rock salt. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 112:1317–1329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-019-01264-w
Conesa A, Götz S, García-Gómez JM, Terol J, Talón M et al (2005) Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 21:3674–3676. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bti610
Cui HL, Lin ZY, Dong Y, Zhou PJ, Liu SJ (2007) Halorubrum litoreum sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon from a solar saltern. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2204–2206. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.65268-0
Cui HL, Li XY, Gao X, Xu XW, Zhou YG et al (2010a) Halopelagius inordinatus gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Halobacteriaceae isolated from a marine solar saltern. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2089–2093. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.018598-0
Cui HL, Gao X, Yang X, Xu XW (2010b) Halorussus rarus gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Halobacteriaceae isolated from a marine solar saltern. Extremophiles 14:493–499. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-010-0329-0
Cui HL, Sun FF, Gao X, Dong Y, Xu XW et al (2010c) Haladaptatus litoreus sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon from a marine solar saltern, and emended description of the genus Haladaptatus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:1085–1089. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.015933-0
Delcher AL, Bratke KA, Powers EC, Salzberg SL (2007) Identifying bacterial genes and endosymbiont DNA with Glimmer. Bioinformatics 23:673–679. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm009
Ding JY, Chen SC, Lai MC, Liao TL (2017) Haloterrigena mahii sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon from a solar saltern. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1333–1338. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001811
Dussault HP (1955) An improved technique for staining red halophilic bacteria. J Bacteriol 70:484–485. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-019-01264-w
Eddy SR (1998) Profile hidden Markov models. Bioinformatics 14:755–763. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/14.9.755
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01734359
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791. https://doi.org/10.2307/2408678
Finn RD, Coggill P, Eberhardt RY, Eddy SR, Mistry J et al (2016) The Pfam protein families database: towards a more sustainable future. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D279-285. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1344
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Zool 20:406–416. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/20.4.406
Goris J, Konstantinidis KT, Klappenbach JA, Coenye T, Vandamme P et al (2007) DNA–DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:81–91. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64483-0
Gupta RS, Naushad S, Baker S (2015) Phylogenomic analyses and molecular signatures for the class Halobacteria into an emended order Halobacteriales and two new orders, Haloferacales ord. nov. and Natrialbales ord. nov., containing the novel families Haloferacaceae fam. nov. and Natrialbaceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:1050–1069. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.070136-0
Gutiérrez MC, Castillo AM, Kamekura M, Ventosa A (2008) Haloterrigena salina sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from a salt lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2880–2884. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.2008/001602-0
Han J, Gao QX, Zhang YG, Li L, Mohamad OAA et al (2018) Transcriptomic and ectoine analysis of halotolerant Nocardiopsis gilva YIM 90087T under salt stress. Front Microbiol 9:618. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00618
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Kawashima S, Okuno Y, Hattori M (2004) The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D277-280. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh063
Kates M (1972) Techniques of lipidology; isolation, analysis and identification of lipids. Lab Tech Biochem Mol Biol 3:347–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-0491(74)90118-7
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01731581
Krogh A, Larsson B, Von Heijne G, Sonnhammer EL (2001) Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol 305:567–580. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2000.4315
Krzywinski M, Schein J, Birol I, Connors J, Gascoyne R et al (2009) Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res 19:1639–1645. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.092759.109
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA et al (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Lee I, Chalita M, Ha SM, Na SI, Yoon SH et al (2017) ContEst16S: an algorithm that identifies contaminated prokaryotic genomes using 16S RNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:2053–2057. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001872
Liu B, Pop M (2009) ARDB–Antibiotic Resistance Genes Database. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D443-447. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn656
Liu Y, Ho KK, Su J, Gong H, Chang AC et al (2013) Potassium transport of Salmonella is important for type III secretion and pathogenesis. Microbiology (reading) 159:1705–1719. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.068700-0
