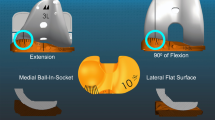
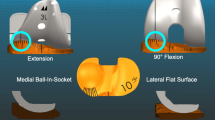
Abstract
Purpose
Balancing the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) with posterior cruciate-retaining total knee replacement (PCR-TKR) aims to restore femoral rollback. In practice, paradoxical roll forward persists. The purpose of this study is to propose a technique for optimizing PCL tension. Because PCL function starts above 60° of flexion, we hypothesize that PCL balancing requires flexion gap tightening by oversizing the femoral component and increasing posterior condylar offset (PCO).
Methods
PCR-TKR was performed in 21 osteoarthritis patients with a gap-balancing technique. The femoral component was oversized if more than a 5-mm posterior drawer existed after tibial component implantation. Kinematics was recorded intra-operatively in two steps with dedicated navigation software (Praxim, La Tronche, Isère, France): antero-posterior (AP) displacements of condylo-tibial contact points were observed in native and implanted knees, with each knee serving as its own control. The absence of paradoxical displacements was verified once the final implants were inserted.
Results
Paradoxical medial condyle displacement (11 mm) persisted in a single case. On average, posterior displacement of the medial condyle decreased from 9 ± 9 to 1 ± 6 mm (p = 0.001) and that of the lateral condyle from 16 ± 14 to 6 ± 6 mm (p = 0.006). In the 0°–30° flexion interval, posterior displacement was 2 times less than before implantation for the medial condyle (p = 0.001), and 4 times less for the lateral condyle (p = 0.004). The course of the lateral condyle decreased from 2 ± 3 to 0 ± 4 mm in the 90°–120° flexion interval (p = 0.046). Six-month flexion was 124° ± 17°.
Conclusion
Femoral component oversizing allows us to control paradoxical forward displacements in 95 % of cases. When balancing PCR prostheses, AP laxity should be taken into account. Increasing PCO appears to be a reliable technique for adjusting PCL balance. Thus, it may optimize extensor mechanism action and, subsequently, the functional results of PCR-TKR.
Level of evidence
Diagnostic study, Level II.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Argenson JN, Komistek RD, Mahfouz M, Walker SA, Aubaniac JM, Dennis DA (2004) A high flexion total knee arthroplasty design replicates healthy knee motion. Clin Orthop Relat Res 428:174–179
Dejour H, Walch G, Deschamps G, Chambat P (2014) Arthrosis of the knee in chronic anterior laxity. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 100:49–58
Dennis DA, Komistek RD, Colwell CE Jr, Ranawat CS, Scott RD, Thornhill TS, Lapp MA (1998) In vivo anteroposterior femorotibial translation of total knee arthroplasty: a multicenter analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 356:47–57
Dennis DA, Komistek RD, Mahfouz MR, Haas BD, Stiehl JB (2003) Multicenter determination of in vivo kinematics after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 416:37–57
Fantozzi S, Catani F, Ensini A, Leardini A, Giannini S (2006) Femoral rollback of cruciate-retaining and posterior-stabilized total knee replacements: in vivo fluoroscopic analysis during activities of daily living. J Orthop Res 24:2222–2229
Fujimoto E, Sasashige Y, Masuda Y, Hisatome T, Eguchi A, Masuda T, Sawa M, Nagata Y (2013) Significant effect of the posterior tibial slope and medial/lateral ligament balance on knee flexion in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21:2704–2712
Geijsen GJ, Heesterbeek PJ, van Stralen G, Anderson PG, Wymenga AB (2014) Do tibiofemoral contact point and posterior condylar offset influence outcome and range of motion in a mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22:550–555
Heesterbeek PJ, Labey L, Wong P, Innocenti B, Wymenga AB (2014) A new spacer-guided, PCL balancing technique for cruciate-retaining total knee replacement. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22:650–659
Horiuchi H, Akizuki S, Tomita T, Sugamoto K, Yamazaki T, Shimizu N (2012) In vivo kinematic analysis of cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty during weight-bearing and non-weight-bearing deep knee bending. J Arthroplasty 27:1196–1202
Insall JN, Dorr LD, Scott RD, Scott WN (1989) Rationale of the Knee Society clinical rating system. Clin Orthop Relat Res 248:13–14
Li G, Zayontz S, Most E, Otterberg E, Sabbag K, Rubash HE (2001) Cruciate-retaining and cruciate-substituting total knee arthroplasty: an in vitro comparison of the kinematics under muscle loads. J Arthroplasty 16:150–156
Mahoney OM, Noble PC, Rhoads DD, Alexander JW, Tullos HS (1994) Posterior cruciate function following total knee arthroplasty. A biomechanical study. J Arthroplasty 9:569–578
Massin P, Boyer P, Hajage D, Kilian P, Tubach F (2011) Intra-operative navigation of knee kinematics and the influence of osteoarthritis. Knee 18:259–264
Massin P, Boyer P, Sabourin M (2012) Less femorotibial rotation and AP translation in deep-dished total knee arthroplasty. An intraoperative kinematic study using navigation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20:1714–1719
Massin P, Gournay A (2006) Optimization of the posterior condylar offset, tibial slope, and condylar roll-back in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 21:889–896
Matsumoto T, Kubo S, Muratsu H, Matsushita T, Ishida K, Kawakami Y, Oka S, Matsuzaki T, Kuroda Y, Nishida K, Akisue T, Kuroda R, Kurosaka M (2013) Different pattern in gap balancing between the cruciate-retaining and posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21:2338–2345
Miller RK, Goodfellow JW, Murray DW, O’Connor JJ (1998) In vitro measurement of patellofemoral force after three types of knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 80:900–906
Nilsson KG, Karrholm J, Gadegaard P (1991) Abnormal kinematics of the artificial knee. Roentgen stereophotogrammetric analysis of 10 Miller–Galante and five New Jersey LCS knees. Acta Orthop Scand 62:440–446
Ploegmakers MJ, Ginsel B, Meijerink HJ, de Rooy JW, de Waal Malefijt MC, Verdonschot N, Banks SA (2010) Physical examination and in vivo kinematics in two posterior cruciate ligament retaining total knee arthroplasty designs. Knee 17:204–209
Stiehl JB, Komistek RD, Dennis DA, Paxson RD, Hoff WA (1995) Fluoroscopic analysis of kinematics after posterior-cruciate-retaining knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br 77:884–889
Verra WC, van den Boom LG, Jacobs W, Clement DJ, Wymenga AA, Nelissen RG (2013) Retention versus sacrifice of the posterior cruciate ligament in total knee arthroplasty for treating osteoarthritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 10:CD004803
Victor J, Banks S, Bellemans J (2005) Kinematics of posterior cruciate ligament-retaining and -substituting total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomised outcome study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 87:646–655
Yoshiya S, Matsui N, Komistek RD, Dennis DA, Mahfouz M, Kurosaka M (2005) In vivo kinematic comparison of posterior cruciate-retaining and posterior stabilized total knee arthroplasties under passive and weight-bearing conditions. J Arthroplasty 20:777–783
Yue B, Varadarajan KM, Moynihan AL, Liu F, Rubash HE, Li G (2011) Kinematics of medial osteoarthritic knees before and after posterior cruciate ligament retaining total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Res 29:40–46
Acknowledgments
We thank Ovid Da Silva for editing this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
PM has received royalties from Zimmer in relation to materials not included in the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Donadio, J., Pelissier, A., Boyer, P. et al. Control of paradoxical kinematics in posterior cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty by increasing posterior femoral offset. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23, 1631–1637 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-015-3561-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-015-3561-4