Abstract
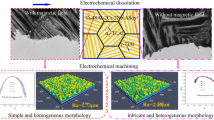
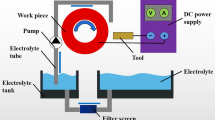
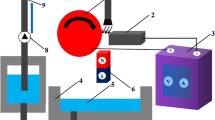
Electrochemical machining (ECM) system shows abundant dynamic phenomena and is a typical nonlinear system; the relationship between the nonlinear dynamic behavior and the surface quality of electrochemical machining is not yet fully understood. In the present work, the nonlinear dynamic behaviors of Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb alloy in the process of electro-dissolution and electrochemical machining with and without magnetic field were researched by phase space reconstruction, saturate correlation dimension, morphology observation, and multifractal spectrum of the machined surface. The relationship between attractor structure and surface morphology was disclosed. The results reveal that a parallel magnetic field enhances the compact degree of the attractor structure whether it is in the electro-dissolution or electrochemical machining system of Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb alloy and increases the number of variables in the electro-dissolution system, that is 8. The surface quality of electrochemical machining of Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb alloy with parallel magnetic field is improved, and the machined surface topography is smoother, simpler, and more homogeneous, which implies that parallel magnetic field facilitates the self-organization behavior in electrochemical machining of Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb alloy. The attractor structure of current density during electrochemical machining of Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb alloy can be used as an indicator for surface quality evaluation.











Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Yes, the data and material are available.
References
Eschenazi EV, Tsega Y, Ballard N, Glass G (1995) Electrochemical oscillations, surface morphology and corrosion of selected thermal sprayed alloys. MRS Proc 407(1):365–376. https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-407-365
Hudson JL, Bassett MR (1991) Oscillatory electro-dissolution of metals. Rev Chem Eng 7(2):109–170. https://doi.org/10.1515/revce-1991-070201
Fahidy TZ, Gu ZH (1995) Recent advances in the study of the dynamics of electrode processes. In: White RE, Bockris JOM, Conway BE (eds) Modern Aspects of Electrochemistry. Springer US, Boston, pp 383–409. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-1724-9_5
Luo S, Elouarzaki K, Xu ZJ (2022) Electrochemistry in magnetic fields. Angew Chem Int Ed 61(27):e202203564. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202203564
Fan Z, Wang T, Zhong L (2004) The mechanism of improving machining accuracy of Ecm by magnetic field. J Mater Process Technol 149(1):409–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2003.12.025
Bradley C, Samuel J (2018) Controlled phase interactions between pulsed electric fields, ultrasonic motion, and magnetic fields in an anodic dissolution cell. J Manuf Sci 140(4):041010. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4038569
Frotscher O, Schaarschmidt I, Lauwers D, Paul R, Meinke M, Steinert P, Schubert A, Schröder W, Richter M (2022) Investigation of Lorentz force–induced flow of NaNO3-electrolyte for magnetic field–assisted electrochemical machining. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 121(1):937–947. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-09349-z
Bund A, Koehler S, Kuehnlein HH, Plieth W (2003) Magnetic field effects in electrochemical reactions. Electrochim Acta 49(1):147–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2003.04.009
Koza JA, Uhlemann M, Gebert A, Schultz L (2008) The effect of magnetic fields on the electrodeposition of cofe alloys. Electrochim Acta 53(16):5344–5353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2008.02.082
Yu Q-K, Miyakita Y, Nakabayashi S, Baba R (2003) Magnetic field effect on electrochemical oscillations during iron dissolution. Electrochem commun 5(4):321–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1388-2481(03)00057-2
Wang Y, Hudson JL (1991) Effect of electrode surface area on chaotic attractor dimensions. AICHE J 37(12):1833–1843. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.690371208
Hashemizadeh A, Ameri MJ (2021) Toward a mechanistic understanding of the magnetic field effect on N-80 carbon steel corrosion in aqueous Hcl solution. Anti-Corros Method Mater 68(4):293–301. https://doi.org/10.1108/ACMM-10-2020-2389
