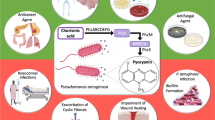
Abstract
Bacteria utilize small signal molecules to monitor population densities. Bacteria arrange gene regulation in a method called Quorum Sensing (QS). The most widespread signalling molecules are N-Acyl Homoserine Lactones (AHLs/HSLs) for Gram-negative bacteria communities. QS plays significant role in the organizing of the bacterial gene that adapts to harsh environmental conditions for bacteria. It is involved in the arrangement of duties, such as biofilm formation occurrence, virulence activity of bacteria, production of antibiotics, plasmid conjugal transfer incident, pigmentation phenomenon and production of exopolysaccharide (EPS). QS obviously impacts on human health, agriculture and environment. AHL-related QS researches have been extensively studied and understood in depth for cell to cell intercommunication channel in Gram-negative bacteria. It is understood that AHL-based QS research has been extensively studied for cell-to-cell communication in Gram-negative bacteria; hence, a comprehensive study of AHLs, which are bacterial signal molecules, is required. The purpose of this review is to examine the effects of QS-mediated AHLs in many areas by looking at them from a different perspectives, such as clinic samples, food industry, aquatic life and wastewater treatment system.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albuquerque P, Casadevall A (2012) Quorum sensing in fungi a review. Med Mycol 50:337–345
Arnaut-Rollier I, De Zutter L, Van Hoof J (1999) Identities of the Pseudomonas spp. in flora from chilled chicken. Int J Food Microbiol 48:87–96
Baker-Austin C, Oliver JD (2018) Vibrio vulnificus: new insights into a deadly opportunistic pathogen. Environ Microbiol 20:423–430
Borch E, Kant-Muermans M-L, Blixt Y (1996) Bacterial spoilage of meat and cured meat products. Int J Food Microbiol 33:103–120
Bruhn JB, Christensen AB, Flodgaard LR et al (2004) Presence of acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) and AHL-producing bacteria in meat and potential role of AHL in spoilage of meat. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4293–4302
Cabello FC (2006) Heavy use of prophylactic antibiotics in aquaculture: a growing problem for human and animal health and for the environment. Environ Microbiol 8:1137–1144
Cámara M, Williams P, Hardman A (2002) Controlling infection by tuning in and turning down the volume of bacterial small-talk. Lancet Infect Dis 2:667–676
Cataldi TRI, Bianco G, Palazzo L, Quaranta V (2007) Occurrence of N-acyl-l-homoserine lactones in extracts of some Gram-negative bacteria evaluated by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2006.11.037
Cepas V, López Y, Muñoz E et al (2019) Relationship between biofilm formation and antimicrobial resistance in gram-negative bacteria. Microb Drug Resist. https://doi.org/10.1089/mdr.2018.0027
Chambers CE, Visser MB, Schwab U, Sokol PA (2005) Identification of N-acylhomoserine lactones in mucopurulent respiratory secretions from cystic fibrosis patients. FEMS Microbiol Lett. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsle.2005.01.055
Chang CY, Krishnan T, Wang H et al (2014) Non-antibiotic quorum sensing inhibitors acting against N-acyl homoserine lactone synthase as druggable target. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep07245
Cuadrado-Silva CT, Castellanos L, Arévalo-Ferro C, Osorno OE (2013) Detection of quorum sensing systems of bacteria isolated from fouled marine organisms. Biochem Syst Ecol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2012.09.010
Davies JD and Department D (2010) Origins and evolution of antibiotic resistance Julian. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.00016-10
Davis BM, Jensen R, Williams P, O’Shea P (2010) The interaction of N-acylhomoserine lactone quorum sensing signaling molecules with biological membranes: implications for inter-kingdom signaling. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0013522
Dcosta VM, King CE, Kalan L et al (2011) Antibiotic resistance is ancient. Nature 2:2
