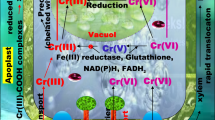
Abstract
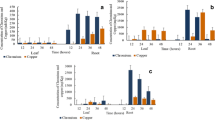
Chromium (Cr) occurs in several oxidation states from trivalent to hexavalent. However, hexavalent forms are more toxic and mainly produced by anthropogenic activities. A hydroponic experiment was conducted to analyse the comparative remediation of Cr by Marsilea minuta and Pistia stratiotes. Plants were exposed to four concentrations of Cr (0.5, 1.0, 1.5, and 2.0 mM) for 3 days. The highest accumulation of Cr was seen at the 1.5 mM concentration after 3 days in Marsilea (11.96 mg/g) and Pistia (18.78 mg/g). Dry weights decreased and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels increased in response to increasing Cr concentrations. Results indicate that both macrophytes are suitable candidates for Cr phytoremediation. Antioxidant-enzyme activity as a function of metal tolerance is imperative for a coherent understanding of plant physiology under metal stress.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akter S, Afrin R, Mia MY, Hossen MZ (2014) Phytoremediation of chromium (cr) from tannery effluent by using water lettuce (Pistia stratiotes). ASA Univ Rev 8(2):149–156
Alvarez CC, Gómez MEB, Zavala AH (2021) Hexavalent chromium: regulation and health effects. J Trace Elem Med Biol 65:126729
Anjum SA, Ashraf U, Imran KHAN, Tanveer M, Shahid M, Shakoor A, Longchang WANG (2017) Phyto-toxicity of chromium in maize: oxidative damage, osmolyte accumulation, anti-oxidative defense and chromium uptake. Pedosphere 27(2):262–273
Ansari AA, Naeem M, Gill SS, AlZuaibr FM (2020) Phytoremediation of contaminated waters: an eco-friendly technology based on aquatic macrophytes application. Egypt J Aquat Res 46(4):371–376
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenol oxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1–15
Avudainayagam S, Megharaj M, Owens G, Kookana RS, Chittleborough D, Naidu R (2003) Chemistry of chromium in soils with emphasis on tannery waste sites. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 178:53–91
Babula P, Adam V, Opatrilova R, Zehnalek J, Havel L, Kizek R (2009) Uncommon heavy metals, metalloids and their plant toxicity: a review. In: Lichtfouse E (ed) Organic Farming, Pest Control and Remediation of Soil Pollutants. Springer, Dordrecht
Becquer T, Quantin C, Sicot M, Boudot JP (2003) Chromium availability in ultramafic soils from New Caledonia. Sci Total Environ 301(1–3):251–261
Cervantes C, Campos-García J, Devars S, Gutiérrez-Corona F, Loza-Tavera H, Torres-Guzmán JC, Moreno-Sánchez R (2001) Interactions of chromium with microorganisms and plants. FEMS Microbiol Rev 25(3):335–347
Dan P, Mandal S, De A, Mandal S (2016) Studies on the toxicity of chromium (VI) to Pistia stratiotes L. plant and its removal. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 5(6):975–982
Das K, Mandal C, Ghosh N, Dey N, Adak MK (2013) Cadmium accumulation in Marsilea minuta Linn. And its antioxidative responses. Am J Plant Sci 4:365–371
Das S, Das A, Mazumder PET, Paul R, Das S (2021) Lead phytoremediation potentials of four aquatic macrophytes under hydroponic cultivation. Int J Phytoremediation 23(12):1279–1288
Dhir B, Sharmila P, Saradhi PP (2009) Potential of aquatic macrophytes for removing contaminants from the environment. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 39(9):754–781
Duxbury AC, Yentsch CS (1956) Plankton pigment nomographs. J. Mar. Res 15:91–100
Fletcher J, Willby N, Oliver DM, Quilliam RS (2020) Phytoremediation using aquatic plants. In: Shmaefsky BR (ed) Phytoremediation. Springer, Cham, pp 205–260
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48(12):909–930
