Abstract
Introduction and hypothesis
The object of this review was to assess the efficacy and safety of urethral bulking agents (UBA), principally Macroplastique and Bulkamid, in the treatment of female stress urinary incontinence (SUI).
Methods
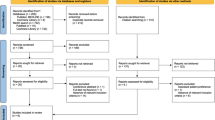
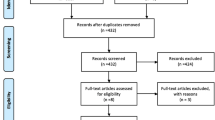
MEDLINE® and EMBASE® databases were systematically searched up to June 2016. Year of publication, study type, outcome measures, urodynamics before and after the procedure, number of participants, procedure complications, proportion requiring repeat injections or surgical procedures, frequency of follow-up, and results were analysed.
Results
The use of Bulkamid and Macroplastique for the treatment of female SUI was described in 26 studies. Studies used modalities including the visual analogue scale, Likert scale, International Consultation on Incontinence Modular Questionnaire (ICIQ), Patient Global Improvement Questionnaire (PGIQ) and Incontinence Impact Questionnaire (IIQ) and showed success rates ranging from 66% to 89.7% at 12 months follow-up. Objective improvements in patient symptoms were measured using urodynamics, 24-h pad tests, cough tests and voiding diaries. Studies showed variable objective success rates ranging from 25.4% to 73.3%. Objective findings for UBAs remain less well documented than those for the midurethral sling procedure.
Conclusions
There are a range of complications associated with UBAs, the most common being urinary tract infection. However, it remains a very well tolerated procedure in the majority of patients. UBAs should be considered as an alternative in patients unsuitable for more invasive procedures and those willing to accept the need for repeat injections. The majority of the literature focuses on subjective improvement measures rather than objective improvement measures. Further randomized controlled trials directly comparing UBAs are required to indicate the most effective agent.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hunskaar S, Burgio K, Diokno A, Herzog AR, Hjälmås K, Lapitan MC. Epidemiology and natural history of urinary incontinence in women. Urology. 2003;62(4 Suppl 1):16–23.
Turner DA, Shaw C, McGrother CW, Dallosso HM, Cooper NJ, Team MI. The cost of clinically significant urinary storage symptoms for community dwelling adults in the UK. BJU Int. 2004;93(9):1246–1252.
Ford AA, Rogerson L, Cody JD, Ogah J. Mid-urethral sling operations for stress urinary incontinence in women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;7:CD006375.
Enhorning G. Simultaneous recording of intravesical and intra-urethral pressure. A study on urethral closure in normal and stress incontinent women. Acta Chir Scand Suppl. 1961;Suppl 276:1–68.
Petros PE, Ulmsten UI. An integral theory and its method for the diagnosis and management of female urinary incontinence. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl. 1993;153:1–93.
Wilson PD, Herbison RM, Herbison GP. Obstetric practice and the prevalence of urinary incontinence three months after delivery. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1996;103(2):154–161.
American Urological Association. Incontinence 2016. Linthicum, MD: American Urological Association; 2017. https://www.auanet.org/education/guidelines/incontinence.cfm. Accessed 30 Jan 2017.
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Intramural urethral bulking procedures for stress urinary incontinence in women. London: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence; 2005. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/IPG138/chapter/2-The-procedure. Accessed 30 Jan 2017.
Ghoniem GM, Miller CJ. A systematic review and meta-analysis of Macroplastique for treating female stress urinary incontinence. Int Urogynecol J. 2013;24(1):27–36.
Kasi AD, Pergialiotis V, Perrea DN, Khunda A, Doumouchtsis SK. Polyacrylamide hydrogel (Bulkamid®) for stress urinary incontinence in women: a systematic review of the literature. Int Urogynecol J. 2016;27(3):367–375.
Klarskov N, Lose G. Urethral injection therapy: what is the mechanism of action? Neurourol Urodyn. 2008;27(8):789–792.
Krhut J, Martan A, Jurakova M, Nemec D, Masata J, Zvara P. Treatment of stress urinary incontinence using polyacrylamide hydrogel in women after radiotherapy: 1-year follow-up. Int Urogynecol J. 2016;27(2):301–305.
Zivanovic I, Rautenberg O, Lobodasch K, von Bünau G, Walser C, Viereck V. Urethral bulking for recurrent stress urinary incontinence after midurethral sling failure. Neurourol Urodyn. 2016. doi:10.1002/nau.23007
Sokol ER, Karram MM, Dmochowski R. Efficacy and safety of polyacrylamide hydrogel for the treatment of female stress incontinence: a randomized, prospective, multicenter north american study. J. Urol. 2014;192(3):843–849.
