Abstract
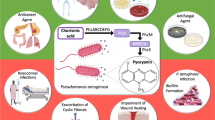
Pyocyanin produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a key virulence factor that often causes heavy damages to airway and lung in patients. Conversion of phenazine-1-carboxylic acid to pyocyanin involves an extrametabolic pathway that contains two enzymes encoded, respectively, by phzM and phzS. In this study, with construction of the rpoS-deficient mutant, we first found that although phenazine production increased, pyocyanin produced in the mutant YTΔrpoS was fourfold much higher than that in the wild-type strain YT. To investigate this issue, we constructed phzM-lacZ fusion on a vector and on the chromosome. By quantifying β-galactosidase activities, we confirmed that expression of the phzM was up-regulated when the rpoS gene was inactivated. However, no changes occurred in the expression of phzS and phzH when the rpoS was knocked out. Taken together, overproduction of the SAM-dependent methyltransferase (PhzM) might contribute to the increased pyocyanin in the absence of RpoS in P. aeruginosa.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Battesti A, Majdalani N, Gottesman S (2011) The RpoS-mediated general stress response in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol 65:189–213. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-micro-090110-102946
Blumer C, Heeb S, Pessi G, Haas D (1999) Global GacA-steered control of cyanide and exoprotease production in Pseudomonas fluorescens involves specific ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:14073–14078. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.24.14073
Chen WP, Kuo TT (1993) A simple and rapid method for the preparation of Gram-negative bacterial genomic DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 21:2260. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/21.9.2260
Chieda Y, Iiyama K, Yasunaga-Aoki C, Lee JM (2005) Pathogenicity of gacA mutant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. FEMS Microbiol Lett 244:181–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsle.2005.01.032
Cui Q, Lv H, Qi Z, Jiang B, Xiao B, Liu L, Ge Y, Hu X (2016) Cross-regulation between the phz1 and phz2 operons maintain a balanced level of phenazine biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. PLoS One 11:e0144447. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0144447
Curran CS, Bolig T, Torabi-Parizi P (2018) Mechanisms and targeted therapies for Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 197:708–727. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201705-1043SO
Greenhagen BT, Shi K, Robinson H, Gamage S, Bera AK, Ladner JE, Parsons JF (2008) Crystal structure of the pyocyanin biosynthetic protein PhzS. Biochemistry 47:5281–5289. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi702480t
Folkesson A, Jelsbak L, Yang L, Johansen HK, Ciofu O, Høiby N, Molin S (2012) Adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the cystic fibrosis airway: an evolutionary perspective. Nat Rev Microbiol 10:841–851. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2907
Hall S, McDermott C, Anoopkumar-Dukie S, McFarland AJ, Forbes A, Perkins AV, Davey AK, Chess-Williams R, Kiefel MJ, Arora D, Grant GD (2016) Cellular effects of pyocyanin, a secreted virulence factor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Toxins 8:236. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8080236
Hassett DJ, Borchers MT, Panos RJ (2014) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): evaluation from clinical, immunological and bacterial pathogenesis perspectives. J Microbiol 52:211–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-014-4068-2
Heeb S, Itoh Y, Nishijyo T, Schnider U, Keel C, Wade J, Walsh U, O'Gara F, Haas D (2000) Small, stable shuttle vectors based on the minimal pVS1 replicon for use in gram-negative, plant-associated bacteria. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 13:232–237. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI.2000.13.2.232
Higgins S, Heeb S, Rampioni G, Fletcher MP, Williams P, Cámara M (2018) Differential regulation of the phenazine biosynthetic operons by quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1-N. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 8:252. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2018.00252
Hoang TT, Karkhoff-Schweizer RR, Kutchma AJ, Schweizer HP (1998) A broad-host-range Flp-FRT recombination system for site-specific excision of chromosomally-located DNA sequences: application for isolation of unmarked Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants. Gene 212:77–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-1119(98)00130-9
Huang J, Xu Y, Zhang H, Li Y, Huang X, Ren B, Zhang X (2009) Temperature-dependent expression of phzM and its regulatory genes lasI and ptsP in rhizosphere isolate Pseudomonas sp. strain M18. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:6568–6580. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01148-09
Huang J, Sonnleitner E, Ren B, Xu Y, Haas D (2012) Catabolite repression control of pyocyanin biosynthesis at an intersection of primary and secondary metabolism in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:5016–5020. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00026-12
Huang R, Feng Z, Chi X, Sun X, Lu Y, Zhang B, Lu R, Luo W, Wang Y, Miao J, Ge Y (2018) Pyrrolnitrin is more essential than phenazines for Pseudomonas chlororaphis G05 in its suppression of Fusarium graminearum. Microbiol Res 215:55–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2018.06.008
Jimenez PN, Koch G, Thompson JA, Xavier KB, Cool RH, Quax WJ (2012) The multiple signaling systems regulating virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 76:46–65. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.05007-11
Kim KJ (2000) Phenazine-1-carboxylic acid resistance in phenazine-1-carboxylic acid producing Bacillus sp. B-6. J Biochem Mol Biol 33:332–336
Kizny Gordon AE, Mathers AJ, Cheong EYL, Gottlieb T, Kotay S, Walker AS, Peto TEA, Crook DW, Stoesser N (2017) The hospital water environment as a reservoir for carbapenem-resistant organisms causing hospital-acquired infections: a systematic review of the literature. Clin Infect Dis 64:1435–1444. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cix132
