Abstract
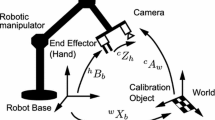
Due to the increase in the difficulty and diversity of tasks performed by robots, robot “hand-eye” collaborative operation has attracted widespread attention. This technology is widely used in aerospace, medical, automotive, and industrial fields. Recently, hand-eye calibration technology is developing towards high precision and high intelligence. However, it has much work to be done in terms of identifying robot and camera parameters. This article introduces in detail the methods and theories involved in hand-eye calibration. According to the structure of the algorithm and the type of the optimization method, this paper summarizes the hand-eye calibration method into four steps: camera pose, mechanical claw pose, mathematical model, and error metrics. The well-known open problems about hand-eye calibration are finally stated, and some new research interests are also pointed out. The results of this review are useful for robot technicians to choose the correct parameter identification method and for researchers to determine further research areas.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Wu L, Ren HL (2017) Finding the kinematic base frame of a robot by hand-eye calibration using 3D position data. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 14(1):314–324
Zhan Q, Wang X (2012) Hand–eye calibration and positioning for a robot drilling system. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 61:691–701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-011-3741-4
Li WL, Xie H, Zhang G, Yan S, Yin Z (2016) Hand–eye calibration in visually-guided robot grinding. IEEE Trans Cybern 46(11):2634–2642. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2015.2483740
Pachtrachai K, Allan M, Pawar V, Hailes S, Stoyanov D (2016) Hand-eye calibration for robotic assisted minimally invasive surgery without a calibration object. 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS): 2485–2491. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2016.7759387
Thompson S, Stoyanov D, Schneider C, Gurusamy K, Ourselin S, Davidson B, Hawkes D, Clarkson MJ (2016) Hand–eye calibration for rigid laparoscopes using an invariant point. Int J CARS 11(6):1071–1080. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-016-1364-9
Corrochano EB, Daniilidis K, Sommer G (2000) Motor algebra for 3D kinematics: the case of the hand-eye calibration. J Math Imaging Vis 13(2):79–100. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026567812984
Hou Z, Xu Y, Xiao R, Chen S (2020) A teaching-free welding method based on laser visual sensing system in robotic GMAW. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 109:1755–1774. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05774-0
Zhang ZY (2000) A flexible new technique for camera calibration. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 22(11):1330–1334
Zhang YZ (2010) Research on hand-eye calibration technology of industrial robot. Dissertation, Harbin Engineering University.
Celozzi C, Paravati G, Sanna A, Lamberti F (2010) A 6-DOF ARTag-based tracking system. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 56(1):203–210. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCE.2010.5439146
Tsai R (1987) A versatile camera calibration technique for high-accuracy 3D machine vision metrology using off-the-shelf TV cameras and lenses. IEEE J Robot Autom 3(4):323–344. https://doi.org/10.1109/JRA.1987.1087109
Heikkila J, Silvcn O (1997). A four-step camera calibration procedure with implicit image correction. Proceedings of IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition: 1106-1112. 10.1109/CVPR.1997.609468
Zhang MY, Tai RK, Li FD, Yang YQ (2016) Calibration of monocular camera based on improved genetic algorithm. Artif Intell Robot Res 5(3):53–62
Fiala M (2005) Comparing ARTag and ARToolkit Plus fiducial marker systems. IEEE International Workshop on Haptic Audio Visual Environments and their Applications:148-153
Kato H, Billinghurst M (2002) Marker tracking and HMD calibration for a video-based augmented reality conferencing system. IEEE & Acm International Workshop on Augmented Reality: 85-94.
Abdullah J, Martinez K (2002) Camera self-calibration for the ARToolkit. The First IEEE International Workshop Agumented Reality Toolkit: 5-10.
Tanaka H, Ogata K, Matsumoto Y (2017) Improving the accuracy of visual markers by four dots and image interpolation. 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Robotics and Intelligent Sensors (IRIS): 178-183. 10.1109/IRIS.2016.8066087
Fiala M (2005) ARTag, A fiducial marker system using digital techniques. 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR'05) 2:590-596. 10.1109/CVPR.2005.74
Atcheson B, Heide F, Heidrich W (2010) CALTag: high precision fiducial markers for camera calibration. Proceedings of the Vision, Modeling, and Visualization Workshop 2010:41–48
Kam HC, Yu YK, Wong KH (2018) An improvement on ArUco marker for pose tracking using Kalman filter. 2018 19th IEEE/ACIS International Conference on Software Engineering, Artificial Intelligence. Networking and Parallel/Distributed Computing (SNPD) 1:65–69
Olson E (2011) AprilTag: a robust and flexible visual fiducial system. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation 2011:3400–3407. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2011.5979561
Wang J, Olson E (2016) AprilTag 2: efficient and robust fiducial detection. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots & Systems: 4193-4198.
