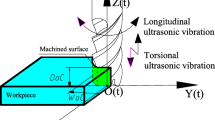
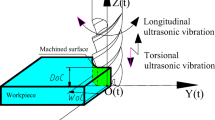
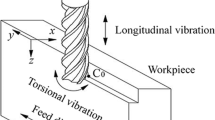
Abstract
Longitudinal-torsional ultrasonic vibration assisted micro-milling (LUVAM) can significantly improve the machinability of TC4 titanium alloy. With the continuous improvement of machining accuracy of many micro parts in the special industry field, the surface formation mechanism of TC4 titanium alloy under LUVAM has gradually become a research hotspot, and it is necessary to develop a reliable prediction model of the three-dimensional (3D) surface morphology of the machined surface of TC4 titanium alloy. In the study, the surface formation mechanism of TC4 titanium alloy under LUVAM is explored by a probabilistic model. Firstly, the mechanism of the intermittent cutting characteristics of LUVAM is analyzed by the trajectories of the tool tip, and the instantaneous undeformed chip thickness (IUCT) of LUVAM is built to analyze the effect of ultrasonic vibration on the surface formation mechanism of TC4 titanium alloy under LUVAM. Secondly, the model of the comprehensive trajectories of the tool tip is established considering the radial runout of the cutter, the flexible deformation of the cutter and the elastic recovery of the machined surface, then a probabilistic model of the machined surface residual material height of TC4 titanium alloy under LUVAM is further established to predict the 3D surface morphology of the machined surface of TC4 titanium alloy under LUVAM. Finally, the 3D surface morphology of the machined surface of TC4 titanium alloy under LUVAM is simulated, and the experiments of LUVAM applied to TC4 titanium alloy were carried out to explore the influence of processing parameters on the surface morphology. The simulated and experimental results show the simulation results are consistent with the experimental results, which verifies the accuracy and reliability of the theoretical model. As a result, the probabilistic model of the residual surface material height of TC4 titanium alloy under LUVAM can provide the theoretical and technical reference for the surface formation mechanism of TC4 titanium alloy under LUVAM, which may further promote the development and application of TC4 titanium alloy in many micro-scale parts processing fields.





















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Ultrasonic amplitude (μm)
- E :
-
Elastic modulus of TC4 titanium alloy workpiece (GPa)
- E t :
-
Elastic modulus of the cutter (GPa)
- f :
-
Ultrasonic vibration frequency (Hz)
- f z :
-
Feed per tooth (μm/z)
- h er :
-
Height of the elastic recovery of the machined surface (μm)
- I :
-
Moment of inertia of the micro-milling cutter (mm4)
- k t :
-
Elastic recovery constant of TC4 titanium alloy
- l a :
-
Extended length of the cutter (mm)
- n :
-
Spindle speed (r/min)
- R :
-
Radius of the micro-milling cutter (mm)
- v ω :
-
Feed rate of the workpiece (mm/s)
- β :
-
Helix angle of the cutter (°)
- ω :
-
Angular velocity of the cutter (rad/s)
- φ :
-
Phase difference of the longitudinal torsional ultrasonic vibration (rad)
- к :
-
Front angle of the cutter (°)
References
Kiswanto G, Mandala A, Azmi M, Ko TJ (2020) The effects of cutting parameters to the surface roughness in high speed cutting of micro-milling titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V. Key Engineering Materials 846:133–138. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/kem.846.133
de Fernanda FQ, Kuroda PAB, dos Karolyne SJS, Tatiani AGD, Grandini CR (2019) Preparation, structural and microstructural characterization of Ti-25Ta-10Zr alloy for biomedical applications. J Mater Res Technol 8(5):4108–4114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.07.020
Lin NM, Xie RZ, Zou JJ, Qin JF, Wang YT, Yuan S, Li DL, Zhao LL, Zhang LX, Wang ZX, Ma Y, Han PJ, Tian W, Liu XP, Wang ZH, Tang B (2019) Surface damage mitigation of titanium and its alloys via thermal oxidation: A brief review. Rev Adv Mater Sci 58(1):132146. https://doi.org/10.1515/rams-2019-0012
Wang ZM, Jia YF, Zhang XC, Fu Y, Zhang CC, Tu ST (2019) Effects of different mechanical surface enhancement techniques on surface integrity and fatigue properties of Ti-6Al-4V: A Review. Crit Rev Solid State Mater Sci 44(6):445–469. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408436.2018.1492368
