Abstract
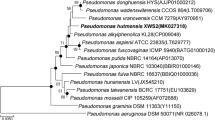
A Gram-stain-negative, aerobic, mobile, and rod-shaped bacterium, designated JJ3T, was isolated from peanut rhizospheric soil in Qingdao, Shandong Province, China, and was characterized using a polyphasic approach. Strain JJ3T grew at 4–40 °C, at pH 5.0–9.0 and 0–4% NaCl. The strain was positive for both catalase and oxidase tests, and was able to degrade aflatoxin B1. According to the 16S rRNA gene sequence comparisons, the strain JJ3T was identified as a member of the genus Pseudomonas and was most closely related to Pseudomonas japonica JCM 21532T and Pseudomonas alkylphenolica JCM 16553T with sequence similarity of 99.0% and 98.9%, respectively. A multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA) of concatenating 16S rRNA, gyrB and rpoD gene sequences showed that strain JJ3T belonged to the Pseudomonas putida subcluster. Genomic comparison of strain JJ3T with its closest phylogenetic type strain using average nucleotide index (ANI) and digital DNA–DNA relatedness revealed 76.7–82.9% and 20.2–37.1%, respectively. All values were distinctly lower than the thresholds established for species differentiation. The predominant cellular fatty acids of strain JJ3T were C17:0 cyclo (24.0%), C16:0 (21.4%), summed features 3 (C16:1ω7c and/or C16:1ω6c) (11.5%) and summed features 8 (C18:1ω7c and/or C18:1ω6c) (10.5%). The major polar lipids of strain JJ3T were phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylglycerol and diphosphatidylglycerol. The physiological, biochemical, and genetic characteristics support the assignment of JJ3T to the genus Pseudomonas, but are different to those of phylogenetically neighboring species to represent a novel species. The name Pseudomonas qingdaonensis sp. nov. is proposed, with JJ3T (= JCM 32579T = KCTC 62384T = CGMCC 1.16493T) as the type strain.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernardet JF, Nakagawa Y, Holmes B (2002) Proposed minimal standards for describing new taxa of the family Flavobacteriaceae and emended description of the family. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1049–1070
Camara B, Strompl C, Verbarg S, Sproer C, Pieper DH, Tindall BJ (2007) Pseudomonas reinekei sp. nov., Pseudomonas moorei sp. nov. and Pseudomonas mohnii sp. nov., novel species capable of degrading chlorosalicylates or isopimaric acid. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:923–931
Dai X, Shi X, Gao X, Liu J, Zhang XH (2014) Roseivivax marinus sp. nov., isolated from deep water. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:2540–2544
Dorn E, Hellwig M, Reineke W, Knackmuss HJ (1974) Isolation and characterization of a 3-chlorobenzoate degrading pseudomonad. Arch Microbiol 99:61–70
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Goris J, Konstantinidis KT, Klappenbach JA, Coenye T, Vandamme P, Tiedje JM (2007) DNA-DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:81–91
Hwang CY, Zhang GI, Kang SH, Kim HJ, Cho BC (2009) Pseudomonas pelagia sp. nov., isolated from a culture of the Antarctic green alga Pyramimonas gelidicola. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:3019–3024
Kim KH, Roh SW, Chang HW, Nam YD, Yoon JH, Jeon CO, Oh HM, Bae JW (2009) Pseudomonas sabulinigri sp. nov., isolated from black beach sand. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:38–41
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Kimura N, Watanabe T, Suenaga H, Fujihara H, Futagami T, Goto M, Hanada S, Hirose J (2018) Pseudomonas furukawaii sp. nov., a polychlorinated biphenyl-degrading bacterium isolated from biphenyl-contaminated soil in Japan. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:1429–1435
King EO, Ward MK, Rainey DE (1954) Two simple media for demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescein. J Lab Clin Med 44:301–307
Komagata K, Suzuki K (1987) Lipid and cell-wall analysis in bacterial systematics. Methods Microbiol 19:161–207
Lang E, Burghartz M, Spring S, Swiderski J, Spröer C (2010)) Pseudomonas benzenivorans sp. nov. and Pseudomonas saponiphila sp. nov., represented by xenobiotics degrading type strains. Curr Microbiol 60:85–91
Li R, Zhu H, Ruan J, Qian W, Fang X, Shi Z, Li Y, Li S, Shan G, Kristiansen K, Li S, Yang H, Wang J, Wang J (2010) De novo assembly of human genomes with massively parallel short read sequence. Genome Res 20:265–272
