Abstract
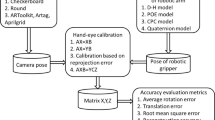
In the application scenario of robot autonomous tasks, the robot needs to be able to complete calibration online and automatically to achieve self-maintenance, which differs from traditional robot hand-eye calibration in that the traditional robot hand-eye calibration requires a dedicated calibration board to assist offline completion. Aiming at the problem that the existing self-calibration methods cannot be optimized as a whole, which leads to low accuracy and instability of the solution, a multi-stage objective function optimization self-calibration algorithm is proposed, which describes the solution of hand-eye self-calibration as a minimization objective function problem involving multiple stages. An optimization method based on the minimization of re-projection error is designed to compensate for the results, which uses an efficient Oriented fast and rotated brief (ORB) feature extraction algorithm and introduces a scoring mechanism to retain more correct matching points in the feature matching stage. Two different types of experiments were designed to validate our method. One is a single camera dataset experiment, which shows that our method is more accurate and robust than the existing self-calibration method; the other is an application platform experiment, which verifies the feasibility and availability of our method.
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.: 62073249).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiang, J., Luo, X., Luo, Q., Qiao, L., Li, M.: An overview of hand-eye calibration. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 1–21 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-08233-6
Shiu, Y.C., Ahmad, S.: Calibration of wrist-mounted robotic sensors by solving homogeneous transform equations of the form AX=XB. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 5(1), 16–29 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1109/70.88014
Tsai, R.Y., Lenz, R.K.: A new technique for fully autonomous and efficient 3D robotics hand/eye calibration. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 5(3), 345–358 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1109/70.34770
Zhang, Y., Qiu, Z., Zhang, X.: A simultaneous optimization method of calibration and measurement for a typical hand-eye positioning system. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 70, 1–11 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/tim.2020.3013308
Daniilidis, K.: Hand-eye calibration using dual quaternions. Int. J. Robot. Res. 18(3), 286–298 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1177/02783649922066213
Liu, Z., Liu, X., Duan, G., Tan, J.: Precise hand-eye calibration method based on spatial distance and epipolar constraints. Robot. Auton. Syst. 145, 103868 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.robot.2021.103868
Andreff, N., Horaud, R., Espiau, B.: On-line hand-eye calibration. In: Second IEEE International Conference on 3-D Digital Imaging and Modeling, pp. 430–436. IEEE, New York (1999). https://doi.org/10.1109/im.1999.805374
Heller, J., Havlena, M., Pajdla, T.: A branch-and-bound algorithm for globally optimal hand-eye calibration. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1608–1615. IEEE, New York (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2012.6247853
Xie, X., Peng, Z.: A hand-eye calibration method based on robot with stationary viewpoint. China Measur. Test (2018)
Zhi, X., Schwertfeger, S.: Simultaneous hand-eye calibration and reconstruction. In: IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 1470–1477. IEEE, New York (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/iros.2017.8205949
Ng, P.C., Henikoff, S.: SIFT: predicting amino acid changes that affect protein function. Nucleic Acids Res. 31(13), 3812–3814 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkg509
Xu, G.S., Yan, Y.H.: A scene feature-based auto hand-eye calibration method for industrial robot. Mach. Des. Res. 4, 179–191 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-43703-9_15
Xu, J., Hoo, J.L., Dritsas, S.: Hand-eye calibration for 2D laser profile scanners using straight edges of common objects. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 73, 102221 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2021.102221
Rublee, E., Rabaud, V., Konolige, K., et al.: ORB: an efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF. In: 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2564–2571. IEEE, New York (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/iccv.2011.6126544
Mair, E., Hager, G.D., Burschka, D., Suppa, M., Hirzinger, G.: Adaptive and generic corner detection based on the accelerated segment test. In: Daniilidis, K., Maragos, P., Paragios, N. (eds.) ECCV 2010. LNCS, vol. 6312, pp. 183–196. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15552-9_14
Calonder, M., Lepetit, V., Strecha, C., Fua, P.: BRIEF: binary robust independent elementary features. In: Daniilidis, K., Maragos, P., Paragios, N. (eds.) ECCV 2010. LNCS, vol. 6314, pp. 778–792. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15561-1_56
Campos, C., Elvira, R., Rodríguez, J.J.G., et al.: ORB-SLAM3: an accurate open-source library for visual, visual-inertial, and multimap SLAM. IEEE Trans. Rob. 37(6), 1874–1890 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/tro.2021.3075644
Bian, J.-W., et al.: GMS: grid-based motion statistics for fast, ultra-robust feature correspondence. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 128(6), 1580–1593 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-019-01280-3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liu, K., Zheng, W., Min, H., Lin, Y. (2023). Multi-stage Objective Function Optimized Hand-Eye Self-calibration of Robot in Autonomous Environment. In: Pan, L., Zhao, D., Li, L., Lin, J. (eds) Bio-Inspired Computing: Theories and Applications. BIC-TA 2022. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1801. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1549-1_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1549-1_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-1548-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-1549-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)