Sui H, Zhang XY, Zhang DY, Jiang XG, Wu RB (2017) Feasibility study of high-speed ultrasonic vibration cutting titanium alloy. J Mater Process Tech 247:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.03.017
Lei Z, Pei L (2021) Cutting mechanism of straight-tooth milling process of titanium alloy TC21 based on simulation and experiment. PLoS One 16(10):e0258403. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0258403
Yip WS, To S (2017) Tool life enhancement in dry diamond turning of titanium alloys using an eddy current damping and a magnetic field for sustainable manufacturing. J Clean Prod 168:929–939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.100
Shokrani A, Newman S (2019) A new cutting tool design for cryogenic machining of Ti–6Al–4V titanium alloy. Materials 12(3):477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030477
Liu MZ, Li CH, Zhang YB, Yang M, Gao T, Cui X, Wang XM, Xu WH, Zhou ZM, Liu B, Said Z, Li RZ, Sharma S (2022) Analysis of grinding mechanics and improved grinding force model based on randomized grain geometric characteristics. Chinese J Aeronaut 36(7):160–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cja.2022.11.005
García-Martínez E, Miguel V, Martínez-Martínez A, Manjabacas MC, Coello J (2019) Sustainable lubrication methods for the machining of Titanium Alloys: An Overview. Materials 12(23):3852. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12233852
Pramanik A, Basak AK, Littlefair G, Debnath S, Prakash C, Singh MA, Marla D, Singh RK (2020) Methods and variables in electrical discharge machining of titanium alloy – A review. Heliyon 6(12):2405–8440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05554
Pramanik A, Basak AK (2023) Laser beam machining of Titanium Alloy—A Review. Metals 13(9):1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13091536
Rotella G, Imbrogno S, Candamano S, Umbrello D (2018) Surface integrity of machined additively manufactured Ti alloys. J Mater Process Tech 259:180–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.04.030
Ahmed N, Ishfaq K, Moiduddin K, Ali R, Al-Shammary N (2019) Machinability of titanium alloy through electric discharge machining. Mater Manuf Process 34(1):93–102. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2018.1532092
Wang PX, Yu DG, Li ML (2022) A study on ultrasonic-assisted micro-EDM of titanium alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 121:2815–2829. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-09355-1
Cao WJ, Wang DY, Zhu D (2022) Improvement of surface quality for titanium alloys during counter-rotating electrochemical machining using an auxiliary cathode. J Electrochem Soc 169:12. https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/acad2f
Wang ML, Qu NS (2021) Investigation on material removal mechanism in mechano-electrochemical milling of TC4 titanium alloy. J Mater Process Tech 295:0924–0136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2021.117206
Ahmed N, Ahmad S, Anwar S, Hussain A, Rafaqat M, Zaindin M (2019) Machinability of titanium alloy through laser machining: material removal and surface roughness analysis. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 105:3303–3323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04564-7
Zhu XT, Liu PT, Zhang C, Liang H, Hua J (2023) Study on surface integrity and fatigue properties of TC4 titanium alloy by surface ultrasonic rolling. Materials 16(2):485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020485
Qin SQ, Zhu LD, Wiercigroch MR, Ren TY, Hao YP, Ning JS, Zhao JZ (2022) Material removal and surface generation in longitudinal-torsional ultrasonic assisted milling. Int J Mech Sci 227:0020–7403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2022.107375
Ren WF, Xu JK, Lin JQ, Yu ZJ, Yu P, Lian ZX, Yu HD (2019) Research on homogenization and surface morphology of Ti-6Al-4V alloy by longitudinal-torsional coupled ultrasonic vibration ball-end milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 104:301–313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03668-4
Chen FY, Wang DZ, Wu SJ (2021) Influence of ultrasonic vibration-assisted cutting on ploughing effect in cutting Ti6Al4V. Arch Civ Mech Eng 21:42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-021-00196-5
