Abstract
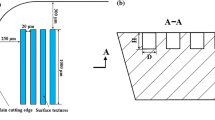
Setting the micro-texture in the cutter–chip contact area of a micro-textured tool rake face can effectively improve the tool’s cutting performance. However, an unreasonable design for the micro-groove morphology and size and the selection of inappropriate cutting parameters will cause a secondary cutting phenomenon during the cutting process. To explore the optimum micro-texture morphology size and cutting parameters, micro-texture self-lubricating ceramic cutting tools with different morphology parameters (micro-texture location distribution: MSTD-1, MSTD-2, MSTD-3; groove spacing: MSTS-1, MSTS-2, MSTS-3; groove width: MSTW-1, MSTW-2, MSTW-3) were formed in situ and by hot pressing sintering, and a dry cutting 40Cr comparison test with a non-textured tool (MST-0) was conducted. The results revealed that the MSTD-2 tool effectively reduced the cutting force, friction factor, and rake face wear and relieved the secondary cutting phenomenon while cutting 40Cr. A theoretical analysis showed that the micro-texture morphology parameters and cutting speed were the main factors affecting the secondary cutting, with a smaller groove width and higher cutting speed associated with a lighter chip impact.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang XL, Kato K, Adachi K, Aizawa K (2003) Loads carrying capacity map for the surface texture design of SiC thrust bearing sliding in water. Tribol Int 36(3):189–197
Wang Z, Zhao QZ, Wang CW (2015) Reduction of friction of metals using laser-induced periodic surface nanostructures. Micromachines 6(11):1606–1616
Broghi A, Gualtieri E, Marchetto D, Moretti L, Valeri S (2008) Tribological effects of surface texturing on nitriding steel for high -performance engine applications. Wear 265(7):1046–1051
Etsion I (2005) State of the art in laser surface texturing. J Tribol 127(1):248–253
Wang T, Huang WF, Liu XF, Li YJ, Wang YM (2014) Experimental study of two-phase mechanical face seals with laser surface texturing. Tribol Int 72:90–97
Sinanoğlu C, Nair F, Karamış MB (2005) Effects of shaft surface texture on journal bearing pressure distribution. J Mater Process Technol 168(2):344–353
Tala-Ighil N, Maspeyrot P, Fillon M, Bounif A (2007) Effects of surface texture on journal-bearing characteristics under steady-state operating conditions. Proce Ins Mech Engin Part J: J Engin Tribol 221(6):623–633
Marian VG, Gabriel D, Knoll G, Filippone S (2011) Theoretical and experimental analysis of a laser textured thrust bearing. Tribol Lett 44(3):335–343
Hua XJ, Sun JG, Zhang PY, Ge HQ, Fu YH, Ji JH, Yin BF (2016) Research on discriminating partition laser surface micro-texturing technology of engine cylinder. Tribol Int 98:190–196
Jeng YR (1996) Impact of plateaued surfaces on tribological performance. Tribol Trans 39(2):354–361
Sabri L, Mansori EIM (2009) Process variability in honing of cylinder liner with vitrified bonded diamond tools. Surf Coat Technol 204(6):1046–1050
Zhu WL, Xing YQ, Ehmann KF, Ju BF (2016) Ultrasonic elliptical vibration texturing of the rake face of carbide cutting tools for adhesion reduction. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 85(9–12):2669–2679
Su YS, Li Z, Li L, Wang JB (2017) Cutting performance of micro-textured polycrystalline diamond tool in dry cutting. J Manuf Process 27:1–7
Kurniawan R, Kiswanto G, Ko TJ (2016) Micro-dimple pattern process and orthogonal cutting force analysis of elliptical vibration texturing. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 106:127–140
Xing YQ, Deng JX, Zhao J, Zhang GD, Zhang KD (2014) Cutting performance and wear mechanism of nanoscale and microscale textured Al2O3/TiC ceramic tools in dry cutting of hardened steel. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater 43(3):46–58
Wu Z, Deng JX, Chen Y, Xing YQ, Zhao J (2012) Performance of the self-lubricating textured tools in dry cutting of Ti-6Al-4V. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 62(9–12):943–951
Feng YH, Zhang JY, Wang L, Zhang WQ, Tian Y, Kong X (2017) Fabrication techniques and cutting performance of micro-textured self-lubricating ceramic cutting tools by in-situ forming of Al2O3-TiC. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater 68:121–129
Chen RY (1992) Principle of metal cutting. China Machine Press, Beijing
Shaw MC (1984) Metal cutting principles. Oxford University Press, New York
Liu HW (2011) Mechanics of materials. Higher Education Press, Beijing
Funding
This work was supported by the Key Research and Development Plan of Shandong Province (2018GGX103006) and the National Science Foundation of China (51675289).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Y., Zhang, J., Wang, L. et al. Study on secondary cutting phenomenon of micro-textured self-lubricating ceramic cutting tools with different morphology parameters formed via in situ forming of Al2O3-TiC. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 104, 3821–3833 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04045-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04045-x