Abstract
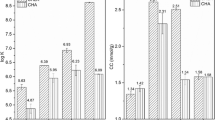
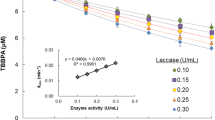
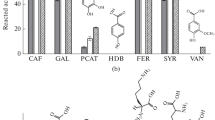
We used 14 C-radiolabelling to study the non-extractable residues (NERs) formation of tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) in a humic acid (HA) suspension under catalysis of laccase in the presence of copper. When entering the suspension after TBBPA adsorbing to HA supramolecular associates, Cu2+ at low concentrations (even without toxicity to laccase) significantly reduced the amount and first-order kinetic constant of the NER formation, while Cu2+ had no significant effect on the formation after it was complexed with HA. The inhibition effect of Cu2+ on the NER formation is explained to be attributed to the prevention of laccase-induced oxidation of TBBPA in the voids of HA associates by complexation of Cu2+ with periphery molecules of the associates. The results provide insights into varying effects of heavy metals on the environmental fate of organic contaminants and suggest that co-existing heavy metals could increase their environmental risk by reducing their NER formation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asif MB, Hai FI, Hou JW, Price WE, Nghiem LD (2017) Impact of wastewater derived dissolved interfering compounds on growth, enzymatic activity and trace organic contaminant removal of white rot fungi - a critical review. J Environ Manage 201:89–109
Berns AE, Philipp H, Lewandowski H, Choi JH, Lamshoft M, Narres HD (2018) Interactions of 15 N-sulfadiazine and soil components as evidenced by 15 N -CPMAS NMR. Environ Sci Technol 52:3748–3757
Cao S, Wang S, Zhao Y, Wang L, Ma Y, Schaffer A, Ji R (2020) Fate of bisphenol S (BPS) and characterization of non-extractable residues in soil: Insights into persistence of BPS. Environ Int 143:105908–105908
Chen JY, Zhu DQ, Sun C (2007) Effect of heavy metals on the sorption of hydrophobic organic compounds to wood charcoal. Environ Sci Technol 41:2536–2541
Chen MY, Waigi MG, Li SY, Sun K, Si YB (2019) Fungal laccase-mediated humification of estrogens in aquatic ecosystems. Water Res 166:115040
Das R, Li GY, Mai BX, An TC (2018) Spore cells from BPA degrading bacteria Bacillus sp. GZB displaying high laccase activity and stability for BPA degradation, Sci. Total Environ 640:798–806
Dou S, Shan J, Song XY, Cao R, Wu M, Li CL, Guan S (2020) Are humic substances soil microbial residues or unique synthesized compounds? A perspective on their distinctiveness. Pedosphere 30:159–167
Farnet AM, Gil G, Ferre E (2008) Effects of pollutants on laccase activities of Marasmius quercophilus, a white-rot fungus isolated from a Mediterranean schlerophyllous litter. Chemosphere 70:895–900
Feng Y, Colosi LM, Gao S, Huang Q, Mao L (2013) Transformation and removal of tetrabromobisphenol A from water in the presence of natural organic matter via laccase-catalyzed reactions: Reaction rates, products, and pathways. Environ Sci Technol 47:1001–1008
Gulkowska A, Sander M, Hollender J, Krauss M (2013) Covalent binding of sulfamethazine to natural and synthetic humic acids: Assessing laccase catalysis and covalent bond stability. Environ Sci Technol 47:6916–6924
Guo XR, Liu YH, Sun FF, Zhou DS, Guo RX, Dong TL, Chen YF, Ji R, Chen JQ (2019) Fate of 14 C-bisphenol F isomers in an oxic soil and the effects of earthworm. Sci Total Environ 657:254–261
Hayes MHB, Clapp CE (2001) Humic substances: Considerations of compositions, aspects of structure, and environmental influences. Soil Sci 166:723–737
Kästner M, Nowak KM, Miltner A, Trapp S, Schäffer A (2014) Classification and modelling of nonextractable residue (NER) formation of xenobiotics in soil – a synthesis. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 44:2107–2171
Kumar GN, Srikumar K (2012) Characterization of xerophytic thermophilic laccase exhibiting metal ion-dependent dye decolorization potential. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 167:662–676
