Abstract
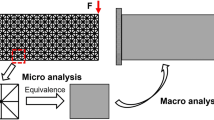
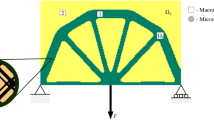
This work develops a topological optimization framework for parametric lattice structure design under harmonic load based on the scale-dependent multiscale finite element method (MsFEM). Two different design variables are introduced and optimized simultaneously in the topology optimization, i.e., the control parameters represent the lattice cell’s material consumption and the configuration. To improve analysis accuracy and efficiency, the MsFEM with periodic boundary condition is used for structures with strong periodicity and the MsFEM with six nodes on each edge of the coarse element is used for those with weak periodicity, respectively. Then the scale-dependent lattice cell’s equivalent stiffness and mass matrices can be established. The surrogate model of the relationship between the lattice control parameters and stiffness matrices and mass matrices is built based on the proper orthogonal decomposition and diffusion approximation methods. Therefore, sensitivity analysis of the dynamic responses concerning the control parameters can be performed. Finally, numerical examples and vibration testing results are presented to show the validity of the optimization framework using gradient lattice structures to suppress vibration under frequency band loading and its potential application in engineering practice.

























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreassen E, Jensen JS (2014) Topology optimization of periodic microstructures for enhanced dynamic properties of viscoelastic composite materials. Struct Multidisc Optim 49:695–705. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-013-1018-2
Babuška I, Osborn JE (1983) Generalized finite element methods: their performance and their relation to mixed methods. SIAM J Numer Anal 20:510–536
Bendsoe MP, Kikuchi N (1988) Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 71:197
Bendsøe MP, Sigmund O (2013) Topology optimization: theory, methods and applications. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Berkooz G, Holmes P, Lumley JL (1993) The proper orthogonal decomposition in the analysis of turbulent flows. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 25:539
Breitkopf P, Touzot G, Villon P (1998) Consistency approach and diffuse derivation in element free methods based on moving least squares approximation. Comput Assist Mech Eng Sci 5(4):479–501
Bruggi M, Taliercio A (2012) Maximization of the fundamental eigenfrequency of micropolar solids through topology optimization. Struct Multidisc Optim 46:549–560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-012-0779-3
Bruggi M, Zega V, Corigliano A (2017) Synthesis of auxetic structures using optimization of compliant mechanisms and a micropolar material model. Struct Multidisc Optim 55:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-016-1589-9
Chandrasekhar A, Sridhara S, Suresh K (2023) Graded multiscale topology optimization using neural networks. Adv Eng Softw. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2022.103359
Chen L, Wan J, Chu X, Liu H (2021) Parameterized level set method for structural topology optimization based on the Cosserat elasticity. Acta Mech Sin 37:620–630. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-020-01045-z
Ding H, Xu B, Duan Z, Zhao Y (2022) Concurrent design of the free damping structure for minimizing the frequency response in a broad frequency band. Eng Optim 54:1273–1288. https://doi.org/10.1080/0305215X.2021.1921170
Esfarjani SM, Dadashi A, Azadi M (2022) Topology optimization of additive-manufactured metamaterial structures: a review focused on multi-material types. Forces Mech 7:100100
Gori L, Silva Penna S, da Silva Pitangueira RL (2019) A computational framework for the constitutive modeling of nonlinear micropolar media. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-019-1779-7
Hassani B, Hinton E (1998) A review of homogenization and topology optimization I—homogenization theory for media with periodic structure. Comput Struct 69:707–717. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-7949(98)00131-X
Humar J (2012) Dynamics of structures. CRC Press
Jung J, Hyun J, Goo S, Wang S (2015) An efficient design sensitivity analysis using element energies for topology optimization of a frequency response problem. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 296:196–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2015.06.019
Jung J, Goo S, Kook J (2021) Predicting anti-resonance frequencies using a novel eigenvalue formulation. Finite Elements Anal Design. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.finel.2021.103525
Kim JE, Park K (2021) Multiscale topology optimization combining density-based optimization and lattice enhancement for additive manufacturing. Int J Precision Eng Manuf Green Technol 8:1197–1208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-020-00289-1
Léger P, Idé IM, Paultre P (1990) Multiple-support seismic analysis of large structures. Comput Struct 36:1153–1158. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-7949(90)90224-P
Li H, Zhang H, Zheng Y, Zhang L (2016) A peridynamic model for the nonlinear static analysis of truss and tensegrity structures. Comput Mech 57:843–858. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-016-1264-4