De Kievit TR, Iglewski BH (2000) Bacterial quorum sensing in pathogenic relationships. Infect Immun 68:4839–4849
de la Fuente M, Miranda CD, Jopia P et al (2015) Growth inhibition of bacterial fish pathogens and quorum-sensing blocking by bacteria recovered from Chilean salmonid farms. J Aquat Anim Health. https://doi.org/10.1080/08997659.2014.1001534
Defoirdt T (2018) Quorum-sensing systems as targets for antivirulence therapy. Trends Microbiol 26:313–328
Defoirdt T, Thanh LD, Van Delsen B et al (2011) N-acylhomoserine lactone-degrading Bacillus strains isolated from aquaculture animals. Aquaculture. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2010.11.046
Derome N, Gauthier J, Boutin S, Llewellyn M (2016) Bacterial opportunistic pathogens of fish
Ducel G, Fabry J (2002) Prevention of hospital-acquired infections: A practical guide, 2nd edn. World Health Organization, Geneva
Erdönmez D, Rad AY, Aksöz N (2017) Quorum sensing molecules production by nosocomial and soil isolates Acinetobacter baumannii. Arch Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-017-1408-8
Falcão JP, Sharp F, Sperandio V (2004) Cell-to-cell signaling in intestinal pathogens. Curr Issues Intest Microbiol
Gennari M, Dragotto F (1992) A study of the incidence of different fluorescent Pseudomonas species and biovars in the microflora of fresh and spoiled meat and fish, raw milk, cheese, soil and water. J Appl Bacteriol 72:281–288
Ghafur A (2014) Emergence of pan-drug resistance amongst gram negative bacteria! The First case series from India. J Microbiol Infect Dis. https://doi.org/10.5799/ahinjs.02.2014.03.0145
Gopu V, Shetty PH (2016) Regulation of acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) in beef by spice marination. J Food Sci Technol 53:2686–2694
Gui M, Liu L, Wu R et al (2018) Detection of new quorum sensing N-acyl homoserine lactones from aeromonas veronii. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01712
Habimana JD, Ji J, Pi F, et al (2018) A class-specific artificial receptor-based on molecularly imprinted polymer-coated quantum dot centers for the detection of signaling molecules, N-acyl-homoserine lactones present in gram-negative bacteria. Analytica Chimica Acta doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.05.018
Holmström K, Gräslund S, Wahlström A et al (2003) Antibiotic use in shrimp farming and implications for environmental impacts and human health. Int J Food Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2621.2003.00671.x
Honda R, Phan PT, Tobino T et al (2019) Diversity of N-acyl homoserine lactones in activated sludge detected by Fourier transform mass spectrometry. NPJ Clean Water. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-019-0035-0
Hou HM, Zhu YL, Wang JY et al (2017) Characteristics of N-Acylhomoserine lactones produced by Hafnia alvei H4 isolated from spoiled instant sea cucumber. Sensors (switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/s17040772
Huang J, Shi Y, Zeng G et al (2016) Acyl-homoserine lactone-based quorum sensing and quorum quenching hold promise to determine the performance of biological wastewater treatments: An overview. Chemosphere 157:137–151
Huang S, Zhang H, Ng TCA et al (2020) Analysis of N-Acy-L-homoserine lactones (AHLs) in wastewater treatment systems using SPE-LLE with LC-MS/MS. Water Res 177:115756
Jacobi CA, Bach A, Eberl L et al (2003) Detection of N-(3-oxohexanoyl)-l-homoserine lactone in mice infected with yersinia enterocolitica serotype O8. Infect Immun. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.71.11.6624-6626.2003
Jamuna Bai A (2016) Effect of small chain N acyl homoserine lactone quorum sensing signals on biofilms of food-borne pathogens. J Food Sci Technol 53:3609
Jay JM, Vilai JP, Hughes ME (2003) Profile and activity of the bacterial biota of ground beef held from freshness to spoilage at 5–7 C. Int J Food Microbiol 81:105–111
Jefferson KK (2004) What drives bacteria to produce a biofilm?—Jefferson - 2006 - FEMS Microbiology Letters - Wiley Online Library. FEMS Microbiol. Lett.
