Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the clinical outcomes of medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) reconstruction combined with derotational distal femur osteotomy in patients with recurrent patellar dislocation who had excessive femoral anteversion angle and trochlear dysplasia.
Methods
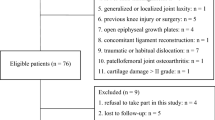
Between 2015 and 2020, 64 patients (64 knees) with recurrent patellar dislocation, who had excessive femoral anteversion angle (≥ 25°) and trochlear dysplasia and were surgically treated using derotational distal femur osteotomy and MPFL reconstruction, were eligible for this retrospective study. These patients were assigned to two groups according to the grade of trochlear dysplasia. Group A (type A trochlear dysplasia, n = 33) and Group B (type B, C, D trochlear dysplasia, n = 31). Preoperative and postoperative patellar tilt angle (PTA), Caton–Deschamps index (CD-I), tibial tubercle–trochlear groove (TT–TG) distance and femoral anteversion angle were evaluated. Patient outcomes were assessed using the preoperative and postoperative International Knee Documentation Committee (IKDC) score, Kujala score, Lysholm score, Tegner score, and visual analog scale (VAS) score.
Results
A total of 64 patients (64 knees) were evaluated in this study, with a mean follow-up period of 28.4 ± 3.6 months. There were no cases of wound infection, osteotomy site fractures, deep venous thrombosis of the lower extremities, or re-dislocation in the two groups during the postoperative follow-up period. All patients returned to full extension and flexion. The postoperative Tegner score, Lysholm score, Kujala score, IKDC score, VAS score, PTA, CD-I, TT–TG distance, and femoral anteversion angle were significantly improved compared with the preoperative status (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference between the two groups (n.s.).
Conclusion
MPFL reconstruction combined with derotational distal femur osteotomy showed satisfactory clinical outcomes during follow-up in patients with recurrent patellar dislocation who had excessive femoral anteversion angle and trochlear dysplasia. Even patients with high-grade trochlear dysplasia showed satisfactory results. For those patients, additional surgery is not necessary.
Level of evidence
Level III.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Carstensen SE, Feeley SM, Burrus MT, Deasey M, Rush J, Diduch DR (2020) Sulcus deepening trochleoplasty and medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction for patellofemoral instability: a 2-year study. Arthroscopy 36(8):2237–2245
Dejour H, Walch G, Nove-Josserand L, Guier C (1994) Factors of patellar instability: an anatomic radiographic study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2(1):19–26
Deng X, Li L, Zhou P, Deng F, Li Y, He Y, Chen G, Li Z, Liu J (2021) Medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction combined with biplanar supracondylar femoral derotation osteotomy in recurrent patellar dislocation with increased femoral internal torsion and genu valgum: a retrospective pilot study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 22(1):990. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-021-04816-2
Drapeau-Zgoralski V, Swift B, Caines A, Kerrigan A, Carsen S, Pickell M (2023) Lateral patellar instability. J Bone Joint Surg Am 105(5):397–409
Ferrua P, Compagnoni R, Calanna F, Randelli PS, Dejour D (2022) Good patient satisfaction with low complications rate after trochleoplasty in patellofemoral instability. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 30(10):3444–3450
Frodl A, Lange T, Siegel M, Meine H, Taghizadeh E, Schmal H, Izadpanah K (2022) Individual influence of trochlear dysplasia on patellofemoral kinematics after isolated MPFL reconstruction. J Pers Med 12(12):2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12122049
Giovannetti de Sanctis E, Mesnard G, Dejour DH (2022) Trochlear dysplasia: when and how to correct. Clin Sports Med 41(1):77–88
Hiemstra LA, Kerslake S, Lafave MR, Tucker A (2021) Patella alta is reduced following MPFL reconstruction but has no effect on quality-of-life outcomes in patients with patellofemoral instability. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 29(2):546–552
Hiemstra LA, Peterson D, Youssef M, Soliman J, Banfield L, Ayeni OR (2019) Trochleoplasty provides good clinical outcomes and an acceptable complication profile in both short and long-term follow-up. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 27(9):2967–2983
Hodax JD, Leathers MP, Ding DY, Feeley BT, Allen CR, Ma CB, Zhang AL (2019) Tibial tubercle osteotomy and medial patellofemoral ligament imbrication for patellar instability due to trochlear dysplasia. Orthop J Sports Med 7(8):2325967119865172
Huntington LS, Webster KE, Devitt BM, Scanlon JP, Feller JA (2020) Factors associated with an increased risk of recurrence after a first-time patellar dislocation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med 48(10):2552–2562