Wei L, Wang DZ (2019) Comparative study on drilling effect between conventional drilling and ultrasonic-assisted drilling of Ti-6Al-4V/Al2024-T351 laminated material. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 103:141–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03507-6
Wang Q, Wang DZ, Fang Y (2023) Research on chip mechanism of Inconel 718 with ultrasonic assisted drilling by step drill. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 126:2579–2594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-11212-8
Revuru RS, Posinasetti NR, VSN V, M A (2017) Application of cutting fluids in machining of titanium alloys—a review. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 91(5):2477–2498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9883-7
Gupta MK, Sood PK, Sharma VS (2016) RETRACTED: Optimization of machining parameters and cutting fluids during nano-fluid based minimum quantity lubrication turning of titanium alloy by using evolutionary techniques. J Clean Prod 135:1276–1288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.06.184
Zhang ZC, Sui MH, Li CH, Zhou ZM, Bo L, Chen Y, Said Z, Debnath SJ, Sharma S (2022) Residual stress of grinding cemented carbide using MoS2 nano-lubricant. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 119:5671–5685. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-08660-z
Zhang DY (2017) Ultrasonic processing in China. J Mech Eng 53(19):1–2. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=A67obWUfw0lZ85k45GiTLfDtyliTowmlpjq2jS7whA15RHLCFUTkjE7-S-4lP12AdCXhM4SwjdIyd9kpgQQh-zhwhiD06dVHJUUSK-aLcXYn0ArH8WiAuDLlKlxqcKIG8CddLaZCylJbT-XIUJmUuw==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS. Accessed 5 Oct 2017
Hu WJ, Du PF, Qiu X, Zhao XS, Hu ZJ, Zhang JJ, Liu YX (2022) Enhanced dry machinability of TC4 titanium alloy by longitudinal-bending hybrid ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling. J Clean Prod 379:2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134866
Zhang XY, Peng ZL, Li ZM, Sui H, Zhang DY (2020) Influences of machining parameters on tool performance when high-speed ultrasonic vibration cutting titanium alloys. J Manuf Process 60:188–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.10.053
Gao HH, Ma BJ, Zhu YP, Yang H (2022) Enhancement of machinability and surface quality of Ti-6Al-4V by longitudinal ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling under dry conditions. Measurement 187:0263–2241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2021.110324
Meng JB, Huang BQ, Dong XJ, Hu YZ, Zhao YG, Wei XT, Luan XS (2020) Experimental investigation on ultrasonic atomization assisted turning of titanium alloy. Micromachines 11(2):168. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11020168
Chen P, Tong JL, Zhao JS, Zhang ZM, Zhao B (2020) A study of the surface microstructure and tool wear of titanium alloys after ultrasonic longitudinal-torsional milling. J Manuf Process 53:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.01.040
Chen G, Ren CZ, Zou YH, Qin XD, Lu LP, Li SP (2019) Mechanism for material removal in ultrasonic vibration helical milling of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Int J Mach Tool Manu 138:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2018.11.001
Ni CB, Zhu LD, Yang ZC (2019) Comparative investigation of tool wear mechanism and corresponding machined surface characterization in feed-direction ultrasonic vibration assisted milling of Ti–6Al–4V from dynamic view. Wear 436:203006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2019.203006
Zhang ML, Zhang DY, Geng DX, Shao ZY, Liu YH, Jiang XG (2020) Effects of tool vibration on surface integrity in rotary ultrasonic elliptical end milling of Ti–6Al–4V. J Alloys Compd 821:0925–8388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.153266
Liu JL, Liu ZP, Yan YY, Wang XX (2022) Study on the CBN wheel wear mechanism of longitudinal-torsional ultrasonic-assisted grinding applied to TC4 titanium alloy. Micromachines 13(9):1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13091480
Lu MM, Wang H, Guan L, Lin JQ, Gu Y, Chen B, Zhao DP (2018) Modeling and analysis of surface topography of Ti6Al4V alloy machining by elliptical vibration cutting. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 98(9–12):2759–2768. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2452-5
