Abstract
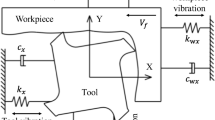
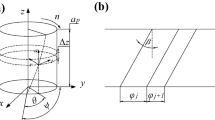
The development of the machining technology is restricted by the problems of serious vibration and low system stability. The variable pitch cutter has certain vibration reduction property due to the unequal pitch angles. In this work, firstly, according to the features of the structure of the variable pitch end mill, the cutting mechanism is analyzed, and a theoretical model of the dynamic cutting force is developed. Secondly, the cutting force coefficients of the model are determined based on the test of hardened steel for verifying the significance of the theoretical model. Then, the time–frequency characteristics and vibration reduction mechanism of variable pitch end mills are analyzed. The frequency characteristics of different types of pitch angle end mills are also explored by the spectrum analysis. Finally, based on the energy and variance methods of the amplitude, the single-objective optimization of the pitch angle is carried out, where the spectrum lines are found evenly distributed, and the optimal result is 80°-97°-100°-83°. For satisfying the machining requirements, the pitch angle of the variable pitch end mill is reasonably selected to reduce the amplitude of the forced vibration, which can play an important role in reducing the vibration of the tool and improving its cutting stability. The superior vibration reduction tool is of great significance for improving the processing technology and accelerating the development of the manufacturing industry.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Slavicek J (1965) The effect of irregular tooth pitch on stability of milling. Proc Sixth MTDR Conf 15–22
Altintas Y, Engin S, Budak E (1999) Analytical stability prediction and design of variable pitch cutters. J Manuf Sci Eng 121(2):173–178
Sims ND, Mann B, Huyanan S (2008) Analytical prediction of chatter stability for variable pitch and variable helix milling tools. J Sound Vib 317:664–686
Budak E (2003) An analytical design method for milling cutters with non-constant pitch to increase stability, Part 1: Theory. J Manuf Sci Eng 125(1):29–34
Budak E (2003) An analytical design method for milling cutters with non-constant pitch to increase stability, Part 2: Application. J Manuf Sci Eng 125(1):35–38
Turner S, Merdol D, Altintas Y, Ridgway K (2007) Modelling of the stability of variable helix end mills. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 47:1410–1416
Olgac N, Sipahi R (2007) Dynamics and stability of variable-pitch milling. J Vib Control 13(7):1031–1043
Zhou C, Guo K, Yang B, Wang H, Lu L (2019) Singularity analysis of cutting force and vibration for tool condition monitoring in milling. IEEE Access 7:134113–134124
Li QL, Wang B, Zhao B, Wen BC (2013) Study on stability of machine tool chatter system considering nonlinear hysteretic force. J Mech Eng 49(11):43–49
Freyer BH, Theron NJ, Heyns PS, Pickelmann LA (2021) Self-sensing active control of emulated tangential tool vibration hardware-in-the-loop. Control Eng Pract 109:104729
Suyama DI, Diniz AE (2020) Influence of tool vibrations on tool wear mechanisms in internal turning of hardened steel. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 42(7):1–17
Lawrance G, Paul PS, Vasanth XA, Varadarajan AS, Daniel E (2019) Influence of magnetorheological elastomer on tool vibration and cutting performance during boring of hardened AISI4340 steel. J Mech Sci Technol 33(4):1555–1561
Wu J, Yu G, Gao Y, Wang LP (2018) Mechatronics modeling and vibration analysis of a 2-DOF parallel manipulator in a 5-DOF hybrid machine tool. Mech Mach Theory 121:430–445
Wu J, Wang JS, Wang LP, Li TM (2009) Dynamics and control of a planar 3-DOF parallel manipulator with actuation redundancy. Mech Mach Theory 44(4):835–849
Yu G, Wang LP, Wu J (2018) Prediction of chatter considering the effect of axial cutting depth on cutting force coefficients in end milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 96(9–12):3345–3354
Shirase K, Sano M, Hirao M, Yasui T (1998) Analysis and suppression of chatter vibration in end milling operation (lst Report). J Precis Eng Soc 64(3):465–469
Tang AM (2012) Research on a New type of high-speed end mill based on cutting stability. Doctoral dissertation of Hunan University. Hunan University
Sellmeier K, Denkena B (2011) Stable islands in the stability chart of milling proeesses due to unequal tooth pitch. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 51:152–164
Yusoff AR, Sims ND (2011) Optimisation of variable helix tool geometry for regenerative chatter mitigation. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 51:133–141
Otto A, Rauh S, Ihlenfeldt S, Radons G (2017) Stability of milling with non-uniform pitch and variable helix tools. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 89:2613–2625
Huang PL (2011) Research on variable pitch end mill for titanium alloy milling. Doctoral dissertation of Shandong University. Shandong University
Jin G (2013) Theoretical and experimental study on cutting stability of variable pitch variable spiral milling cutter. Doctoral dissertation of Tianjin University. Tianjin University
Alex I, Zoltan (2018) Optimum selection of variable pitch for chatter suppression in face milling operations. Materials 1(12):112
Song QH, Ai X, Zhao J (2011) Design for variable pitch end mills with high milling stability. International J Adv Manuf Technol 55:891–903
Rice JA (2011) Mathematical Statistics and Data Analysis. Mach Ind Press 102–105
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Central Government for Supporting the Local High Level Talent (number 2020GSP11).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors participated in the analysis and discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nie, W., Zheng, M., Yu, H. et al. Analysis of vibration reduction mechanism for variable pitch end mills. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 119, 7787–7797 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-08713-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-08713-3