Kaiser P, Konschake M, Loth F, Plaikner M, Attal R, Liebensteiner M, Schlumberger M (2020) Derotational femoral osteotomy changes patella tilt, patella engagement and tibial tuberosity trochlear groove distance. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 28(3):926–933
Kang H, Dong C, Tian G, Wang F (2019) A computed tomography study of the association between increased patellar tilt angle and femoral anteversion in 30 patients with recurrent patellar dislocation. Med Sci Monit 25:4370–4376
Kazley JM, Banerjee S (2019) Classifications in brief: the dejour classification of trochlear dysplasia. Clin Orthop Relat Res 477(10):2380–2386
Korthaus A, Dust T, Berninger M, Frings J, Krause M, Frosch K-H, Thürig G (2022) Influence of the fluoroscopy setting towards the patient when identifying the MPFL insertion point. Diagnostics (Basel) 12:1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12061427
Leclerc J-T, Dartus J, Labreuche J, Martinot P, Galmiche R, Migaud H, Pasquier G, Putman S (2021) Complications and outcomes of trochleoplasty for patellofemoral instability: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 1000 trochleoplasties. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 107(7):103035
Levy BJ, Tanaka MJ, Fulkerson JP (2021) Current concepts regarding patellofemoral trochlear dysplasia. Am J Sports Med 49(6):1642–1650
Liska F, von Deimling C, Otto A, Willinger L, Kellner R, Imhoff AB, Burgkart R, Voss A (2019) Distal femoral torsional osteotomy increases the contact pressure of the medial patellofemoral joint in biomechanical analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 27(7):2328–2333
Mengis N, Zimmermann F, Schemel L, Rippke JN, Milinkovic DD, Balcarek P (2022) Return to sports and patients’ rehabilitation continuum after deepening trochleoplasty and concomitant patellar-stabilizing procedures: a case series of 111 patients at 2 to 4 years of follow-up. Am J Sports Med 50(3):674–680
Nelitz M, Lippacher S (2014) Arthroscopic evaluation of trochlear dysplasia as an aid in decision making for the treatment of patellofemoral instability. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22(11):2788–2794
Song G-Y, Hong L, Zhang H, Zhang J, Li X, Li Y, Feng H (2014) Trochleoplasty versus nontrochleoplasty procedures in treating patellar instability caused by severe trochlear dysplasia. Arthroscopy 30(4):523–532
Wierer G, Krabb N, Kaiser P, Ortmaier R, Schützenberger S, Schlumberger M, Hiller B, Ingruber F, Smekal V, Attal R, Seitlinger G (2022) The patellar instability probability calculator: a multivariate-based model to predict the individual risk of recurrent lateral patellar dislocation. Am J Sports Med 50(2):471–477
Woodmass JM, Johnson NR, Cates RA, Krych AJ, Stuart MJ, Dahm DL (2018) Medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction reduces radiographic measures of patella alta in adults. Orthop J Sports Med 6(1):2325967117751659
Zhang Z, Song G, Li Y, Zheng T, Ni Q, Feng H, Zhang H (2021) Medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction with or without derotational distal femoral osteotomy in treating recurrent patellar dislocation with increased femoral anteversion: a retrospective comparative study. Am J Sports Med 49(1):200–206
Zhang Z, Zhang H, Song G, Wang X, Zhang J, Zheng T, Ni Q, Feng H (2020) A high-grade j sign is more likely to yield higher postoperative patellar laxity and residual maltracking in patients with recurrent patellar dislocation treated with derotational distal femoral osteotomy. Am J Sports Med 48(1):117–127
Zhang Z, Zhang H, Song G, Zheng T, Ni Q, Feng H (2020) Increased femoral anteversion is associated with inferior clinical outcomes after MPFL reconstruction and combined tibial tubercle osteotomy for the treatment of recurrent patellar instability. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 28(7):2261–2269
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all the staff of the participating departments.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province of China (No.H2022206557).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KZ: writing the manuscript, evaluating the radiographs, collecting and analyzing the data. ZS, HG and AF: writing the manuscript, evaluating the radiographs, collecting and analyzing the data. XW and RS: evaluating the radiographs, collecting and analyzing the data. YN and LL: project coordinator, designing the study, writing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Academic Ethics Committee of the Third Hospital of Hebei Medical University.
Informed consent
All patients provided informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, K., Sun, Z., Feng, A. et al. Derotational distal femur osteotomy combined with medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction yields satisfactory results in recurrent patellar dislocation with excessive femoral anteversion angle and trochlear dysplasia. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 31, 4347–4354 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-023-07476-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-023-07476-y