Abbas SM, Aslam S, Berns K, Muhammad A (2019) Analysis and improvements in AprilTag based state estimation. Sensors 19(24):5480–5512. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19245480
Maybank SJ, Faugeras OD (1992) A theory of self-calibration of a moving camera. Int J Comput Vis 8(2):123–151
Sinha D, Giardina C (1990) Discrete black and white object recognition via morphological functions. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence 26(3):275–293. https://doi.org/10.1109/34.49053
Li H, Zhang H, Wu F, Hu Z (2002) A new linear camera self-calibration technique. Chin J Comput 11:1121–1129
Li F, Sekkati H, Deglint J, Scharfenberger C, Lamm M, Clausi D, Zelek J, Wong A (2017) Simultaneous projector-camera self-calibration for three-dimensional reconstruction and projection mapping. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging 3(1):74–83. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCI.2017.2652844
Denavit J, Hartenberg RS (1965) A kinematic notation for lower-pair mechanisms based on matrices. J Appl Mech 22(2):215–221
Hayati SA (1983) Robot arm geometric link parameter estimation. The 22nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control:1477-1483. 10.1109/CDC.1983.269783
Hayati S, Tso K, Roston G (1988) Robot geometry calibration. 988 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation 2: 947-951.
Gan Y, Duan J, Dai X (2019) A calibration method of robot kinematic parameters by drawstring displacement sensor. Int J Adv Robot Syst 5:1–9
Chen Q, Zhou Z, Liu C, Sun X (2020) Design of a vision calibration method of ksinematic parameters for 6-DoF manipulator. J Tongji Univ 48(07):1023–1029
Li Z, Li S, Luo X (2021) An overview of calibration technology of industrial robots. J Automat Sin 8(1):23–36. https://doi.org/10.1109/JAS.2020.1003381
Okamura K, Park FC (1996) Kinematic calibration using the product of exponentials formula. Robotica 14(4):415–422
Chen IM, Yang G (1997) Kinematic calibration of modular reconfigurable robots using product-of- exponentials formula. J Robot Syst 14(11):807–821
Chen IM, Yang G, Tan CT, Song HY (2001) Local POE model for robot kinematic calibration. Mech Mach Theory 36(11):1215–1239
Li C, Wu Y, Harald L, Li Z (2016) Poe-based robot kinematic calibration using axis configuration space and the adjoint error model. IEEE Trans Robot 32(5):1264–1279. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2016.2593042
Toan NV, Khoi PB (2018) A svd-least-square algorithm for manipulator kinematic calibration based on the product of exponentials formula. J Mech Sci Technol 32(11):5401–5409
Zhuang H, Roth ZS (1992) A complete and parametrically continuous kinematic model. IEEE Trans Robot Autom 8(4):451–463
Roberts KS (1988) A new representation for a line. Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition:635–640
Meng Y, Zhuang H (2007) Autonomous robot calibration using vision technology. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 23(4):436–446
Zorski W (2017) Quaternion-based determination of 3D objects orientation. 2017 22nd International Conference on Methods and Models in Automation and Robotics (MMAR):232-237
Li G, Zhang F, Fu Y, Wang S (2019) Kinematic calibration of serial robot using dual quaternions. Industrial robot: the international journal of robotics research and application 46:247–258
Wang W, Liu F, Yun C (2015) Calibration method of robot base frame using unit quaternion form. Precis Eng 41:47–54
Wang G, Liu X, Han S (2018) A method of robot base frame calibration by using dual quaternion algebra. IEEE Access 6:74865–74873
Ozgur E, Mezouar Y (2016) Kinematic modeling and control of a robot arm using unit dual quaternions. Robot Auton Syst 77:66–73
Tsai RY, Lenz RK (1989) A new technique for fully autonomous and efficient 3D robotics hand/eye calibration. IEEE Trans Rob Autom 5(3):345–358
Shiu YC, Ahmad S (1989) Calibration of wrist-mounted robotic sensors by solving homogeneous transform equations of the form AX=XB 5(1):16-29.