Lee J, Zhang L (2015) The hierarchy quorum sensing network in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Protein Cell 6:26–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-014-0100-x
Liang H, Li L, Dong Z, Surette MG, Duan K (2008) The YebC family protein PA0964 negatively regulates the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quinolone signal system and pyocyanin production. J Bacteriol 190:6217–6227. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00428-08
Mavrodi DV, Bonsall RF, Delaney SM, Soule MJ, Phillips G, Thomashow LS (2001) Functional analysis of genes for biosynthesis of pyocyanin and phenazine-1-carboxamide from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J Bacteriol 183:6454–6465. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.183.21.6454-6465.2001
Mavrodi DV, Blankenfeldt W, Thomashow LS (2006) Phenazine compounds in fluorescent Pseudomonas spp. biosynthesis and regulation. Annu Rev Phytopathol 44:417–445. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.phyto.44.013106.145710
Mavrodi DV, Peever TL, Mavrodi OV, Parejko JA, Raaijmakers JM, Lemanceau P, Mazurier S, Heide L, Blankenfeldt W, Weller DM, Thomashow LS (2010) Diversity and evolution of the phenazine biosynthesis pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:866–879. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02009-09
Miller JH (1972) Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Minton NP (1984) Improved plasmid vectors for the isolation of translational lac gene fusions. Gene 31:269–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1119(84)90220-8
Mulcahy LR, Isabella VM, Lewis K (2014) Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms in disease. Microb Ecol 68:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-013-0297-x
Nathwani D, Raman G, Sulham K, Gavaghan M, Menon V (2014) Clinical and economic consequences of hospital-acquired resistant and multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control 3:32. https://doi.org/10.1186/2047-2994-3-32
Parejko JA, Mavrodi DV, Mavrodi OV, Weller DM, Thomashow LS (2012) Population structure and diversity of phenazine-1-carboxylic acid producing fluorescent Pseudomonas spp. from dryland cereal fields of central Washington State (USA). Microb Ecol 64:226–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-012-0015-0
Parsons JF, Greenhagen BT, Shi K, Calabrese K, Robinson H, Ladner JE (2007) Structural and functional analysis of the pyocyanin biosynthetic protein PhzM from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochemistry 46:1821–1828. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi6024403
Pierson LS 3rd, Pierson EA (2010) Metabolism and function of phenazines in bacteria: impacts on the behavior of bacteria in the environment and biotechnological processes. Appl Microbiol Biotech 86:1659–1670. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2509-3
Rada B, Leto TL (2013) Pyocyanin effects on respiratory epithelium: relevance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa airway infections. Trends Microbiol 21:73–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2012.10.004
Recinos DA, Sekedat MD, Hernandez A, Cohen TS, Sakhtah H, Prince AS, Price-Whelan A, Dietrich LE (2012) Redundant phenazine operons in Pseudomonas aeruginosa exhibit environment-dependent expression and differential roles in pathogenicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:19420–19425. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1213901109
Sakhtah H, Koyama L, Zhang Y, Morales DK, Fields BL, Price-Whelan A, Hogan DA, Shepard K, Dietrich LE (2016) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa efflux pump MexGHI-OpmD transports a natural phenazine that controls gene expression and biofilm development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:E3538–E3547. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1600424113
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a Laboratory Manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Schuster M, Hawkins AC, Harwood CS, Greenberg EP (2004) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa RpoS regulon and its relationship to quorum sensing. Mol Microbiol 51:973–985. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03886.x
Schweizer HD (1993) Small broad-host-range gentamycin resistance cassettes for site-specific insertion and deletion mutagenesis. BioTechniques 15:831–834
Smith AW, Iglewski BH (1989) Transformation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res 17:10509. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/17.24.10509
Suh SJ, Silo-Suh L, Woods DE, Hassett DJ (1999) Effect of rpoS mutation on the stress response and expression of virulence factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 181:3890–3897
Valentini M, Gonzalez D, Mavridou DA, Filloux A (2018) Lifestyle transitions and adaptive pathogenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Curr Opin Microbiol 41:15–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2017.11.006
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Stephan Heeb (the University of Nottingham, Nottingham, United Kingdom) for his gifts of plasmid pME6010 and pME6522, Stephen Perle (University of Bridgeport, Connecticut, the United States) for his help in preparation and revision of this manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31260080 and 31571997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Performed the experiments: WK, KL, and ZK; quantified phenazines and analyzed the data: HM, YY, and XX; prepared and wrote the manuscript: YZ and CL; conceived and designed the experiments: CX and GY.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors in this study declared no conflict of any interests.
Ethical statement
As all experiments in this study did not involve any animals or human bodies, ethics approval was not sought.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, K., Kai, L., Zhang, K. et al. Overexpression of phzM contributes to much more production of pyocyanin converted from phenazine-1-carboxylic acid in the absence of RpoS in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Arch Microbiol 202, 1507–1515 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-01837-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-01837-8