Abstract
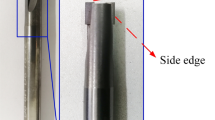
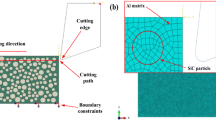
Directing at the hard machinability of high volume fraction 70% SiCp/Al composites, a longitudinal and torsional ultrasonic-assisted milling (LTUAM) method is proposed to improve the edge quality and machining efficiency. By observing the metallographic structure of the material, a three-dimensional (3D) finite element model of random distribution of spherical, elliptical and polygonal SiC particles is established and analyzed by ABAQUS simulation software. The formation mechanism of edge defects, stress distribution, defect characteristics and the effect of machining parameters on milling forces are investigated during ultrasonic-assisted milling. The results show that the edge defects appear at the inlet, outlet and middle edge position, especially is more serious at the outlet position. The SiC particles failure modes mainly include particle pullout, particle shearing, and crushing, moreover, the edge defects mainly include matrix tearing, edge breakage, burrs, bulges and pits. Ultrasonic-assisted milling (UAM) with a certain range of ultrasonic amplitude could effectively reduce the surface fragmentation rate and milling force, and it not only could slow down the expansion of cracks, but also increase the plastic flow of material, and obtain better edge quality compared with the traditional machining method. Comparing the results of finite element analysis and experimental tests, it shows that the simulation results are in good agreement with that of tests.





















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Chawla N, Shen Y-L (2001) Mechanical behavior of particle reinforced metal matrix composites. Adv Eng Mater 3(6):357–370
Basak A, Pramanik A, Prakash C (2019) Deformation and strengthening of SiC reinforced Al-MMCs during in-situ micro-pillar compression. Mater Sci Eng A 763:138141
Lu SJ, Zhang JJ, Li ZQ, Zhang JG, Wang XH, Hartmaier A, Xu JF, Yan YD, Sun T (2021) Cutting path-dependent machinability of SiCp/Al composite under multi-step ultra-precision diamond cutting. Chin J Aeronaut 34:241–252
Zhao GL, Mao PC, Li L, Iqbal A, He N (2020) Micro-milling of 65 vol% SiCp/Al composites with a novel laser-assisted hybrid process. Ceram Int 46:26121–26128
Zhou L, Cui C, Zhang P, Ma Z (2017) Finite element and experimental analysis of machinability during machining of high-volume fraction SiCp/Al composites. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 91:1935–1944
Kadivar MA, Akbari J, Yousefi R, Rahi A, Nick MG (2014) Investigating the effects of vibration method on ultrasonic-assisted drilling of Al/SiCp metal matrix composites. Robot Cim-Int Manuf 30(3):344–350
Aurich JC, Dornfeld D, Arrazola PJ (2009) Burrs—Analysis, control and removal. CIRP Ann 58(2):519–542
Yang B, Shen X, Lei S (2009) Mechanisms of edge chipping in laser-assisted milling of silicon nitride ceramics Int. J Mach Tool Manufact 49:344–350
Woo WS, Lee CM (2018) A study on the edge chipping according to spindle speed and inclination angle of workpiece in laser-assisted milling of silicon nitride. Opt Laser Technol 99:351–362
Chen J, An Q, Ming W, Chen M (2020) Investigation on machined surface quality in ultrasonic-assisted grinding of Cf/SiC composites based on fracture mechanism of carbon fibers. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 109:1583–1599
Chen J, Ming W, An Q, Chen M (2020) Mechanism and feasibility of ultrasonic-assisted milling to improve the machined surface quality of 2D Cf/SiC composites. Ceram Int 46(10):15122–15136
Wang J, Zha H, Feng P, Zhang J (2016) On the mechanism of edge chipping reduction in rotary ultrasonic drilling: A novel experimental method. Precis Eng 44:231–235
Juri AZ, Zhang YZ, Kotousov A, Ling Y (2021) Zirconia responses to edge chipping damage induced in conventional and ultrasonic vibration-assisted diamond machining. J Mater Res Technol 13:573–589
Fang B, Yuan Z, Li D, Gao L (2021) Effect of ultrasonic vibration on finished quality in ultrasonic vibration assisted micromilling of Inconel718. Chin J Aeronaut 34(6):209–219
Yadav AK, Bajpai V, Singh NK, Singh RK (2017) FE modeling of burr size in high- speed micro-milling of Ti6Al4V. Precis Eng 49:287–292
Yu W, Chen J, Ming W, An Q, Chen M (2021) Experimental and FEM study of cutting mechanism and damage behavior of ceramic particles in orthogonal cutting SiCp/Al composites. Ceram Int 47:7183–7194
Zhou L, Wang Y, Ma ZY, Yu XL (2014) Finite element and experimental studies of the formation mechanism of edge defects during machining of SiCp/Al composites. Int J Mach Tool Manufact 84:9–16
Niu Q, Jing L, Li C et al (2021) Study on effects of tool nose radius on the formation mechanism of edge defects during milling SiCp /Al composites. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 114:2261–2269
Nasr MNA, Ghandehariun A, Kishawy HA (2017) A physics-based model for metal matrix composites deformation during machining: a modified constitutive equation. J Eng Mater Technol 139(1):011003
Ghandehariun A, Kishawy HA, Umer U, Hussein HM (2016) Ontool–workpiece interactions during machining metal matrix composites: investigation of the effect of cutting speed. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 84:2423–2435
Wu J, Yu G, Gao Y, Wang L (2018) Mechatronics modeling and vibration analysis of a 2-DOF parallel manipulator in a 5-DOF hybrid machine tool. Mech Mach Theory 121:430–445
Wu J, Wang J, Lp W, Li T, Zheng Y (2009) Study on the stiffness of a 5-DOF hybrid machine tool with actuation redundancy. Mech Mach Theory 44(2):289–305
Wu J, Wang J, Li T, Wang LP (2007) Dynamic analysis of the 2-DOF planar parallel manipulator of a heavy duty hybrid machine tool
Funding
We are very grateful to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 5197052714) for their strong support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Peicheng Peng: Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Writing-review & editing. Daohui Xiang: Project administration, Formal analysis, Writing—review & editing. Xiaofei Lei: Data curation, Investigation. Zhanli Shi: Data curation, Investigation. Bo Li: Data curation, Investigation. Gaofeng Liu: Data curation, Investigation. Bo Zhao: Writing—review & editing. Guofu Gao: Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
I would like to declare on behalf of my co-authors that the work described was an application that has not been published previously, and not under consideration for publication elsewhere, in whole or in part.
Consent to participate
All authors know and agree to be co-authors.
Consent to publish
All authors agreed to be published.
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection: New Intelligent Manufacturing Technologies through the Integration of Industry 4.0 and Advanced Manufacturing
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, P., Xiang, D., Lei, X. et al. Study on the edge defects of high volume fraction 70% SiCp/Al composites in ultrasonic-assisted milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 122, 485–498 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-08586-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-08586-y