Liu BB, Zhao WY, Chu X, Hozzein WN, Prabhu DM et al (2014) Haladaptatus pallidirubidus sp. nov., a halophilic archaeon isolated from saline soil samples in Yunnan and Xinjiang, China. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 106:901–910. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-014-0259-4
Liu BB, Narsing RMP, Yin XQ, Li X, Salam N et al (2019) Description of Halegenticoccus soli gen. nov., sp. nov., a halophilic archaeon isolated from a soil sample of Ebi lake. Extremophiles 23:521–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-019-01104-9
Lowe TM, Eddy SR (1997) tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 25:955–964. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.5.0955
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform 14:60. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-60
Minegishi H, Kamekura M, Itoh T, Echigo A, Usami R et al (2010) Further refinement of the phylogeny of the Halobacteriaceae based on the full-length RNA polymerase subunit B’ (rpoB’) gene. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2398–2408. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.017160-0
Nawrocki EP, Eddy SR (2013) Infernal 1.1: 100-fold faster RNA homology searches. Bioinformatics 29:2933–2935. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt509
Nawrocki EP, Burge SW, Bateman A, Daub J, Eberhardt RY et al (2015) Rfam 12.0: updates to the RNA families database. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D130-137. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn766
Oren A, Ventosa A, Grant WD (1997) Proposed minimal standards for description of new taxa in the order Halobacteriales. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 47:233–238. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-47-1-233
Petersen TN, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H (2011) SignalP 4.0: discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat Methods 8:785–786. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1701
Romano I, Poli A, Finore I, Huertas FJ, Gambacorta A et al (2007) Haloterrigena hispanica sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon from Fuente de Piedra, southern Spain. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1499–1503. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64895-0
Saier MH Jr, Tran CV, Barabote RD (2006) TCDB: the Transporter Classification Database for membrane transport protein analyses and information. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D181-186. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkj001
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Shabala L, Bowman J, Brown J, Ross T, McMeekin T et al (2009) Ion transport and osmotic adjustment in Escherichia coli in response to ionic and non-ionic osmotica. Environ Microbiol 11:137–148. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01748.x
Tatusov RL, Galperin MY, Natale DA, Koonin EV (2000) The COG database: a tool for genome-scale analysis of protein functions and evolution. Nucleic Acids Res 28:33–36. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.33
Ventosa A, Kamekura M (2015) Haloterrigena. In: Trujillo ME, Dedysh S, DeVos P, Hedlund B, Kämpfer P, Rainey FA, Whitman WB (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematics of archaea and bacteria. Wiley, Hoboken. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118960608.gbm00488
Ventosa A, Gutiérrez MC, Kamekura M, Dyall-Smith ML (1999) Proposal to transfer Halococcus turkmenicus, Halobacterium trapanicum JCM 9743 and strain GSL-11 to Haloterrigena turkmenica gen. nov., comb. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49:131–136. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-49-1-131
Winnenburg R, Baldwin TK, Urban M, Rawlings C, Köhler J et al (2006) PHI-base: a new database for pathogen host interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D459-464. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkj047
Wu M, Scott AJ (2012) Phylogenomic analysis of bacterial and archaeal sequences with AMPHORA2. Bioinformatics 28:1033–1034. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts079
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y et al (2017a) Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613–1617. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001755
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Lim J, Kwon S, Chun J (2017b) A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 110:1281–1286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0844-4
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Prof. Yu-Guang Zhou (CGMCC, China) for providing the reference type strains.
Funding
This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31800001, 31850410475), Science and Technology Development Special Fund Program of Guangdong Province (2017A030310206), Key Scientific Research Project of Colleges and Universities in Henan Province (20A180019), Henan Province University Youth Researcher Support Project (2021GGJS153), Key Technologies R&D Program of Henan Province (212102310232) and Key Technologies R&D Program of Nanyang city (KJGG079).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S-XG and W-JL conceived the study; B-BL, NS, SC, Y-GX, Y-RZ and X-YY performed the experiments; B-BL, M-PNR, L-YW and NS wrote the draft manuscript; S-XG and W-JL finalized the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, BB., Salam, N., Narsing Rao, M.P. et al. Haloterrigena gelatinilytica sp. nov., a new extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from salt-lake. Arch Microbiol 204, 176 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-02783-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-02783-3