Abstract
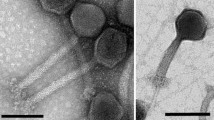
In this study, the genome of a new strain of lytic Staphylococcus aureus Herelleviridae, vBSM-A1, was characterized and annotated. The phage was isolated from sewage samples collected in Xinjiang Province, China. The genome of vBSM-A1 was found to comprise a linear double-stranded DNA of 140,654 bp length, with a G + C content of 30.33%. A total of 215 ORFs were detected in the phage DNA, 74 of which were functionally assigned. The 3D structure model of endolysin LysK (ORF 143) was created using Phyre2.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basanisi MG, Bella GL, Nobili G et al (2017) Genotyping of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolated from milk and dairy products in South Italy. Food Microbiol 62:141–146
Bolger AM, Marc L, Bjoern U (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30(15):2114–2120
Cecilia B, Juan Carlos LF, Stéphanie B et al (2013) X-ray structure of a superinfection exclusion lipoprotein from phage TP-J34 and identification of the tape measure protein as its target. Mol Microbiol 89(1):152–165
Dwivedi B, Xue B, Lundin D et al (2013) A bioinformatic analysis of ribonucleotide reductase genes in phage genomes and metagenomes. BMC Evol Biol 13(1):33
Geng H, Zou W, Zhang M et al (2019) Evaluation of phage therapy in the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis in mice. Folia Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-019-00729-9
Haran KP, Godden SM, Boxrud D et al (2012) Prevalence and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, isolated from bulk tank milk from Minnesota dairy farms. J Clin Microbiol 50(3):688
Iwano H, Inoue Y, Takasago T et al (2018) Bacteriophage ΦSA012 has a broad host range against Staphylococcusaureus and effective lytic capacity in a mouse mastitis model. Biology 7(1):8
Jamali H, Barkema HW, Jacques M et al (2018) Invited review: incidence, risk factors, and effects of clinical mastitis recurrence in dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 101(6):4729–4746
Kane TL, Carothers KE, Lee SW (2018) Virulence factor targeting of the bacterial pathogen Staphylococcus aureus for vaccine and therapeutics. Curr Drug Targets 19:111–127
Liu H, Li S, Meng L et al (2017) Prevalence, antimicrobial susceptibility, and molecular characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from dairy herds in northern China. J Dairy Sci 100(11):8796–8803
Nelson DC, Schmelcher M, Rodriguez-Rubio L (2012) Endolysins as antimicrobials. Adv Virus Res 83:299–365
Notebaert S, Meyer E (2006) Mouse models to study the pathogenesis and control of bovine mastitis. A review. Vet Q 28(1):2–13
Pell LG, Voula K, Donaldson LW et al (2009) The phage lambda major tail protein structure reveals a common evolution for long-tailed phages and the type VI bacterial secretion system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(11):4160–4165
Peter S, Brooks AN, Lowe TM (2005) The tRNAscan-SE, snoscan and snoGPS web servers for the detection of tRNAs and snoRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 33(Web Server issue):686–689
Roches ADBD, Lussert A, Faure M et al (2018) Dairy cows under experimentally-induced Escherichia coli mastitis show negative emotional states assessed through Qualitative Behaviour Assessment. Appl Anim Behav Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applanim.2018.06.004
Ronco T, Klaas IC, Stegger M et al (2018) Genomic investigation of Danish Staphylococcus aureus isolates from bulk tank milk and dairy cows with clinical mastitis. Vet Microbiol 215:35
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, pp 182–186
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Wall RJ, Powell AM, Paape MJ et al (2005) Genetically enhanced cows resist intramammary Staphylococcus aureus infection. Nat Biotechnol 23(4):445–451
Yuan Y, Zhao F, Wang L et al (2019) Complete genome analysis of the novel Enterococcus faecalis phage vB_EfaS_AL3. Arch Virol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-019-04341-7
Yuksel SA, Thompson KD, Ellis AE et al (2001) Purification of Piscirickettsia salmonis and associated phage particles. Dis Aquat Organ 44(3):231–235
Zandkarimi F, Vanegas J, Fern X et al (2018) Metabotypes with elevated protein and lipid catabolism and inflammation precede clinical mastitis in prepartal transition dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 101(6):S1331041478
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant no. 2018YFD0500600). We would like to thank Dr. Alan K Chang for his valuable discussion and help in editing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
203_2020_1867_MOESM1_ESM.png
Secondary structures of the tRNAs in the phage vBSM-A1. a tRNA-Asp (GTC); b tRNA-Phe (GAA); c tRNA-Pseudo (CCA); d tRNA-Met (CAT) (PNG 426 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geng, H., Zhang, M., Li, X. et al. Complete genome analysis of a Staphylococcus aureus phage (vBSM-A1). Arch Microbiol 202, 1617–1626 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-01867-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-01867-2