Li H, Luo Z, Xiao M, Gao L, Gao J (2019) A new multiscale topology optimization method for multiphase composite structures of frequency response with level sets. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 356:116–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2019.07.020
Li S, Yuan S, Zhu J, Wang C, Li J, Zhang W (2020) Additive manufacturing-driven design optimization: building direction and structural topology. Addit Manuf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2020.101406
Liu H, Lv J (2017) An equivalent continuum multiscale formulation for 2D geometrical nonlinear analysis of lattice truss structure. Compos Struct 160:335–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.10.072
Liu H, Zhang HW (2013) A uniform multiscale method for 3D static and dynamic analyses of heterogeneous materials. Comput Mater Sci 79:159–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2013.06.006
Liu H, Zhang HW (2014) An equivalent multiscale method for 2D static and dynamic analyses of lattice truss materials. Adv Eng Softw 75:14–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2014.04.006
Liu H, Zhang L, Yang DS, Zhang HW (2014) An efficient multiscale method for 2D large displacement—small strain analysis of heterogeneous materials. Comput Mater Sci 83:443–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2013.11.055
Liu H, Zhang W, Gao T (2015) A comparative study of dynamic analysis methods for structural topology optimization under harmonic force excitations. Struct Multidisc Optim 51:1321–1333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-014-1218-4
Liu T, Zhu JH, He F, Zhao H, Liu Q, Yang C (2017) A MAC based excitation frequency increasing method for structural topology optimization under harmonic excitations. Int J Simul Multidisc Design Optim. https://doi.org/10.1051/smdo/2016012
Liu H, Wang Y, Zong H, Wang MY (2018) Efficient structure topology optimization by using the multiscale finite element method. Struct Multidisc Optim 58:1411–1430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-018-1972-9
Liu T, Zhu JH, Zhang WH, Zhao H, Kong J, Gao T (2019) Integrated layout and topology optimization design of multi-component systems under harmonic base acceleration excitations. Struct Multidisc Optim 59:1053–1073. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02200-2
Liu H, Yang D, Wu J, Zeng Y, Zhang H (2022) An open-source matlab implementation for elastic analyses of heterogeneous materials using the extended multiscale finite element method. Int J Multiscale Comput Eng 20:19–43. https://doi.org/10.1615/IntJMultCompEng.2021039777
Montemurro M, Bertolino G, Roiné T (2020) A general multi-scale topology optimisation method for lightweight lattice structures obtained through additive manufacturing technology. Compos Struct 258:113360
Montero DS, Silva OM, Cardoso EL (2020) Topology optimization for harmonic vibration problems using a density-weighted norm objective function. Struct Multidisc Optim 62:3301–3327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-020-02695-0
Nightingale M, Hewson R, Santer M (2021) Multiscale optimisation of resonant frequencies for lattice-based additive manufactured structures. Struct Multidisc Optim 63:1187–1201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-020-02752-8
Nikbakht S, Kamarian S, Shakeri M (2019) A review on optimization of composite structures Part II: functionally graded materials. Compos Struct 214:83–102
Panettieri E, Boissin E, Montemurro M, Catapano A, Jalocha D (2022) On the accuracy of a homogenized continuum model of lattice structures in modal analyses. Mech Adv Mater Struct 29:6768–6785. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376494.2021.1985196
Pecullan S, Gibiansky LV, Torquato S (1999) Scale effects on the elastic behavior of periodic and hierarchical two-dimensional composites. J Mech Phys Solids 47:1509–1542. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5096(98)00111-2
Rovati M, Veber D (2007) Optimal topologies for micropolar solids. Struct Multidisc Optim 33:47–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-006-0031-0
Sanders C, Norato J, Walsh T, Aquino W (2020) An error-in-constitutive equations strategy for topology optimization for frequency-domain dynamics. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2020.113330
Sivapuram R, Dunning PD, Kim HA (2016) Simultaneous material and structural optimization by multiscale topology optimization. Struct Multidisc Optim 54:1267–1281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-016-1519-x
Svanberg K (1987) The method of moving asymptotes—a new method for structural optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 24:359–373
Tanskanen P (2002) The evolutionary structural optimization method: theoretical aspects. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 191:5485
Tuna M, Trovalusci P (2022) Topology optimization of scale-dependent non-local plates. Struct Multidisc Optim. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-022-03351-5