Giripunje MD, Fulke AB, Meshram PU (2015) Remediation techniques for heavy-metals contamination in lakes: a mini‐review. CLEAN–Soil Air Water 43(9):1350–1354
Hayat S, Khalique G, Irfan M, Wani AS, Tripathi BN, Ahmad A (2012) Physiological changes induced by chromium stress in plants: an overview. Protoplasma 249(3):599–611
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125(1):189–198
Hemeda HM, Klein BP (1990) Effects of naturally occurring antioxidants on peroxidase activity of vegetable extracts. J Food Sci 55(1):184–185
Huffman EW Jr, Allaway WH (1973) Chromium in plants. Distribution in tissues, organelles, and extracts and availability of bean leaf chromium to animals. J Agric Food Chem 21(6):982–986
Kaur M, Kumar M, Sachdeva S, Puri SK (2018) Aquatic weeds as the next generation feedstock for sustainable bioenergy production. Bioresour Technol 251:390–402
Khellaf N, Djelal H, Amrane A (2022) An overview of the valorization of aquatic plants in effluent depuration through phytoremediation processes. Appl Microbiol 2(2):309–318
Kumar N, Bauddh K, Dwivedi N, Barman SC, Singh DP (2012) Accumulation of metals in selected macrophytes grown in mixture of drain water and tannery effluent and their phytoremediation potential. J Environ Biol 33(5):923
Kumari A, Lal B, Rai UN (2015) Assessment of native plant species for phytoremediation of heavy metals growing in the vicinity of NTPC sites, Kahalgaon, India. Int J Phytoremediation 18(6):592–597
Manorama Thampatti KC, Beena VI, Meera AV, Ajayan AS (2020) Phytoremediation of metals by aquatic macrophytes. In: Shmaefsky BR (ed) Phytoremediation. Springer, Cham, pp 153–204
Mishra VK, Tripathi BD (2008) Concurrent removal and accumulation of heavy metals by the three aquatic macrophytes. Bioresour Technol 99(15):7091–7097
Mondal NK, Nayek P (2020) Hexavalent chromium accumulation kinetics and physiological responses exhibited by Eichhornia sp. and Pistia sp. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17:1397–1410
Newete SW, Byrne MJ (2016) The capacity of aquatic macrophytes for phytoremediation and their disposal with specific reference to water hyacinth. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:10630–10643
Nishikimi M, Rao NA, Yagi K (1972) The occurrence of superoxide anion in the reaction of reduced phenazine methosulfate and molecular oxygen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 46(2):849–854
Oláh V, Lakatos G, Bertók C, Kanalas P, Szőllősi E, Kis J, Mészáros I (2010) Short-term chromium (VI) stress induces different photosynthetic responses in two duckweed species, Lemna gibba L. and Lemna minor L. Photosynthetica 48:513–520
Panda SK, Choudhury S (2005) Chromium stress in plants. Braz J Plant Physiol 17:95–102
Prado C, Ponce SC, Pagano E, Prado FE, Rosa M (2016) Differential physiological responses of two Salvinia species to hexavalent chromium at a glance. Aquat Toxicol 175:213–221
Reale L, Tedeschini E, Rondoni G, Ricci C, Bin F, Frenguelli G, Ferranti F (2016) Histological investigation on gall development induced by a worldwide invasive pest, Dryocosmus kuriphilus, on Castanea sativa. Plant Biosystems – Int J Dealing Asp Plant Biol 150(1):35–42
Romero-Hernández JA, Amaya-Chávez A, Balderas-Hernández P, Roa-Morales G, González-Rivas N, Balderas-Plata M (2017) Tolerance and hyperaccumulation of a mixture of heavy metals (Cu, Pb, hg, and zn) by four aquatic macrophytes. Int J Phytoremediation 19(3):239–245
Saraswat S, Rai DJ (2018) Aquatic macrophytes mediated remediation of toxic metals from moderately contaminated industrial effluent. Int J Phytoremediation 20(9):876–884