Li CL, Ji F, Wang S, Zhang JJ, Gao Q, Wu JG, Zhao LP, Wang LC, Zheng LR (2015a) Adsorption of Cu(II) on humic acids derived from different organic materials. J Integr Agric 14:168–177
Li FJ, Wang JJ, Jiang BQ, Yang X, Nastold P, Kolvenbach B, Wang LH, Ma YN, Corvini PFX, Ji R (2015b) Fate of tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) and formation of ester- and ether-linked bound residues in an oxic sandy soil. Environ Sci Technol 49:12758–12765
Liu XQ, Xu XY, Zhang HX, Li C, Shao XS, Ye QF, Li Z (2015) Bioavailability and release of nonextractable (bound) residues of chiral cycloxaprid using geophagous earthworm Metaphire guillelmi in rice paddy soil. Sci Total Environ 526:243–250
Luo L, Zhang SZ, Christie P (2010) New insights into the influence of heavy metals on phenanthrene sorption in soils. Environ Sci Technol 44:7846–7851
Ma YN, Zhao YY, Wang YF, Li XZ, Sun FF, Corvini PFX, Ji R (2017) Effects of Cu2+ and humic acids on degradation and fate of TBBPA in pure culture of Pseudomonas sp strain CDT. J Environ Sci 62:60–67
Maurer F, Christl I, Fulda B, Voegelin A, Kretzschmar R (2013) Copper redox transformation and complexation by reduced and oxidized soil humic acid. 2. Potentiometric titrations and dialysis cell experiments. Environ Sci Technol 47:10912–10921
Nagai M, Sato T, Watanabe H, Saito K, Kawata M, Enei H (2002) Purification and characterization of an extracellular laccase from the edible mushroom Lentinula edodes, and decolorization of chemically different dyes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:327–335
Paul EA (2016) The nature and dynamics of soil organic matter: Plant inputs, microbial transformations, and organic matter stabilization. Soil Biol Biochem 98:109–126
Piccolo A (2001) The supramolecular structure of humic substances. Soil Sci 166:810–832
Sadhasivam S, Savitha S, Swaminathan K, Lin FH (2008) Production, purification and characterization of mid-redox potential laccase from a newly isolated Trichoderma harzianum WL1, Process Biochem. 43, 736–742
Schaffer A, Kastner M, Trapp S (2018) A unified approach for including non-extractable residues (NER) of chemicals and pesticides in the assessment of persistence. Environ Sci Eur 30:51
Sutton R, Sposito G (2005) Molecular structure in soil humic substances: The new view. Environ Sci Technol 39:9009–9015
Wu YY, Li YY, Kang D, Wang JJ, Zhang YF, Du DL, Pan BS, Lin ZK, Huang CJ, Dong QX (2016) Tetrabromobisphenol A and heavy metal exposure via dust ingestion in an e-waste recycling region in southeast china. Sci Total Environ 541:356–364
Xu S, Wang YF, Yang LY, Ji R, Miao AJ (2018) Transformation of tetrabromobisphenol A by Rhodococcus jostii RHAl: Effects of heavy metals. Chemosphere 196:206–213
Zhang L, Chen R, Liu Y, Deng Y, Li Z, Dong Y (2019) Influence of metal ions on sulfonamide antibiotics biochemical behavior in fiber coexisting system. J Environ Sci 80:267–276
Zhou Y, Sun F, Wu X, Cao S, Guo X, Wang Q, Wang Y, Ji R (2022) Formation and nature of non-extractable residues of emerging organic contaminants in humic acids catalyzed by laccase. Sci Total Environ 829:154300
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2021YFA0910300), National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (No. 31861133003, 21607071), Fujian Department of Science and Technology (No. 2021J05107), and Quanzhou Bureau of Science and Technology (No. 2020CT002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Jiang, B., Wang, Y. et al. Effect of Cu2+ on the Laccase-Inducted Formation of Non-Extractable Residues of Tetrabromobisphenol A in Humic Acids. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 109, 1162–1166 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-022-03602-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-022-03602-7