Abstract
Purpose
Rotator cuff tears are one of the most common causes of shoulder malfunction and pain, which lead to a significant reduction in the quality of life. This present study investigated the effects of subacromial platelet-rich plasma injections [i.e. autologous conditioned plasma (ACP) injections] as compared to standard subacromial cortisone injection therapy in 50 patients with partial rotator cuff tears.
Methods
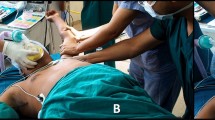
Before injection, and 6 weeks, 12 weeks and 6 months thereafter, the patients were assessed by the Constant–Murley score (CMS), the American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons Standardized Shoulder Assessment Form (ASES), the simple shoulder test (SST) and a pain visual analogue scale (VAS). An MRI was also performed before and 6 months after injection.
Results
Both patient groups had statistically significant better shoulder score outcomes over time. ASES, SST and CMS outcomes after 12 versus 6 weeks were better in the ACP group as compared to the cortisone group. VAS, ASES and CMS outcomes after 12 weeks versus baseline in the ACP group were better as compared to the cortisone group. There was a statistically significant difference between ACP group and cortisone group 12 weeks after injection regarding VAS, ASES, SST and CMS in favour of the ACP group. The MRI showed an improvement in grade of tendinopathy in both groups, however, without statistically significant differences between the two groups.
Conclusion
Compared with cortisone injections, ACP injections show earlier benefit as compared to cortisone injections although a statistically significant difference after 6 months could not be found. Therefore, subacromial ACP injections are a good alternative to subacromial cortisone injections, especially in patients with contraindication to cortisone.
Level of evidence
Therapeutic study, Level III.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antuna S, Barco R, Martinez Diez JM, Sanchez Marquez JM (2013) Platelet-rich fibrin in arthroscopic repair of massive rotator cuff tears: a prospective randomized pilot clinical trial. Acta Orthop Belg 79(1):25–30
Barber FA, Hrnack SA, Snyder SJ, Hapa O (2011) Rotator cuff repair healing influenced by platelet-rich plasma construct augmentation. Arthroscopy 27(8):1029–1035
Bergeson AG, Tashjian RZ, Greis PE, Crim J, Stoddard GJ, Burks RT (2012) Effects of platelet-rich fibrin matrix on repair integrity of at-risk rotator cuff tears. Am J Sports Med 40(2):286–293
Bosch G, Moleman M, Barneveld A, van Weeren PR, van Schie HT (2011) The effect of platelet-rich plasma on the neovascularization of surgically created equine superficial digital flexor tendon lesions. Scand J Med Sci Sports 21(4):554–561
Castricini R, Longo UG, De BM et al (2011) Platelet-rich plasma augmentation for arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med 39(2):258–265
Cervellin M, de Girolamo L, Bait C, Denti M, Volpi P (2012) Autologous platelet-rich plasma gel to reduce donor-site morbidity after patellar tendon graft harvesting for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a randomized, controlled clinical study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20(1):114–120
Chahal J, Van Thiel GS, Mall N et al (2012) The role of platelet-rich plasma in arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a systematic review with quantitative synthesis. Arthroscopy 28(11):1718–1727
Charousset C, Zaoui A, Bellaiche L, Piterman M (2014) Does autologous leukocyte-platelet-rich plasma improve tendon healing in arthroscopic repair of large or massive rotator cuff tears? Arthroscopy 30(4):428–435
Constant CR, Murley AG (1987) A clinical method of functional assessment of the shoulder. Clin Orthop Relat Res 214:160–164
Cook JL, Purdam CR (2009) Is tendon pathology a continuum? A pathology model to explain the clinical presentation of load-induced tendinopathy. Br J Sports Med 43(6):409–416
Creaney L, Hamilton B (2008) Growth factor delivery methods in the management of sports injuries: the state of play. Br J Sports Med 42(5):314–320