Vicente WM, Zuo ZH, Pavanello R, Calixto TKL, Picelli R, Xie YM (2016) Concurrent topology optimization for minimizing frequency responses of two-level hierarchical structures. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 301:116–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2015.12.012
Wang C, Zhu JH, Zhang WH, Li SY, Kong J (2018) Concurrent topology optimization design of structures and non-uniform parameterized lattice microstructures. Struct Multidisc Optim 58:35–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-018-2009-0
Weinan E, Björn E (2005) The heterogeneous multi-scale method for homogenization problems. In: Engquist B, Runborg O, Lötstedt P (eds) Multiscale methods in science and engineering. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 89–110
Wu Z, Fan F, Xiao R, Yu L (2020) The substructuring-based topology optimization for maximizing the first eigenvalue of hierarchical lattice structure. Int J Numer Methods Eng 121:2964–2978. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.6342
Wu J, Sigmund O, Groen JP (2021) Topology optimization of multi-scale structures: a review. Struct Multidisc Optim 63:1455–1480
Xia Z, Zhou C, Yong Q, Wang X (2006) On selection of repeated unit cell model and application of unified periodic boundary conditions in micro-mechanical analysis of composites. Int J Solids Struct 43:266–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2005.03.055
Xu B, Xie YM (2015) Concurrent design of composite macrostructure and cellular microstructure under random excitations. Compos Struct 123:65–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2014.10.037
Yamamoto T, Maruyama S, Nishiwaki S, Yoshimura M (2009) Topology design of multi-material soundproof structures including poroelastic media to minimize sound pressure levels. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 198:1439–1455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2008.12.008
Yan J, Hu WB, Wang ZH, Duan ZY (2014) Size effect of lattice material and minimum weight design. Acta Mech Sin 30:191–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-014-0001-5
Yoon GH (2010) Structural topology optimization for frequency response problem using model reduction schemes. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199:1744–1763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2010.02.002
Zhang X, Kang Z (2014) Dynamic topology optimization of piezoelectric structures with active control for reducing transient response. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 281:200–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2014.08.011
Zhang HW, Wu JK, Fu ZD (2010a) Extended multiscale finite element method for elasto-plastic analysis of 2D periodic lattice truss materials. Comput Mech 45:623–635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-010-0475-3
Zhang HW, Wu JK, Lü J, Fu ZD (2010b) Extended multiscale finite element method for mechanical analysis of heterogeneous materials. Acta Mech Sin 26:899–920. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-010-0393-9
Zhang Y, Xiao M, Gao L, Gao J, Li H (2020) Multiscale topology optimization for minimizing frequency responses of cellular composites with connectable graded microstructures. Mech Syst Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2019.106369
Zhang C, Xu S, Liu J, Ma Y (2022) Comprehensive clustering-based topology optimization for connectable multi-scale additive manufacturing structures. Addit Manuf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2022.102786
Zheng S, Zhao X, Yu Y, Sun Y (2017) The approximate reanalysis method for topology optimization under harmonic force excitations with multiple frequencies. Struct Multidisc Optim 56:1185–1196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1714-4
Zheng J, Luo Z, Jiang C, Gao J (2019) Robust topology optimization for concurrent design of dynamic structures under hybrid uncertainties. Mech Syst Signal Process 120:540–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.10.026
Zhou H, Zhu J, Wang C, Zhang Y, Wang J, Zhang W (2022) Hierarchical structure optimization with parameterized lattice and multiscale finite element method. Struct Multidisc Optim 65:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-021-03149-x
Zhu JH, He F, Liu T, Zhang WH, Liu Q, Yang C (2018) Structural topology optimization under harmonic base acceleration excitations. Struct Multidisc Optim 57:1061–1078. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1795-0
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFB3402200) and Key Project of NSFC (92271205). Especially the authors would like to thank Krister Svanberg for sharing his MATLAB code of the moving asymptotes (MMA) method.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Replication of results
The necessary information for the replication of the results is present in the manuscript. The interested readers may contact the corresponding author for further implementation details.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Marco Montemurro.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Zhu, J., Liu, T. et al. Topology optimization of gradient lattice structure under harmonic load based on multiscale finite element method. Struct Multidisc Optim 66, 202 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-023-03652-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-023-03652-3