Abstract
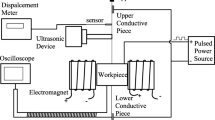
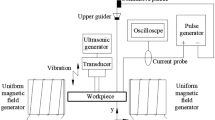
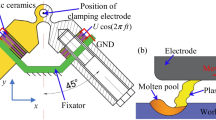
The spatial vibration model of the electrode wire in ultrasonic vibration (USV)-assisted low-speed wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM-LS) under continuous discharges is proposed for analyzing its vibration state, and subsequently, a theoretical model of material removal from the TiNi-01 shape memory alloy workpiece is established by means of Gaussian heat source in single-pulse discharge process and the principle of the nearest-point discharge breakdown. Then, the topological matrix of the surface morphology is developed for investigating the surface characteristics and the distribution of discharge points by simulation. Finally, the experiment of photographing the discharge channel position is accomplished to validate the reliability and feasibility of the model. The results show that the discharge channels are more uniformly distributed in the hybrid process, which enhance effectively the success rate of the discharge pulses and decrease the surface roughness. In addition, a mathematical model to evaluate the uniformity of the discharge point distribution is employed as an evaluation index of the burn degree on the workpiece surface. The distribution uniformity coefficient obtained by the compound process is higher than that of the traditional WEDM-LS. This is consistent with the phenomenon of alleviated surface burn under the hybrid machining technology, and the average errors of the simulated and experimental values of the uniformity coefficient of traditional WEDM-LS and the hybrid process are 4.9% and 3.4%, respectively. The maximum errors of surface roughness between simulated value and experimental value about the WEDM-LS and hybrid process are 7.4% and 8.2%, respectively. It is demonstrated that the model can effectively and accurately predict the surface roughness and the surface burn of the workpiece.

























Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The manuscript has no associated data or the data will not be deposited.
References
Kuriakose S, Shunmugam MS (2004) Characteristics of wire-electro discharge machined Ti6Al4V surface. Mater Lett 58:2231–2237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2004.01.037
Guo ZN, Lee TC, Yue TM, Lau W.S (1997) A study of ultrasonic-aided wire electrical discharge machining. J Mater Process Technol 63:823-828. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(96)02732-X.
Han GC, Soo SL, Aspinwall DK, Bhaduri D (2013) Research on the ultrasonic assisted WEDM of Ti-6Al-4V. Adv Mater Res 797:315–319. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.797.315
Radhakrishnan P, Vijayaraghavan L, Babu NR (2017) Assessment of material removal capability with vibration-assisted wire electrical discharge machining. J Manuf Process 26:323–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2017.03.002
Hoang KT, Yang SH (2013) A study on the effect of different vibration-assisted methods in micro-WEDM. J Mater Process Technol 213:1616–1622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2013.03.025
Gao CS, Liu Z (2013) A study of ultrasonically aided micro electrical discharge machining by the application of workpiece vibration. J Mater Process Technol 139:226–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(03)00224-3
Wang Y, Wang Q, Ding ZJ, He DX, Xiong W, Chen SY, Li ZX (2018) Study on the mechanism and key technique of ultrasonic vibration and magnetic field complex assisted WEDM-LS thick shape memory alloy workpiece. J Mater Process Technol 261:251–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.06.006
Zhang QH, Du R, Zhang JH, Zhang QB (2006) An investigation of ultrasonic-assisted electrical discharge machining in gas. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 46:1582–1588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2005.09.023
Goiogana M, Sarasua JA, Ramos JM, Echavarri L, Cascón I (2016) Pulsed ultrasonic assisted electrical discharge machining for finishing operations. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 109:87–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2016.07.005
Izquierdo B, Sánchez JA, Plaza S, Pombo I, Ortega N (2009) A numerical model of the EDM process considering the effect of multiple discharges. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 49:220–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2008.11.003
Chen Z, Huang Y, Huang H, Zhang Z, Zhang G (2015) Three-dimensional characteristics analysis of the wire-tool vibration considering spatial temperature field and electromagnetic field in WEDM. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 92:85–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2015.03.003
Hargrove SK, Ding D (2007) Determining cutting parameters in wire EDM based on workpiece surface temperature distribution. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 34:295–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-006-0609-0
Dibitonto DD, Eubank PT, Patel MR (1989) Theoretical models of the electrical discharge machining process II. The anode erosion model. J Appl Phys 66:4095–4103. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.343995
Joshi K, Sharma G, Dongre G, Joshi SS (2017) Numerical modelling of wire-EDM for predicting erosion rate of silicon. J Inst Eng 98:63–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40032-016-0237-x
Li ZX (2019) Analysis and mechanism study of discharge channel in ultrasonic vibration and magnetic field complex assisted WEDM-LS. Dissertation, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology.
Jameson EC (1970) Electrical discharge grinding, Iee, pp 135-142.
Roy T, Datta D, Balasubramaniam R (2018) Numerical modelling and simulation of surface roughness of 3-D hemispherical convex micro-feature generated by reverse micro-EDM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 97:979–992. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-1971-4
Liu Y, Chang H, Zhang W, Ma F, Sha Z, Zhang S (2018) A simulation study of debris removal process in ultrasonic vibration assisted electrical discharge machining (EDM) of deep holes. Micromachines 9:378. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9080378
Shabgard M, Ahmadi R, Seyedzavvar M, Oliaei SNB (2013) Mathematical and numerical modeling of the effect of input-parameters on the flushing efficiency of plasma channel in EDM process. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 65:79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2012.10.004
Sanchez I, Faci JM, Zapata N (2011) The effects of pressure, nozzle diameter and meteorological conditions on the performance of agricultural impact sprinklers. Agric Water Manag 102:13–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2011.10.002
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai for supporting the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yan Wang: conceptualization, methodology, supervision, writing—review and editing. Cheng-Zhen Wu: formal analysis, visualization, writing-original draft. Hua-Yi Chai: investigation, software. Wei Xiong: resources, data curation. Rui Wang: visualization, software. Jie Yang: software, data curation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
This work has not been published elsewhere.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Wu, CZ., Chai, HY. et al. Study on surface characteristics in ultrasonic vibration-assisted WEDM-LS based on spatial vibration of electrode wire. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 114, 2677–2695 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07017-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07017-2