Abstract
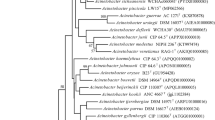
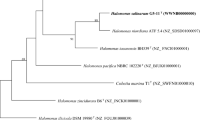
A novel aerobic, non-motile, halotolerant, alkalitolerant, hydrocarbon degrading, and rod shaped bacterium, designated strain R160T, was isolated from soil in South Korea. Cells were Gram-staining-negative, catalase-positive, and oxidase-negative. This strain grew up to 7% of NaCl and in the pH range of 6–11 (optimum 7.0–10.0). The isolate degraded 51.7 ± 1.3% of hydrocarbon components (C-18, C-20, and C-22) and 45.8 ± 1.4% oil components (kerosene, diesel, and gasoline). Phylogenetic analysis based on 16 S rRNA gene sequences revealed that strain R160T formed a lineage within the genus Acinetobacter, and was closely related to ‘Acinetobacter oleivorans’ DR1T (97.47%, sequence similarity). Other closely related members have sequence similarity between 97.47 to 96.52%. The predominant respiratory lipoquinones of strain R160T were ubiquinone 9 (Q-9) and ubiquinone 8 (Q-8). The major polar lipids were phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), diphosphatidylglycerol (DPG), phosphatidylglycerol (PG), and phosphatidylcholine (PC). The major cellular fatty acids were 9-octadecenoic acid (C18:1 ω9c), hexadecanoic acid (C16:0), and summed feature (comprising C16:1 ω7c and/or C16:1 ω6c). The DNA G + C content of strain R160T was 44.9 mol%. On the basis of phenotypic, genotypic, chemotaxonomic, and phylogenetic characteristics, strain R160T represents a novel species of the genus Acinetobacter, for which the name Acinetobacter halotolerans sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is R160T (= KEMB 9005-333T = KACC 18453T = JCM 31009T).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albarracin VH, Pathak GP, Douki T, Cadet J, Borsarelli CD, GÓ“rtner W, Farias ME (2012) Extremophilic Acinetobacter strains from high altitude lakes in Argentinean Puna: Remarkable UV-B and efficient DNA damage repair. Orig Life Evol Biosph 42:201–221
Breznak JA, Costilow RN (2007) Physicochemical factors in growth. In: Beveridge TJ, Breznak JA, Marzluf GA, Schmidt TM, Snyder LR (eds) Methods for General and Molecular Bacteriology, 3rd edn. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D. C., pp 309–329
Brisou J, Prévot AR (1954) Etudes de systématique bactérienne. X. Révision des especes reunites dans le genre Achromobacter. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 86:722–728 (French)
Card GL (1973) Metabolism of phosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylethanolamide and cardiolipin of Bacillus stearothermaphilus. J Bacteriol 114:1125–1137
Chaudhary DK (2016) Bioremediation: an eco-friendly approach for polluted agriculture soil. Emer Life Sci Res 2:73–75
Dahal RH, Kim J (2016a) Pedobacter humicola sp. nov., a member of the genus Pedobacter isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:2205–2211
Dahal RH, Kim J (2016b) Rhabdobacter roseus gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:308–314
Doetsch RN (1981) Determinative methods of light microscopy. In: Gerhardt P (ed) Manual of methods for general bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 21–33
Ezaki T, Hashimoto Y, Yabuuchi E (1989) Fluorometric DNA-DNA hybridization in microdilution wells as an alternative to member filter hybridization in which radioisotopes are used to determine genetic relatedness among bacterial strains. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 39:224–229
Fatajeva E, Gailiütė I, Paliulis D, Grigiškis S (2014) The use of Acinetobacter sp. for oil hydrocarbon degradation in saline waters. Biologija 60:126–133
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evol Int J org Evol 39:783–791
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Zool 20:406–416
Frank JA, Reich CI, Sharma S, Weisbaum JS, Wilson BA, Olsen GJ (2008) Critical evaluation of two primers commonly used for amplification of bacterial 16 S rRNA gene. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:2461–2470
Hairaishi A, Ueda Y, Ishihara J, Mori T (1996) Comparative lipoquinone analysis of influent sewage and activated sludge by high-performance liquid chromatography and photodiode array detection. J Gen Appl Microbiol 42:457–469
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Ishige T, Tani A, Saki Y, Kato N (2000) Long-chain aldehyde dehydrogenase that participates in n-alkane utilization and wax ester synthesis in Acinetobacter sp. strain M−1. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3481–3486
Jawad A, Seifert H, Snelling M, Heritage J, Hawkey PM (1998) Survival of Acinetobacter baumannii on dry surfaces: comparison of outbreak and sporadic isolates. J Clin Microbiol 36:1938–1941
Kang SK, Jung J, Jeon CO, Park W (2011) Acinetobacter oleivorans sp. nov. is capable of adhering to and growing on diesel-oil. J Microbiol 49:29–34
Kim D, Baik KS, Kim MS, Park SC, Kim SS, Rhee MS, Kwak YS, Seong CN (2008) Acinetobacter soli sp. nov., isolated from forest soil. J Microbiol 46:396–401
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16 S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Komagata K, Suzuki K (1987) Lipids and cell wall analysis in bacterial systematics. Methods Microbiol 19:161–203
Krizova L, Maixnerova M, Sedo O, Nemec A (2014) Acinetobacter bohemicus sp. nov. widespread in natural soil and water ecosystems in the Czech republic. Syst Appl Microbial 37:467–473
La Scola B, Gundi VA, Khamis A, Raoult D (2006) Sequencing of the rpoB gene and flanking spacers for molecular identification of Acinetobacter species. J Clin Microbiol 44:827–832
Li Y, Piao CG, Ma YC, He W, Wang HM, Chang JP, Guo LM, Wang XZ, Xie SJ, Guo MW (2013) Acinetobacter puyangensis sp. nov., isolated from healthy and diseased part of Populs xeuramericana canker bark. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:2963–2969