Wang CC (2002) Extrinsic calibration of a vision sensor mounted on a robot. IEEE Trans Rob Autom 8(2):161–175
Park FC, Martin BJ (2002) Robot sensor calibration: solving AX=XB on the Euclidean group. IEEE Trans Rob Autom 10(5):717–721
Ma SD (1996) A self-calibration technique for active vision systems. IEEE Trans Robotics Automat 12(1):114–120
Andreff N, Horaud R, Espiau B (1999) On-line hand-eye calibration. Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on 3-D digital imaging and modeling: 430-436. https://doi.org/10.1109/IM.1999.805374
Wang Y, Duan S, Gao RZ, Zhuang W (2019) Research on robot hand-eye calibration algorithm based on dual quaternion. Mechanical and electrical engineering 36(7):755–765
Daniilidis K (1999) Hand-eye calibration using dual quaternions. Int J Robot Res 18(3):286–298
Wang C, Li L (2019) Robot hand-eye calibration algorithm based on quaternion. Sens Microsyst 38(012):133–135
Luo B, Zhang X, Luo C (2019) Binocular robot hand-eye calibration algorithm integrating rodrigue matrix and whole least squares. J Surv Mapp Sci Technol 3:244–249
Horaud R, Dornaika F (1995) Hand-eye calibration. Int J Robot Res 14(3):195–210
Andreff N, Horaud R, Espiau B (2001) Robot hand-eye calibration using structure-from-motion. Int J Robot Res 20(3):228–248
Zhang Y (2009) Research on hand-eye calibration technology of industrial robot. Dissertation, Harbin Engineering University
Zhao Z (2011) Hand-eye calibration using convex optimization. IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation: 2947-2952.
Heller J, Havlena M, Pajdla T (2016) Globally optimal hand-eye calibration using branch-and-bound. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 38(5):1027–1033
Zhuang H, Roth ZS, Sudhakar R (1994) Simultaneous robot/world and tool/flange calibration by solving homogeneous transformation equations of the form AX=YB. IEEE Trans Robot Autom 10(4):549–554
Dornaika F, Horaud R (1998) Simultaneous robot-world and hand-eye calibration. IEEE Trans Rob Autom 14(4):617. https://doi.org/10.1109/70.704233
Hirsh RL, Desouza GN, Kak AC (2001) An iterative approach to the hand-eye and base-world calibration problem. IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation 3:2171–2176
Shah M (2013) Solving the robot-world/hand-eye calibration problem using the Kronecker product. J Mech Robot 5(3):031007
Tabb AL, Ahmad Yousef KM (2017) Solving the robot-world hand-eye(s) calibration problem with iterative methods. Mach Vis Appl 28(5-6):1–22
Li A, Lin W, Wu D (2010) Simultaneous robot-world and hand-eye calibration using dual-quaternions and Kronecker product. Int J Phys Sci 5(10):1530–1536
Strobl KH, Hirzinger G (2007) Optimal hand-eye calibration. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots & Systems: 4647-4653.
Xu C, Liu Y, Jia M, Xiao Y, Cao J (2019) Hand-eye calibration method of wood-grabbing robot. J Agric Mach 050(012):420–426
Zhao Z (2019) Simultaneous robot-world and hand-eye calibration by the alternative linear programming. Pattern Recogn Lett 127:174–180
Zhi X, Schwertfeger S (2017) Simultaneous hand-eye calibration and reconstruction. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots & Systems 2017:1470–1477
Ali I, Suominen O, Gotchev A, Morales ER (2019) Methods for simultaneous robot-world-hand–eye calibration: a comparative study. Sensors 19(12):2837–2853. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19122837
Tian P, Yang S, Wu Z, Li Z, Hu P, Qu X (2020) An optimal hand-eye calibration method for robots based on precision compensation. J Xi'an Jiaotong Univ 54(8):99–106
Wang G, Li WL, Jiang C, Zhu DH, Ding H (2021) Simultaneous calibration of multicoordinates for a dual-robot system by solving the AXB = YCZ problem. IEEE Trans Robot:1–14
Yan SJ, Ong SK, Nee A (2016) Registration of a hybrid robot using the Degradation-Kronecker method and a purely nonlinear method. Robotica 1(12):1–12
Wu L, Wang J, Qi L, Ren H, Meng M (2016) Simultaneous hand–eye, tool–flange, and robot–robot calibration for comanipulation by solving the problem. IEEE Trans Robot 32(2):413–428
Ma Q, Goh Z, Chirikjian G S. Probabilistic approaches to the AXB = YCZ calibration problem in multi-robot systems. Robot Sci Syst: 1-9. 10.15607/RSS.2016.XII.014
Acknowledgements
We also thank Shanda Wang for useful discussions and all our colleagues for providing all types of help during the preparation of this manuscript.
Funding
This research is supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFC0803000, 2016YFC0803005). Data availability and materials
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Not applicable.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, J., Luo, X., Luo, Q. et al. An overview of hand-eye calibration. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 119, 77–97 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-08233-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-08233-6