Abstract
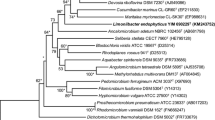
A novel Gram-staining-negative, non-motile, rod-shaped and aerobic bacterial strain, designated EGI 60015T, was isolated from healthy roots of Glycyrrhiza uralensis F. collected from Yili County, Xinjiang Province, Northwest China. The 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain EGI 60015T was found to show 97.6 % sequence similarity with Novosphingobium pentaromativorans US6-1T. The phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences showed that the strain formed a clade with N. pentaromativorans US6-1T in the neighbor-joining tree. Q-10 was identified as the respiratory quinone of strain EGI 60015T. The major fatty acids were summed feature 8 (C18:1 ω6c and/or C18:1 ω7c; 55.04 %), summed feature 4 (C17:1 anteiso B and/or iso I; 18.34 %) and summed feature 3 (C16:1 ω6c and/or C16:1 ω7c; 8.53 %). The polar lipids detected were phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylmethylethanolamine, phosphatidylglycerol, diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylcholine and sphingoglycolipids. The DNA G+C content of strain EGI 60015T was determined to be 66.6 mol%. The genomic DNA relatedness value between EGI 60015T and N. pentaromativorans US6-1T (54 %) was below the 70 % limit for species identification. Based on the result of the molecular studies supported by its morphological, physiological, chemotaxonomic and other differentiating phenotypic characteristics, strain EGI 60015T was considered to represent a novel species within the genus Novosphingobium, for which the name Novosphingobium endophyticum sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is EGI 60015T (=CGMCC 1.15095T = KCTC 42486T = DSM 29948T).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baek SH, Lim JH, Jin L, Lee HG, Lee ST (2011) Novosphingobium sediminicola sp. nov. isolated from freshwater sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:2464–2468
Cappuccino JG, Sherman N (2002) Microbiology: a laboratory manual, 6th edn. Benjamin/Cummings, Menlo Park
Cerny G (1978) Studies on aminopeptidase for the distinction of Gram-negative from Gram-positive bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 5:113–122
Chen Q, Zhang J, Wang CH, Jiang J, Kwon SW, Sun LN, Shen WB, He J (2014) Novosphingobium chloroacetimidivorans sp. nov., a chloroacetamide herbicide-degrading bacterium isolated from activated sludge. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:2573–2578
Christensen H, Angen O, Mutters R, Olsen JE, Bisgaard M (2000) DNA–DNA hybridization determined in microwells using covalent attachment of DNA. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:1095–1102
Collins MD, Jones D (1980) Lipids in the classification and identification of coryneform bacteria containing peptidoglycan based on 2, 4-diaminobutyric acid. Appl Bacteriol 48:459–470
Collins MD, Pirouz T, Goodfellow M, Minnikin DE (1977) Distribution of menaquinones in actinomycetes and corynebacteria. J Gen Microbiol 100:221–230
Ezaki T, Hashimoto Y, Yabuuchi E (1989) Fluorometric deoxyribonucleic acid–deoxyriboribonucleic acid hybridization in microdilution wells as an alternative to membrane filter hybridization in which radioisotopes are used to determine genetic relatedness among bacterial strains. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:224–229
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Zool 20:406–416
Fujii K, Satomi M, Morita N, Motomura T, Tanaka T, Kikuchi S (2003) Novosphingobium tardaugens sp. nov., an oestradiol-degrading bacterium isolated from activated sludge of a sewage treatment plant in Tokyo. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:47–52
Gupta SK, Lal D, Lal R (2009) Novosphingobium panipatense sp. nov. and Novosphingobium mathurense sp. nov., from oil-contaminated soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:156–161
He L, Li W, Huang Y, Wang LM, Liu ZH, Lanoot BJ, Vancanneyt M, Swings J (2005) Streptomyces jietaisiensis sp. nov., isolated from soil in northern China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1939–1944
Huo YY, You H, Li ZY, Wang CS, Xu XW (2015) Novosphingobium marinum sp. nov., isolated from seawater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:676–680
Kämpfer P, Young CC, Busse HJ, Lin SY, Rekha PD, Arun AB, Chen WM, Shen FT, Wu YH (2011) Novosphingobium soli sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:259–263
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Kroppenstedt RM (1982) Separation of bacterial menaquinones by HPLC using reverse phase (RP18) and a silver loaded ion exchanger as stationary phases. J Liq Chromatogr 5:2359–2387
Lee LH, Azman AS, Zainal N, Eng SK, Fang CM, Hong K, Chan KG (2014) Novosphingobium malaysiense sp. nov. isolated from mangrove sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:1194–1201
Leifson E (1960) In atlas of bacterial flagellation. Academic Press, London
Li WJ, Xu P, Schumann P, Zhang YQ, Pukall R, Xu LH, Stackebrandt E, Jiang CL (2007) Georgenia ruanii sp. nov., a novel actinobacterium isolated from forest soil in Yunnan (China), and emended description of the genus Georgenia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1424–1428