Shen XH, Shi YL, Zhang JH, Zhang QJ, Tao GC, Bai LJ (2020) Effect of process parameters on micro-textured surface generation in feed direction vibration assisted milling. Int J Mech Sci 167:0020–7403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.105267
Chern GL, Chang YC (2006) Using two-dimensional vibration cutting for micro-milling. Int J Mach Tool Manu 46:659–666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2005.07.006
Zheng L, Chen WQ, Huo DH (2018) Experimental investigation on burr formation in vibration-assisted micro-milling of Ti-6Al-4V. Proc Inst Mech Eng C J Mec Eng Sci 233(12):203–210. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954406218792360
Qiu X (2021) Development and technology of ultrasonic vibration assisted micro-milling device for TC4 titanium alloy. Dissertation, Harbin Institute of Technology, pp 20–41. https://doi.org/10.27061/d.cnki.ghgdu.2021.002653
Yang YY, Yang M, Li CH, Li RZ, Said Z, Ali HM, Sharma S (2023) Machinability of ultrasonic vibration assisted micro-grinding in biological bone using nanolubricant. Front Mech Eng 18:1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11465-022-0717-z
Jia DZ, Li CH, Zhang YB, Yang M, Zhang XP, Li RZ, Ji HJ (2018) Experimental evaluation of surface topographies of NMQL grinding ZrO2 ceramics combining multiangle ultrasonic vibration. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 100(1):457–473. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2718-y
Gao T, Zhang XP, Li CH, Zhang YB, Yang M, Jia DZ, Ji HJ, Zhao YJ, Li RZ, Yao P, Zhu LD (2020) Surface morphology evaluation of multi-angle 2D ultrasonic vibration integrated with nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication grinding. J Manuf Process 51:44–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.01.024
Ni CB, Zhu LD, Liu CF, Yang ZC (2018) Analytical modeling of tool-workpiece contact rate and experimental study in ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling of Ti–6Al–4V. Int J Mech Sci 142–143:97–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2018.04.037
Niu Y, Jiao F, Zhao B, Gao G (2019) Investigation of cutting force in longitudinal-torsional ultrasonic-assisted milling of Ti-6Al-4V. Materials 12(12):1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121955
Liu HW (2011) Mechanics of materials, 6th edn. Higher Education Press, China, pp 187–193
Arcona C, Dow TA (1998) An empirical tool force model for precision machining. J Manuf Sci Engineer 120(4):700–707. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2830209
Chen WQ, Lu Z, Xie WK, Yang K, Huo DH (2019) Modelling and experimental investigation on textured surface generation in vibration-assisted micro-milling. J Mater Process Tech 266:339–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.11.011
Zhu LD, Ni CB, Yang ZC, Liu CF (2019) Investigations of micro-textured surface generation mechanism and tribological properties in ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling of Ti–6Al–4V. Precis Eng 57:229–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2019.04.010
Mekhiel S, Koshy P, Elbestawi MA (2020) Additive texturing of metallic surfaces for wetting control. Addit Manuf 37:101631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2020.101631
Zhao CY, Wang XB, Zhao B, Jiao F (2018) Microstructure of high-performance aluminum alloy surface processed by the single-excitation same-frequency longitudinal–torsional coupled ultrasonic vibration milling. Materials 11(10):1975. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11101975
Funding
This research is supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China project (Project code: 51575163) and Key R&D and Promotion Projects in Henan Province(Project code: 232102221018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All related authors contributed to the conceptualization, data curation, investigation, methodology, writing–original draft, writing–review, and editing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Y., Jiang, C. & Yan, H. Probabilistic model of the surface residual height under longitudinal-torsional ultrasonic vibration assisted micro-milling TC4. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 131, 2837–2855 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-12548-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-12548-x