Dunne P, Coey JMD (2019) Influence of a magnetic field on the electrochemical double layer. J Phys Chem C 123(39):24181–24192. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b07534
Liao CJ, Zhang XM, Luo ZJ (2023) Magnetic field effects on electrochemical dissolution behavior and surface quality of electrochemical machining of Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb alloy. J Appl Electrochem 53(1):49–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-022-01756-0
Kaur C, Bisht A, Singh P, Joshi G (2021) Eeg signal denoising using hybrid approach of variational mode decomposition and wavelets for depression. Biomed Signal Proces 65:102337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2020.102337
Takens F (1981) Detecting strange attractors in turbulence. In: Rand D, Young L-S (eds) Dynamical systems and turbulence, Warwick, 1980. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, pp 366–381
Grassberger P, Procaccia I (1983) Characterization of strange attractors. Phys Rev Lett 50(5):346–349. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.50.346
Grassberger P, Procaccia I (1984) Dimensions and entropies of strange attractors from a fluctuating dynamics approach. Physica D 13(1):34–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-2789(84)90269-0
Liao CJ, Liu Q, Ma XZ, Liu JH (2019) Relationship between surface heterogeneity and electrochemical interface behavior of the TiAl alloy electrode. J Phys Chem C 123(1):473–484. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b09123
Hudson JL, Tsotsis TT (1994) Electrochemical reaction dynamics: a review. Chem Eng Sci 49(10):1493–1572. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2509(94)85063-1
Mangiarotti S, Huc M (2019) Can the original equations of a dynamical system be retrieved from observational time series? Chaos 29(2):023133. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5081448
Wu X, Sun Y, Wang Y, Chen Y (2021) Correlation Dimension and bifurcation analysis for the planar slider-crank mechanism with multiple clearance joints. Multibody Syst Dyn 52(1):95–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11044-020-09769-3
Desroches M, Guckenheimer J, Krauskopf B, Kuehn C, Osinga HM, Wechselberger M (2012) Mixed-mode oscillations with multiple time scales. SIAM Rev 54(2):211–288. https://doi.org/10.1137/100791233
Modabberasl A, Sharifi M, Shahbazi F, Kameli P (2019) Multifractal analysis of Dlc thin films deposited by pulsed laser deposition. Appl Surf Sci 479:639–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.02.062
Epstein IR, Showalter K (1996) Nonlinear chemical dynamics: oscillations, patterns, and chaos. J Phys Chem 100(31):13132–13147. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp953547m
Kousaka T, Ogura Y, Shimizu K, Asahara H, Inaba N (2017) Analysis of mixed-mode oscillation-incrementing bifurcations generated in a nonautonomous constrained Bonhoeffer-Van Der Pol oscillator. Physica D 353–354:48–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physd.2017.05.001
Shen K, Wang Z, Bi X, Ying Y, Zhang D, Jin C, Hou G, Cao H, Wu L, Zheng G, Tang Y, Tao X, Lu J (2019) Magnetic field–suppressed lithium dendrite growth for stable lithium-metal batteries. Adv Energy Mater 9(20):1900260. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201900260
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 22072040) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (grant number 2020JJ4271).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Cui Jiao Liao: methodology, investigation, and the first draft. Rong Lian Lin: review of nonlinear dynamics analysis and the revised manuscript. Xian Miao Zhang: main experimental implementation. Hao Nan Sui: assistance in the electrochemical machining experiment.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The paper follows the guidelines of the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE).
Consent participate
All authors approved the manuscript to participate.
Consent for publication
All authors approved the manuscript for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, C.J., Lin, R.L., Zhang, X.M. et al. Magnetic field effects on nonlinear dynamic behavior in electro-dissolution and pulse electrochemical machining of Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 126, 4543–4554 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-11424-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-11424-y