Jiang H, Jiang D, Shao J, Sun X (2016) Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles based electrochemical sensor for the measurement of Gram-negative bacterial quorum signaling molecules (N-acyl-homoserine-lactones). Biosens Bioelectron. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.07.045
Jiang D, Liu Y, Jiang H et al (2018) A novel screen-printed mast cell-based electrochemical sensor for detecting spoilage bacterial quorum signaling molecules (N-acyl-homoserine-lactones) in freshwater fish. Biosens Bioelectron. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.11.040
Kalia VC, Patel SKS, Kang YC, Lee JK (2019) Quorum sensing inhibitors as antipathogens: biotechnological applications. Biotechnol Adv 37:68–90
Kaper JB, Sperandio V (2005) Bacterial cell-to-cell signaling in the gastrointestinal tract. Infect Immun 2:3197–3209
Karunasagar I, Pai R, Malathi GR, Karunasagar I (1994) Mass mortality of Penaeus monodon larvae due to antibiotic-resistant Vibrio harveyi infection. Aquaculture. https://doi.org/10.1016/0044-8486(94)90309-3
Kawaguchi T, Yung PC, Norman RS, Decho AW (2008) Rapid screening of quorum-sensing signal N-acyl homoserine lactones by an in vitro cell-free assay. Appl Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02869-07
Kendall MM, Sperandio V (2007) Quorum sensing by enteric pathogens. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 23:10–15
Khajanchi BK, Kirtley ML, Brackman SM, Chopra AK (2011) Immunomodulatory and protective roles of quorum-sensing signaling molecules N-Acyl homoserine lactones during infection of mice with Aeromonas hydrophila. Infect Immun. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00096-11
Kim S-R, Oh H-S, Jo S-J et al (2013) Biofouling control with bead-entrapped quorum quenching bacteria in membrane bioreactors: physical and biological effects. Environ Sci Technol 47:836–842
Kjelleberg S, Molin S (2002) Is there a role for quorum sensing signals in bacterial biofilms? Curr Opin Microbiol 5:254–258
Kraft AA (1992) Spoilage of dairy products, vegetables, fruits and other foods. Psychrotrophic Bacteria Foods Dis Spoil 2:113–120
Kravchenko VV, Kaufmann GF, Mathison JC et al (2006) N-(3-oxo-acyl)homoserine lactones signal cell activation through a mechanism distinct from the canonical pathogen-associated molecular pattern recognition receptor pathways. J Biol Chem. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M606613200
Kumari A, Pasini P, Daunert S (2008) Detection of bacterial quorum sensing N-acyl homoserine lactones in clinical samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 5:1619–1627
Kušar D, Šrimpf K, Isaković P et al (2016) Determination of N-acylhomoserine lactones of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in clinical samples from dogs with otitis externa. BMC Vet Res. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-016-0843-0
Labbate M, Queck SY, Koh KS et al (2004) Quorum sensing-controlled biofilm development in Serratia liquefaciens MG1. J Bacteriol 186:692–698
Lade H, Paul D, Kweon JH (2014) Quorum quenching mediated approaches for control of membrane biofouling. Int J Biol Sci 2014:1–25
Li YH, Tian X (2012) Quorum sensing and bacterial social interactions in biofilms. Sensors 12:2519–2538
Liu M, Gray JM, Griffiths MW (2006) Occurrence of proteolytic activity and N-acyl-homoserine lactone signals in the spoilage of aerobically chill-stored proteinaceous raw foods. J Food Prot 69:2729–2737
Liu S, Gunawan C, Barraud N et al (2016) Understanding, monitoring, and controlling biofilm growth in drinking water distribution systems. Environ Sci Technol 50:8954–8976
Liu J, Eng CY, Ho JS et al (2019) Quorum quenching in anaerobic membrane bioreactor for fouling control. Water Res 156:159–167
Ma H, Wang X, Zhang Y et al (2018) The diversity, distribution and function of N-acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) in industrial anaerobic granular sludge. Biores Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.043
Medina-Martinez MS, Uyttendaele M, Demolder V, Debevere J (2006) Influence of food system conditions on N-acyl-l-homoserine lactones production by Aeromonas spp. Int J Food Microbiol 112:244–252
Middleton B, Rodgers HC, Cámara M et al (2002) Direct detection of N-acylhomoserine lactones in cystic fibrosis sputum. FEMS Microbiol Lett. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1097(01)00556-0
Miller MB, Bassler BL (2002) Quorum sensing in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.micro.55.1.165
