Abstract
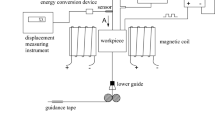
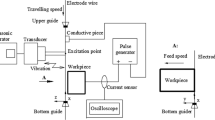
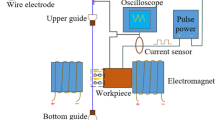
NiTi shape memory alloy (SMA) is the most successful shape memory alloy in engineering and medical fields because of its unique shape memory effect (SME) and good superelasticity (SE). In order to overcome the disadvantages of low machining efficiency and poor machining stability of NiTi SMA machined by low speed wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM-LS), a complex process of vertical ultrasonic vibration and magnetic field (VUV-MF) assisted WEDM-LS is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the flow velocity distribution of flow field and the motion law of debris between the electrodes are analyzed under different amplitudes and frequencies of ultrasonic vibration. Then the distribution of temperature field and crater shape during one pulse discharge are simulated based on an amended Gaussian heat source model of the complex process, and the surface topography of machined workpiece under continuous pulse discharges is obtained. The simulated results show that the additional ultrasonic vibration could enhance the fluidity of working fluid near the workpiece surface in the machining gap, thereby promoting the debris being flushed out of the machining gap. Finally, the validation experiment of vertical ultrasonic vibration and magnetic field assisted WEDM-LS is accomplished, the experimental results obtained by the complex process reveal that the surface roughness value of machined workpiece decreased, surface burn of workpiece is significantly alleviated, and the average machining speed is 1.33 times than that in traditional WEDM-LS, which greatly reduce energy consumption. Additionally, the average error of the surface roughness values obtained by simulation and experiment is 12.2%.













source model under vertical ultrasonic vibration assisted






source model under random discharge












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The manuscript has no associated data or the data will not be deposited.
References
Takale AM, Chougule NK (2019) Effect of wire electro discharge machining process parameters on surface integrity of Ti49.4Ni50.6 shape memory alloy for orthopedic implant application. Mater Sci Eng C 97:264–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2018.12.029
Chen Z, Zhang YM, Zhang GJ, Huang Y, Liu CH (2017) Theoretical and experimental study of magnetic-assisted finish cutting ferromagnetic material in WEDM. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 123:36–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2017.07.009
Guo ZN, Lee TC, Yue TM, Lau WS (1997) A study of ultrasonic-aided wire electrical discharge machining. J Mater Process Technol 63(1–3):823–828. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(96)02732-X
Nakwong P, Muttamara A (2019) Effect of frequency to ultrasonic vibration-assisted wire-EDM. Key Eng Mater 814:127–131. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.814.127
Zhang GJ, Huang H, Zhang Z, Zhang YM (2019) Study on the effect of three dimensional wire vibration on WEDM based on a novel thermophysical model. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 100(5–8):2089–2101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2796-x
Nani VM (2017) The ultrasound effect on technological parameters for increase in performances of W-EDM machines. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 88(1–4):519–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8783-1
Joshi S, Govindan P, Malshe A, Rajurkar K (2011) Experimental characterization of dry EDM performed in a pulsating magnetic field. CIRP Ann-Manuf Technol 60(1):239–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2011.03.114
Yan HZ, Bakadiasa KD, Chen Z, Yan ZJ, Zhou HB, Han FL (2020) Attainment of high corner accuracy for thin-walled sharp corner part by WEDM based on magnetic field-assisted method and parameter optimization. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 106(11–12):4845–4857. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-04966-y
Wang Y, Wang QZ, Xiong W, Liu JG, Wang YX (2021) Investigation on the kerf and surface formation in the magnetic field-assisted WEDM-LS based on successive discharges. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 114(3–4):841–856. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-06906-w
Okada A, Uno Y, Onoda S, Habib S (2009) Computational fluid dynamics analysis of working fluid flow and debris movement in wire EDMed kerf. CIRP Ann-Manuf Technol 58(1):209–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2009.03.003
Wang Y, Yao SW, Ding ZJ, Wu CZ, Xiong W (2020) Machining characteristics of USV-MF complex assisted WEDM-LS based on multi-physical coupling. Int J Precis Eng Manuf-Green Technol 8(2):387–404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-020-00209-3
Hargrove SK, Ding DW (2007) Determining cutting parameters in wire EDM based on workpiece surface temperature distribution. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 34(3–4):295–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-006-0609-0
Joshi K, Sharma G, Dongre G, Joshi SS (2017) Numerical modelling of wire-EDM for predicting erosion rate of silicon. J Inst Eng (India) Ser C 98(1):63–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40032-016-0237-x
Chen Z, Zhang GJ, Han FL, Zhang YM, Rong YM (2018) Determination of the optimal servo feed speed by thermal model during multi-pulse discharge process of WEDM. Int J Mech Sci 142:359–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2018.05.006
Rajurkar KP, Pandit SM (1986) Formation and ejection of EDM debris. J Manuf Sci Eng 108(1):22–26. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3187036
Dibitonto DD, Eubank PT, Patel MR (1989) Theoretical models of the electrical discharge machining process. II. The anode erosion model. J Appl Phys 66(9):4095–4103. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.343995
Li MH (1989) Theory of EDM. National Defense Industry Press, Beijing
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by Shanghai Special Fund for Artificial Intelligence Innovation and Development (2019-RGZN-01040).
Funding
This work was financially supported by Shanghai Special Fund for Artificial Intelligence Innovation and Development (2019-RGZN-01040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yan Wang contributed to conceptualization, methodology, supervision and writing—review and editing. ChengZhen Wu performed formal analysis, visualization and writing—original draft. CaiCong Tang and RuiQi Jin contributed to investigation and software. LingXiao Jiang contributed to resources and data curation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This work has not been published elsewhere. It’s not being submitted to any other journal as well.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Wu, C.Z., Tang, C.C. et al. Study on machining characteristics of VUV-MF assisted WEDM-LS based on flow field and temperature field analysis. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 121, 4431–4454 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-09556-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-09556-8