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance function. BMC Bioinform 14:60
Minnikin M, O’Donnell A, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M, Schaal A, Parlett J (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241
Mulet M, Lalucat J, García-Valdés E (2010) DNA sequence-based analysis of the Pseudomonas species. Environ Microbiol 12:1513–1530
Mulet M, Sanchez D, Lalucat J, Lee K, García-Valdés E (2015) Pseudomonas alkylphenolica sp. nov., a bacterial species able to form special serial structures when grown on p-cresol. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:4013–4018
Nishimori E, Kita-Tsukamoto K, Wakabayashi H (2000) Pseudomonas plecoglossicida sp. nov., the causative agent of bacterial haemorrhagic ascites of ayu, Plecoglossus altivelis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:83–89
Pungrasmi W, Lee HS, Yokota A, Ohta A (2008) Pseudomonas japonica sp. nov., a novel species that assimilates straight chain alkylphenols. J Gen Appl Microbiol 54:61–69
Richter M, Rosselló-Móra R (2009) Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:19126–19131
Romanenko LA, Uchino M, Falsen E, Frolova GM, Zhukova NV, Mikhailov VV (2005) Pseudomonas pachastrellae sp. nov., isolated from a marine sponge. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:919–924
Romanenko LA, Tanaka N, Svetashev VI, Kurilenko VV, Mikhailov VV (2013) Luteimonas vadosa sp. nov., isolated from seashore sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:261–1266
Romanenko LA, Tanaka N, Svetashev VI, Mikhailov VV (2015) Pseudomonas glareae sp. nov., a marine sediment-derived bacterium with antagonistic activity. Arch Microbiol 197:693–699
Sangare L, Zhao Y, Folly YME, Chang J, Li J, Selvaraj JN, Xiang F, Zhou L, Wang Y, liu Y (2014) Aflatoxin B1 degradation by a Pseudomonas strain. Toxins 6:3028–3040
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids, MIDI Technical Note 101. MIDI Inc, Newark
Schreiber L, Kjeldsen KU, Obst M, Funch P, Schramm A (2016) Description of Endozoicomonas ascidiicola sp. nov., isolated from Scandinavian ascidians. Syst Appl Microbiol 39:313–318
Stackebrandt E, Ebers J (2006) Taxonomic parameters revisited: tarnished gold standards. Microbiol Today 45:153–155
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Wang MQ, Sun L (2016) Pseudomonas oceani sp. nov., isolated from deep seawater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:4250–4255
Wang LT, Tai CJ, Wu YC, Chen YB, Lee FL, Wang SL (2010) Pseudomonas taiwanensis sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2094–2098
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR, Grimont PAD, Kandler O, Krichevsky MI, Moore LH, Moore WEC, Murray RGE, Stackebrandt E, Starr MP, Trüper HG (1987) Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematic. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–564
Xie CH, Yokota A (2003) Phylogenetic analyses of Lampropedia hyalina based on the 16S rRNA gene sequence. J Gen Appl Microbiol 49:345–349
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2016CM43, ZR2016YL021, ZR2017MC060, ZR2017MC062), the Innovation Project of AgriculturalScience and Technology of Shandong Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CXGC2018E21), the Major Scientific and Technological Achievements Cultivation Program of Shandong Academy of Agricultural Sciences (2016CGPY10), Shandong Major Agricultural Application Technology Innovation Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The accession numbers of the 16S rRNA, gyrB, and rpoD genes for the type strain JJ3T in GenBank are MG589917, MH758785, and MH758786, respectively. The genome has been deposited in GenBank under the accession number of PHTD00000000 for strain JJ3T. The digital protologue database (DPD) Taxon Number of strain JJ3T is TA00689.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, MQ., Wang, Z., Yu, LN. et al. Pseudomonas qingdaonensis sp. nov., an aflatoxin-degrading bacterium, isolated from peanut rhizospheric soil. Arch Microbiol 201, 673–678 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-019-01636-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-019-01636-w