Lin SY, Hameed A, Liu YC, Hsu YH, Lai WA, Huang HI, Young CC (2014) Novosphingobium arabidopsis sp. nov., a DDT-resistant bacterium isolated from the rhizosphere of Arabidopsis thaliana. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:594–598
Liu ZP, Wang BJ, Liu YH, Liu SJ (2005) Novosphingobium taihuense sp. nov., a novel aromatic-compound-degrading bacterium isolated from Taihu Lake, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1229–1232
Mesbah M, Premachandran U, Whitman WB (1989) Precise measurement of the G+C content of deoxyribonucleic acid by high performance liquid chromatography. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:159–167
Ming H, Nie GX, Jiang HC, Yu TT, Zhou EM, Feng HG, Tang SK, Li WJ (2012) Paenibacillus frigoriresistens sp. nov., a novel psychrotroph isolated from a peat bog in Heilongjiang, Northern China. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 102:297–305
Minnikin DE, Collins MD, Goodfellow M (1979) Fatty acid and polar lipid composition in the classification of Cellulomonas, Oerskovia and related taxa. J Appl Bacteriol 47:87–95
Niharika N, Moskalikova H, Kaur J, Sedlackova M, Hampl A, Damborsky J, Prokop Z, Lal R (2013) Novosphingobium barchaimii sp. nov., isolated from hexachlorocyclohexane-contaminated soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:667–672
Parte AC (2014) LPSN—list of prokaryotic names with standing in nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D613–D616
Qin S, Li J, Chen HH, Zhao GZ, Zhu WY, Jiang CL, Xu LH, Li WJ (2009) Isolation, diversity, and antimicrobial activity of rare actinobacteria from medicinal plants of tropical rain forests in Xishuangbanna, China. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:6176–6186
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. MIDI technical note 101. MIDI Inc., Newark
Sohn JH, Kwon KK, Kang JH, Jung HB, Kim SJ (2004) Novosphingobiumpentaromativorans sp. nov., a high-molecular-mass polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium isolated from estuarine sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1483–1487
Suzuki S, Hiraishi A (2007) Novosphingobium naphthalenivorans sp. nov., a naphthalene-degrading bacterium isolated from polychlorinated-dioxin-contaminated environments. J Gen Appl Microbiol 53:221–228
Takeuchi M, Hamana K, Hiraishi A (2001) Proposal of the genus Sphingomonas sensu stricto and three new genera, Sphingobium, Novosphingobium and Sphingopyxis, on the basis of phylogenetic and chemotaxonomic analyses. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1405–1417
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X Windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR, Grimont PAD, Kandler O, Krichevsky MI, Moore LH, Moore WEC, Murray RGE, Stackebrandt E, Starr MP, Trüper HG (1987) International Committee on Systematic Bacteriology. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–464
Xie F, Quan S, Liu D, He W, Wang Y, Ma H, Chen G, Chao Y, Qian S (2014) Novosphingobium kunmingense sp. nov., isolated from a phosphate mine. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:2324–2329
Xu P, Li WJ, Tang SK, Zhang YQ, Chen GZ, Chen HH, Xu LH, Jiang CL (2005) Naxibacter alkalitolerans gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel member of the family ‘Oxalobacteraceae’ isolated from China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1149–1153
Yabuuchi E, Yano I, Oyaizu H, Hashimoto Y, Ezaki T, Yamamoto H (1990) Proposals of Sphingomonas paucimobilis gen. nov. and comb. nov., Sphingomonas parapaucimobilis sp. nov., Sphingomonas yanoikuyae sp. nov., Sphingomonas adhaesiva sp. nov., Sphingomonas capsulata comb. nov., and two genospecies of the genus Sphingomonas. Microbiol Immunol 34:99–119
Yuan J, Lai Q, Zheng T, Shao Z (2009) Novosphingobium indicum sp. nov., a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium isolated from a deep-sea environment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:2084–2088
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Prof. Dr. Takuji Kudo (JCM) for providing the reference type strain. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81102806, 31200008 and 31400009), projects of China tobacco Yunnan Industrial Co. Ltd. (Nos. 2012JC07, 2012FL02 and 2014YL01), the Hundred Talents Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences, the High-level Talents Program of Xinjiang Autonomous Region and the West Light Foundation of Chinese Academy of Sciences. W.-J. Li was also supported by Guangdong Province Higher Vocational Colleges & Schools Pearl River Scholar Funded Scheme (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Yan-Qiong Li, Li Li and Wei Chen have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, YQ., Li, L., Chen, W. et al. Novosphingobium endophyticum sp. nov. isolated from roots of Glycyrrhiza uralensis . Arch Microbiol 197, 911–918 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-015-1124-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-015-1124-1