Niu Y, Defoirdt T, Baruah K et al (2014) Bacillus sp LT3 improves the survival of gnotobiotic brine shrimp (Artemia franciscana) larvae challenged with Vibrio campbellii by enhancing the innate immune response and by decreasing the activity of shrimp-associated vibrios. Vet Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2014.08.007
Oh H-S, Yeon K-M, Yang C-S et al (2012) Control of membrane biofouling in MBR for wastewater treatment by quorum quenching bacteria encapsulated in microporous membrane. Environ Sci Technol 46:4877–4884
Okutsu N, Morohoshi T, Xie X et al (2016) Characterization of N-acylhomoserine lactones produced by bacteria isolated from industrial cooling water systems. Sensors (switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/s16010044
Pinto UM, de Souza VE, Martins ML, Vanetti MCD (2007) Detection of acylated homoserine lactones in gram-negative proteolytic psychrotrophic bacteria isolated from cooled raw milk. Food Control 18:1322–1327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2006.09.005
Rasmussen TB, Givskov M (2006) Quorum-sensing inhibitors as anti-pathogenic drugs. Int J Med Microbiol 296:149–161
Ravn L, Christensen AB, Molin S et al (2001) Methods for detecting acylated homoserine lactones produced by Gram-negative bacteria and their application in studies of AHL-production kinetics. J Microbiol Methods. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-7012(01)00217-2
Schauder S, Bassler BL (2001) The languages of bacteria. Gen Dev 15:1468–1480
Schikora A, Schenk ST, Stein E et al (2011) N-acyl-homoserine lactone confers resistance toward biotrophic and hemibiotrophic pathogens via altered activation of AtMPK6. Plant Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.180604
Shrout JD, Nerenberg R (2012) Monitoring bacterial twitter: Does quorum sensing determine the behavior of water and wastewater treatment biofilms? Environ Sci Technol 46:1995–2005
Sircili MP, Walters M, Trabulsi LR, Sperandio V (2004) Modulation of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli virulence by quorum sensing. Infect Immun 72:2329–2337. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.72.4.2329-2337.2004
Soares JA, Ahmer BMM (2011) Detection of acyl-homoserine lactones by Escherichia and Salmonella. Curr Opin Microbiol 14:188–193
Sokol PA, Sajjan U, Visser MB et al (2003) The CepIR quorum-sensing system contributes to the virulence of Burkholderia cenocepacia respiratory infections. Microbiology. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.26540-0
Sperandio V, Mellies JL, Nguyen W et al (1999) Quorum sensing controls expression of the type III secretion gene transcription and protein secretion in enterohemorrhagic and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:15196–15201. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.26.15196
Stanbridge LH, Davies AR (1998) The microbiology of chill-stored meat. Microbiol Meat Poultry 174–219
Surette MG, Miller MB, Bassler BL (1999) Quorum sensing in Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium, and Vibrio harveyi: A new family of genes responsible for autoinducer production. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.4.1639
Tamma PD, Putcha N, Suh YD et al (2011) Does prolonged β-lactam infusions improve clinical outcomes compared to intermittent infusions? A meta-analysis and systematic review of randomized, controlled trials. BMC Infect Dis. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-11-181
Tamma PD, Holmes A, Ashley ED (2014) Antimicrobial stewardship: another focus for patient safety? Curr Opin Infect Dis 27:348–355
Tamma PD, Miller MA, Cosgrove SE (2019) Rethinking how antibiotics are prescribed. JAMA. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2018.19509
Tan CH, Koh KS, Xie C et al (2014) The role of quorum sensing signalling in EPS production and the assembly of a sludge community into aerobic granules. ISME J 8:1186–1197
Tateda K, Ishii Y, Matsumoto T et al (1996) Direct evidence for antipseudomonal activity of macrolides: Exposure- dependent bactericidal activity and inhibition of protein synthesis by erythromycin, clarithromycin, and azithromycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.40.10.2271
Ternström A, Lindberg A-M, Molin G (1993) Classification of the spoilage flora of raw and pasteurized bovine milk, with special reference to Pseudomonas and Bacillus. J Appl Bacteriol 75:25–34
Tryfinopoulou P, Tsakalidou E, Nychas G-J (2002) Characterization of Pseudomonas spp. associated with spoilage of gilt-head sea bream stored under various conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:65–72