Macfaddin JF (1980) Bacterial tests for identification of medical bacteria. 2nd edn. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp. 162–218
Margesin R, Schinner F (2001) Bioremediation (natural attenuation and bio-stimulation) of diesel-oil-contaminated soil in an alpine glacier skiing area. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:3127–3133
Mesbah M, Premachandran U, Whitman WB (1989) Precise measurement of the G + C content of deoxyribonucleic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography. Int Syst Bacteriol 39:159–167
Minnikin DE, O’Donnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M, Schaal A, Parlett JH (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241
Mishra S, Sarma PM, Lal B (2004) Crude oil degradation efficiency of a recombinant Acinetobacter baumannii strain and its survival in crude oil-contaminated soil microcosm. FEMS Microbiol Lett 235:323–331
Moore DD, Dowhan D (1995) Preparation and analysis of DNA. In: Assubel FW, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JD, Smith JA, Struhl K (eds) Current protocols in molecular biology. Wiley, New York, pp 2–11
Nemec A, Musilek M, Maixnerová M, De baere T, Van Der Reijden TJK, Vaneechoutte M, Dijkshroorn L (2009) Acinetobacter beijerinckii sp. nov. and Acinetobacter gyllenbergii sp. nov., haemolytic organisms isolated from humans. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:118–124
Nishimura Y, Ino T, Iizuka H (1988) Acinetobacter radioresistens sp. nov. isolated from cotton and soil. Int J Syst Bacteriol 38:209–2011
Pham VHT, Jeong SW, Kim J (2014) Enhanced isolation and culture of highly efficient psychrophilic oil-degrading bacteria from oil-contaminated soils in South Korea. J Environ Biol 35:1145–1149
Pham VHT, Jeong SW, Kim J (2015) Psychrobacillus soli sp. nov., capable of degrading oil, isolated from oil-contaminated soil in Mongolia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:3046–3052
Reichenbach H (1992) The order Cytophagales. In: Balows A, Trüper HG, Dworkin M, Harder W, Schleifer KH (eds) The prokaryotes, 2nd edn, vol 4. Springer, New York, pp 3631–3675
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbour-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids, MIDI Technical Note 101. MIDI Inc, Newark, DE
Schaeffer AB, Fulton M (1933) A simplified method o staining endospores. Science 77:194
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1994) Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp. 607–654
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Throne-Holst M, Markussen S, Winnberg A, Ellingsen TE, Kotlar HK, Zotchev SB (2006) Utilization of n-alkanes by a newly isolated strain of Acinetobacter venetianus: the role of two AlkB-type alkane hydroxylases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:353–360
Tindall BJ, Sikorski J, Smibert RA, Krieg NR (2007) Phenotypic characterization and the principles of comparative systematics. In: Reddy CA, Beveridge TJ, Breznak JA, Marzluf GA, Schmidt TM, Snyder LR (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology, 3rd edn. ASM Press, Washington, D. C., pp 330–393
Tittsler RP, Sandholzer LA (1936) The use of semi-solid agar for the detection of bacterial motility. J Bacteriol 31:575–580
Vaneechoutte M, Tjernberg I, Baldi F, Pepi M, Fani R, Sullivan ER, Toorn JV, Dijkshoorn L (1999) Oil-degrading Acinetobacter strain RAG-1 and strains described as Acinetobacter venetianus sp. nov. belong to the same genomic species. Res Microbiol 150:69–73
Vaughn RH, Mitchell NB, Levine M (1939) The Voges–Proskauer and methyl red reactions in the coli-aerogenes group. J Am Water Works Assoc 31:993–1001
Vermeulen J (2007) Ripening of PAH and TPH polluted sediments: determination and quantification of bioremediation parameters. PhD thesis. Wageningen University, Wageningen
Wayne AB, Copper DG (1992) Hydrocarbon degradation by Acinetibacter calcoaceticus RAG-1 using the self-cycling fermentation technique. Biotechnol Bioeng 40:797–805
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR, Grimont PAD, Kandler O, Krichevsky MI, Moore LH, Moore WEC, Murray RGE, Stackebrandt E, Starr MP, Trüper HG (1987) Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematic. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–464
Yamahira K, Hirota K, Nakajima K, Morita N, Nodasaka Y, Yumoto I (2008) Acinetobacter sp. strain Ths, a novel psychrotolerant and alkalitolerant bacterium that utilizes hydrocarbon. Extremophiles 12:729–734
Yamamoto S, Harayama S (1995) PCR amplification and direct sequencing of gyrB genes with universal primers and their application to the detection and taxonomic analysis of Pseudomonas putida strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:1104–1109
Yamamoto S, Bouvet PJM, Harayama S (1999) Phylogenetic structures of the genus Acinetobacter based on gyrB sequence: comparison with the grouping by DNA–DNA hybridization. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49:87–95
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2016R1D1A1A09916982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
The GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession number for the 16S rRNA, rpoB, and gyrB gene sequences of strain R160T are KT032155, KU958712, and KU958711 respectively.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dahal, R.H., Chaudhary, D.K. & Kim, J. Acinetobacter halotolerans sp. nov., a novel halotolerant, alkalitolerant, and hydrocarbon degrading bacterium, isolated from soil. Arch Microbiol 199, 701–710 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-017-1349-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-017-1349-2