Sasmaz A, Yaman M (2006) Distribution of chromium, nickel and cobalt in different parts of plant species and soil in mining area of Keban, Turkey. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 37(13–14):1945–1857
Sasmaz A, Dogan I, Sasmaz M (2016) Removal of Cr, Ni and Co in the water of chromium mining areas by using Lemna gibba L. and Lemna minor L. Water Environ J 30(3–4):235–242
Shanker AK, Cervantes C, Loza-Tavera H, Avudainayagam S (2005) Chromium toxicity in plants. Environ Int 31(5):739–753
Shanker AK, Djanaguiraman M, Venkateswarlu B (2009) Chromium interactions in plants: current status and future strategies. Metallomics 1(5):375–383
Sharma A, Kapoor D, Wang J, Shahzad B, Kumar V, Bali AS, Yan D (2020) Chromium bioaccumulation and its impacts on plants: an overview. Plants 9(1):100
Shrivastava R, Upreti RK, Seth PK, Chaturvedi UC (2002) Effects of chromium on the immune system. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 34(1):1–7
Singh HP, Mahajan P, Kaur S, Batish DR, Kohli RK (2013) Chromium toxicity and tolerance in plants. Environ Chem Lett 11(3):229–254
Sinha S, Saxena R, Singh S (2005) Chromium induced lipid peroxidation in the plants of Pistia stratiotes L.: role of antioxidants and antioxidant enzymes. Chemosphere 58(5):595–604
Sinha S, Basant A, Malik A, Singh KP (2009) Multivariate modeling of chromium-induced oxidative stress and biochemical changes in plants of Pistia stratiotes L. Ecotoxicology 18:555–566
Srivastava D, Tiwari M, Dutta P, Singh P, Chawda K, Kumari M, Chakrabarty D (2021) Chromium stress in plants: toxicity, tolerance and phytoremediation. Sustainability 13(9):4629
Tabinda AB, Arif RA, Yasar A, Baqir M, Rasheed R, Mahmood A, Iqbal A (2019) Treatment of textile effluents with Pistia stratiotes, Eichhornia crassipes and Oedogonium sp. Int J Phytoremediation 21(10):939–943
Vernay P, Gauthier-Moussard C, Hitmi A (2007) Interaction of bioaccumulation of heavy metal chromium with water relation, mineral nutrition and photosynthesis in developed leaves of Lolium perenne L. Chemosphere 68(8):1563–1575
Vimercati L, Gatti MF, Gagliardi T, Cuccaro F, De Maria L, Caputi A, Baldassarre A (2017) Environmental exposure to arsenic and chromium in an industrial area. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:11528–11535
Wilbur S, Abadin H, Fay M, Yu D, Tencza B, Ingerman L, Klotzbach J, James S (2012) Health effects. In Toxicological Profile for Chromium. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (US). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK158851/
Xu ZH, Yin XA, Yang ZF (2014) An optimisation approach for shallow lake restoration through macrophyte management. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 18(6):2167–2176
Yan SH, Song W, Guo JY (2017) Advances in management and utilization of invasive water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) in aquatic ecosystems–a review. Crit Rev Biotechnol 37(2):218–228
Acknowledgements
The Head of the Botany Department, University of Lucknow is acknowledged for providing central lab facility to execute the experiments and to analyse samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KS: experimental setup, data cumulation and analysis, and manuscript composition. PS: analytical interpretation, statistical analysis on data. AK: conceptualization of experimental design, final editing, overall guidance and submission of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, K., Saxena, P. & Kumari, A. Comparative Study of Chromium Phytoremediation by Two Aquatic Macrophytes. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 111, 16 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-023-03773-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-023-03773-x