Martan A, Masata J, Svabík K, Krhut J. Transurethral injection of polyacrylamide hydrogel (Bulkamid®) for the treatment of female stress or mixed urinary incontinence. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2014;178:199–202.
Mouritsen L, Lose G, Møller-Bek K. Long-term follow-up after urethral injection with polyacrylamide hydrogel for female stress incontinence. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2014;93(2):209–212.
Krause HG, Lussy JP, Goh JT. Use of periurethral injections of polyacrylamide hydrogel for treating post-vesicovaginal fistula closure urinary stress incontinence. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2014;40(2):521–525.
Leone Roberti Maggiore U, Alessandri F, Medica M, Gabelli M, Venturini PL, Ferrero S. Outpatient periurethral injections of polyacrylamide hydrogel for the treatment of female stress urinary incontinence: effectiveness and safety. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2013;288(1):131–137.
Mohr S, Siegenthaler M, Mueller MD, Kuhn A. Bulking agents: an analysis of 500 cases and review of the literature. Int Urogynecol J 2013;24(2):241–247.
Leone Roberti Maggiore U, Alessandri F, Medica M, Gabelli M, Venturini PL, Ferrero S. Periurethral injection of polyacrylamide hydrogel for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence: the impact on female sexual function. J Sex Med. 2012;9(12):3255–3263.
Trutnovsky G, Tamussino K, Greimel E, Bjelic-Radisic V. Quality of life after periurethral injection with polyacrylamide hydrogel for stress urinary incontinence. Int Urogynecol J. 2011;22(3):353–356.
Lose G, Sørensen HC, Axelsen SM, Falconer C, Lobodasch K, Safwat T. An open multicenter study of polyacrylamide hydrogel (Bulkamid®) for female stress and mixed urinary incontinence. Int Urogynecol J. 2010;21(12):1471–1477.
Lose G, Mouritsen L, Neilsen JB. A new bulking agent (polyacrylamide hydrogel) for treating stress urinary incontinence in women. BJU Int 104 100;98(1).
Gumus II, Kaygusuz I, DerbentA, Simavli S, Kafali H. Effect of the Macroplastique Implantation System for stress urinary incontinence in women with or without a history of an anti-incontinence operation. Int Urogynecol J. 2011;22(6):743–749
Lee HN, Lee YS, Han JY, Jeong JY, Choo MS, Lee KS. Transurethral injection of bulking agent for treatment of failed mid-urethral sling procedures. Int Urogynecol J. 2010;21(12):1479–1483.
Ghoniem G, Corcos J, Comiter C, Westney OL, Herschorn S. Durability of urethral bulking agent injection for female stress urinary incontinence: 2-year multicenter study results. J Urol. 2010;183(4):1444–1449.
Zullo MA, Ruggiero A, Montera R, Plotti F, Muzii L, Angioli R, et al. An ultra-miniinvasive treatment for stress urinary incontinence in complicated older patients. Maturitas. 2010;65(3):292–295.
ter Meulen PH, Berghmans LCM, Nieman FHM, van Kerrebroeck PEVA. Effects of Macroplastique® Implantation System for stress urinary incontinence and urethral hypermobility in women. Int Urogynecol J 2009;20(2):177–183.
Ghoniem G, Corcos J, Comiter C, Bernhard P, Westney OL, Herschorn S. Cross-Linked Polydimethylsiloxane Injection for Female Stress Urinary Incontinence: Results of a Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled, Single-Blind Study. J Urol 2009;181(1):204–210.
Plotti F, Zullo MA, Sansone M, Calcagno M, Bellati F, Angioli R, et al. Post radical hysterectomy urinary incontinence: a prospective study of transurethral bulking agents injection. Gynecol Oncol. 2009;112(1):90–94.
Tamanini JT, D’Ancona CA, Netto NR. Macroplastique implantation system for female stress urinary incontinence: long-term follow-up. J Endourol. 2006;20(12):1082–1086.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Financial disclaimer
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siddiqui, Z.A., Abboudi, H., Crawford, R. et al. Intraurethral bulking agents for the management of female stress urinary incontinence: a systematic review. Int Urogynecol J 28, 1275–1284 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-017-3278-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-017-3278-7