de Mos M, van der Windt AE, Jahr H et al (2008) Can platelet-rich plasma enhance tendon repair? A cell culture study. Am J Sports Med 36(6):1171–1178
de Vos RJ, Weir A, van Schie HT et al (2010) Platelet-rich plasma injection for chronic Achilles tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 303(2):144–149
Dhillon MS, Behera P, Patel S, Shetty V (2014) Orthobiologics and platelet rich plasma. Indian J Orthop 48(1):1–9
Everts PA, Devilee RJ, Brown MC et al (2008) Exogenous application of platelet-leukocyte gel during open subacromial decompression contributes to improved patient outcome. A prospective randomized double-blind study. Eur Surg Res 40(2):203–210
Gumina S, Campagna V, Ferrazza G et al (2012) Use of platelet-leukocyte membrane in arthroscopic repair of large rotator cuff tears: a prospective randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 94(15):1345–1352
Hansen M, Boesen A, Holm L, Flyvbjerg A, Langberg H, Kjaer M (2013) Local administration of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) stimulates tendon collagen synthesis in humans. Scand J Med Sci Sports 23(5):614–619
Haraldsson BT, Langberg H, Aagaard P, Zuurmond AM, van El B, Degroot J, Kjaer M, Magnusson SP (2006) Corticosteroids reduce the tensile strength of isolated collagen fascicles. Am J Sports Med 34(12):1992–1997
Heisterbach PE, Todorov A, Fluckiger R, Evans CH, Majewski M (2012) Effect of BMP-12, TGF-beta1 and autologous conditioned serum on growth factor expression in Achilles tendon healing. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20(10):1907–1914
Ho JO, Sawadkar P, Mudera V (2014) A review on the use of cell therapy in the treatment of tendon disease and injuries. J Tissue Eng 18(5):2041731414549678
Ide J, Kikukawa K, Hirose J et al (2009) The effect of a local application of fibroblast growth factor-2 on tendon-to-bone remodeling in rats with acute injury and repair of the supraspinatus tendon. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 18(3):391–398
Jo CH, Kim JE, Yoon KS et al (2011) Does platelet-rich plasma accelerate recovery after rotator cuff repair? A prospective cohort study. Am J Sports Med 39(10):2082–2090
Jo CH, Shin JS, Lee YG et al (2013) Platelet-rich plasma for arthroscopic repair of large to massive rotator cuff tears: a randomized, single-blind, parallel-group trial. Am J Sports Med 41(10):2240–2248
Kaux JF, Janssen L, Drion P et al (2014) Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-111 (VEGF-111) and tendon healing: preliminary results in a rat model of tendon injury. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J 4(1):24–28
Kesikburun S, Tan AK, Yilmaz B, Yasar E, Yazicioglu K (2013) Platelet-rich plasma injections in the treatment of chronic rotator cuff tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial with 1-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med 41(11):2609–2616
Lewis JS (2010) Rotator cuff tendinopathy: a model for the continuum of pathology and related management. Br J Sports Med 44(13):918–923
Lippitt SB, Harryman DT, Matsen FA, Fu FH, Hawkins RJ (1993) A practical tool for evaluating function: the simple shoulder test. In: Matsen F (ed) The shoulder: a balance of mobility and stability, American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, pp 501–518
Malavolta EA, Gracitelli ME, Ferreira Neto AA, Assuncao JH, Bordalo-Rodrigues M, de Camargo OP (2014) Platelet-rich plasma in rotator cuff repair: a prospective randomized study. Am J Sports Med 42(10):2446–24154
Molini L, Mariacher S, Bianchi S (2012) US guided corticosteroid injection into the subacromial-subdeltoid bursa: technique and approach. J Ultrasound 15(1):61–68
Nguyen RT, Borg-Stein J, McInnis K (2011) Applications of platelet-rich plasma in musculoskeletal and sports medicine: an evidence-based approach. PM R 3(3):226–250
Oh JH, Jo KH, Kim WS, Gong HS, Han SG, Kim YH (2009) Comparative evaluation of the measurement properties of various shoulder outcome instruments. Am J Sports Med 37(6):1161–1168
Peerbooms JC, Sluimer J, Bruijn DJ, Gosens T (2010) Positive effect of an autologous platelet concentrate in lateral epicondylitis in a double-blind randomized controlled trial: platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injection with a 1-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med 38(2):255–262