Turan NB, Chormey DS, Büyükpınar Ç et al (2017) Quorum sensing: little talks for an effective bacterial coordination. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 91:1–11
Wang J, Ding L, Li K et al (2017) Development of an extraction method and LC–MS analysis for N-acylated-L-homoserine lactones (AHLs) in wastewater treatment biofilms. J Chromatogr B. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2016.11.029
Ward C, Cámara M, Forrest I et al (2003) Preliminary findings of quorum signal molecules in clinically stable lung allograft recipients. Thorax 58:444–446. https://doi.org/10.1136/thorax.58.5.444
Waters CM, Bassler BL (2005) QUORUM SENSING: cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.cellbio.21.012704.131001
Watson WT, Minogue TD, Val DL et al (2002) Structural basis and specificity of acyl-homoserine mactone signal production in bacterial quorum sensing. Mol Cell. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00480-X
Wen KY, Cameron L, Chappell J, et al (2017) A cell-free biosensor for detecting quorum sensing molecules in P. aeruginosa-infected respiratory samples. ACS Synthetic Biology. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.7b00219
WHO , World Health Organization (2017) Antibacterial agents in clinical development: an analysis of the antibacterial clinical development pipeline, including tuberculosis (WHO/EMP/IAU/2017.11)
Wilson APR, Livermore DM, Otter JA et al (2016) Prevention and control of multi-drug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria: Recommendations from a Joint Working Party. J Hospital Infect 92:S1–S44
Wu H, Song Z, Hentzer M et al (2000) Detection of N-acylhomoserine lactones in lung tissues of mice infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-146-10-2481
Yan X, Zheng S, Huo Z et al (2020) Effects of exogenous N-acyl-homoserine lactones on nutrient removal, sludge properties and microbial community structures during activated sludge process. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126945
Yekani M, Baghi HB, Sefidan FY et al (2018) The rates of quinolone, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole and aminoglycoside resistance among Enterobacteriaceae isolated from urinary tract infections in Azerbaijan, Iran. GMS Hyg Infect Control. https://doi.org/10.3205/dgkh000313
Yeon KM, Cheong WS, Oh HS et al (2009) Quorum sensing: a new biofouling control paradigm in a membrane bioreactor for advanced wastewater treatment. Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1021/es8019275
Yu H, Liang H, Qu F et al (2016a) Biofouling control by biostimulation of quorum-quenching bacteria in a membrane bioreactor for wastewater treatment. Biotechnol Bioeng 113:2624–2632
Yu H, Xu G, Qu F et al (2016b) Effect of solid retention time on membrane fouling in membrane bioreactor: from the perspective of quorum sensing and quorum quenching. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:7887–7897
Yu H, Lee K, Zhang X, Choo K-H (2019) Core-shell structured quorum quenching beads for more sustainable anti-biofouling in membrane bioreactors. Water Res 150:321–329
Zhang LH, Dong YH (2004) Quorum sensing and signal interference: diverse implications. Mol Microbiol 53:1563–1571
Zhao J, Chen M, Quan CS, Fan SD (2015) Mechanisms of quorum sensing and strategies for quorum sensing disruption in aquaculture pathogens. J Fish Dis. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfd.12299
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful for grants of the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (Grant Number: 119Z184) and Aksaray University Scientific Research Projects Coordination (Grant Number: 2018/060). Because the information obtained for preparation of this paper was gathered during these projects studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ÖA: conceptualization, writing review and editing. DE: conceptualization, writing review and editing. BÖA: conceptualization, writing review and editing. MO: conceptualization, writing review and editing. All the authors agreed to submit the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest statement
Nothing declared.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Acet, Ö., Erdönmez, D., Acet, B.Ö. et al. N-acyl homoserine lactone molecules assisted quorum sensing: effects consequences and monitoring of bacteria talking in real life. Arch Microbiol 203, 3739–3749 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02381-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02381-9