Randelli PS, Arrigoni P, Cabitza P, Volpi P, Maffulli N (2008) Autologous platelet rich plasma for arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. A pilot study. Disabil Rehabil 30(20–22):1584–1589
Randelli P, Arrigoni P, Ragone V, Aliprandi A, Cabitza P (2011) Platelet rich plasma in arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a prospective RCT study, 2-year follow-up. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 20(4):518–528
Rha DW, Park GY, Kim YK, Kim MT, Lee SC (2013) Comparison of the therapeutic effects of ultrasound-guided platelet-rich plasma injection and dry needling in rotator cuff disease: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil 27(2):113–122
Richards RR, An KN, Bigliani LU et al (1994) A standardized method for the assessment of shoulder function. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 3(6):347–352
Rickert M, Wang H, Wieloch P et al (2005) Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of growth and differentiation factor-5 into tenocytes and the healing rat Achilles tendon. Connect Tissue Res 46(4–5):175–183
Rocourt MH, Radlinger L, Kalberer F, Sanavi S, Schmid NS, Leunig M, Hertel R (2008) Evaluation of intratester and intertester reliability of the Constant–Murley shoulder assessment. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 17(2):364–369
Rodeo SA, Delos D, Williams RJ, Adler RS, Pearle A, Warren RF (2012) The effect of platelet-rich fibrin matrix on rotator cuff tendon healing: a prospective, randomized clinical study. Am J Sports Med 40(6):1234–1241
Ruiz-Moneo P, Molano-Munoz J, Prieto E, Algorta J (2013) Plasma rich in growth factors in arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a randomized, double-blind, controlled clinical trial. Arthroscopy 29(1):2–9
Rutgers M, Saris DB, Dhert WJ, Creemers LB (2010) Cytokine profile of autologous conditioned serum for treatment of osteoarthritis, in vitro effects on cartilage metabolism and intra-articular levels after injection. Arthritis Res Ther 12(3):R114
Scarpone M, Rabago D, Snell E et al (2013) Effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma injection for rotator cuff tendinopathy: a prospective open-label study. Glob Adv Health Med 2(2):26–31
Schnabel LV, Mohammed HO, Miller BJ et al (2007) Platelet rich plasma (PRP) enhances anabolic gene expression patterns in flexor digitorum superficialis tendons. J Orthop Res 25(2):230–240
Suwalski A, Dabboue H, Delalande A et al (2010) Accelerated Achilles tendon healing by PDGF gene delivery with mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Biomaterials 31(19):5237–5245
Weber SC, Kauffman JI, Parise C, Weber SJ, Katz SD (2013) Platelet-rich fibrin matrix in the management of arthroscopic repair of the rotator cuff: a prospective, randomized, double-blinded study. Am J Sports Med 41(2):263–270
Zavadil DP, Satterlee CC, Costigan JM, Holt DW, Shostrom VK (2007) Autologous platelet gel and platelet-poor plasma reduce pain with total shoulder arthroplasty. J Extra Corpor Technol 39(3):177–182
Zhang Q, Ge H, Zhou J, Cheng B (2013) Are platelet-rich products necessary during the arthroscopic repair of full-thickness rotator cuff tears: a meta-analysis. PLoS One 8(7):e69731
Zheng XQ, Li K, Wei YD, Tie HT, Yi XY, Huang W (2014) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs versus corticosteroid for treatment of shoulder pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 95(10):1824–1831
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the help of Dr. Rolf Pokorny for proofreading.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
von Wehren, L., Blanke, F., Todorov, A. et al. The effect of subacromial injections of autologous conditioned plasma versus cortisone for the treatment of symptomatic partial rotator cuff tears. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 24, 3787–3792 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-015-3651-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-015-3651-3