Abstract
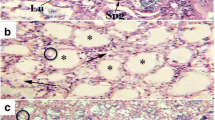
This study aimed to investigate the testicular function of Mugil cephalus that inhabit Wadi El-Rayan lakes. Testes of fish inhabiting the upper lake (site 2) and the lower lake (site 3) of Wadi El-Rayan showed significant decreases in gonadosomatic index, high accumulation levels of six metals, and eight organochlorine pesticide residues. Compared to reference fish, high percentages of histological alterations as testicular degeneration, germ cell reduction, testicular inflammation, vacuolization, and loss of tubular arrangement were observed in sites 2 and 3. Moreover, endocrine disruption signs were recorded based on the percentage of ovotestis appearance and the ovotestis severity index values. The maximum defective testicular antioxidant mechanisms were recorded in site 3 as indicated by sharp decreases in catalase, superoxide dismutase, glutathione reduced levels, and high thiobarbituric acid reactive substances. Finally, long-term exposure to Wadi El-Rayan water may impair the reproductive health of fish via testicular oxidative damage and endocrine disruption.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdel-Khalek AA (2018) Chronic exposure to water of lake Qaroun induced metal-related testicular damage and endocrine disruption in male fish. Biol Trace Elem Res 185:197–204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1220-y
Abdel-Khalek AA, Hamed A, Marie MA (2016) The accumulation potency of bulk and nano zinc metal and their impacts on the hematological and histological perturbations of Oreochromis niloticus. Water Air Soil Pollut 227:206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2908-x
Abdel-Khalek AA, Elhaddad E, Mamdouh S, Marie M-AS (2018) The chronic exposure to discharges of Sabal drain induces oxidative stress and histopathological alterations in Oreochromis niloticus. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 101:92–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2366-9
Abdel-Khalek AA, Zayed HS, Elsayad SM, Zaghloul KH (2020a) Assessment of metal pollution impacts on Tilapia zillii and Mugil cephalus inhabiting Qaroun and Wadi El-Rayan lakes, Egypt, using integrated biomarkers. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:26773–26785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09095-3
Abdel-Khalek AA, Badran SR, Marie MAS (2020b) The efficient role of rice husk in reducing the toxicity of iron and aluminum oxides nanoparticles in Oreochromis niloticus: hematological, bioaccumulation, and histological endpoints. Water Air Soil Pollut 231:53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-4424-2
Abdel-Khalek AA, Al-Quraishy S, Abdel-Gaber R (2021a) Evaluation of Nephrotoxicity in Oreochromis niloticus after exposure to aluminum oxide nanoparticles: exposure and recovery study. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03335-z
Abdel-Khalek AA, Al-Quraishy S, Abdel-Gaber R (2021b) Silver nanoparticles induce time- and tissue-specific genotoxicity in Oreochromis niloticus: utilizing the adsorptive capacities of fruit peels to minimize genotoxicity. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03342-0
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Method Enzymol 105:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Agbohessi PT, Imorou Toko I, Ouédraogo A, Jauniaux T, Mandiki SN, Kestemont P (2015) Assessment of the health status of wild fish inhabiting a cotton basin heavily impacted by pesticides in Benin (West Africa). Sci Total Environ 506–507:567–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.11.047
Ameur WB, Lapuente J, Megdiche Y, Barhoumi B, Trabelsi S, Camps L, Serret J, López DR, Linares JG, Driss MR, Borràs M (2012) Oxidative stress, genotoxicity and histopathology biomarker responses in mullet (Mugil cephalus) and sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) liver from Bizerte Lagoon (Tunisia). Mar Pollut Bull 64(2):241–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.11.026
Amutha C, Subramanian P (2013) Cadmium alters the reproductive endocrine disruption and enhancement of growth in the early and adult stages of Oreochromis mossambicus. Fish Physiol Biochem 39:351–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-012-9704-3
APHA (American Public Health Association) (2005) American Water Works Association. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, New York
Ardry R (1960) The determination of proteins by the biuret reaction. Determination of a specific absorption coefficient. Ann Biol Clin 18:214–222 (PMID: 13794128)
Aydemir B, Kiziler AR, Onaran I, Alici B, Ozkara H, Akyolcu MC (2006) Impact of Cu and Fe concentrations on oxidative damage in male infertility. Biol Trace Elem Res 112(3):193–203. https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:112:3:193
Bateman KS, Stentiford GD, Feist SW (2004) A ranking system for the evaluation of intersex condition in European Flounder (Platichthys flesus). Environ Toxicol Chem 23(12):2831–2836. https://doi.org/10.1897/03-541.1
Bernet D, Schmidt H, Meier W, Burkhardt-Holm P, Wahli T (1999) Histopathology in fish: proposal for a protocol to assess aquatic pollution. J Fish Dis 22(1):25–34. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2761.1999.00134.x
Beutler E, Duron O, Kelly BM (1963) Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med 61:882–888. PMID: 13967893
Cao J, Wang G, Wang T, Chen J, Wenjing G, Wu P, He X, Xie L (2019) Copper caused reproductive endocrine disruption in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat Toxicol 211:124–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.04.003
Deepa S, Murugananthkumar R, Raj Gupta Y, Gowda KSM, Senthilkumaran B (2019) Effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles and zinc sulfate on the testis of common carp Cyprinus Carpio. Nanotoxicology 13(2):240–257. https://doi.org/10.1080/17435390.2018.1541259
El-Sherif SA, Ibrahim SM, Abd El-Gahfour SA (2016) The validity of some dominant fish obtained from Wadi El-Rayan lake for human consumption. Int J of Adv Res 4:1278–1285. https://doi.org/10.21474/IJAR01/1923
Feist SW, Stentiford GD, Kent ML, Ribeiro Santos A, Lorance P (2015) Histopathological assessment of liver and gonad pathology in continental slope fish from the northeast Atlantic ocean. Mar Environ Res 106:42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2015.02.004
Haredi AMM, Mourad M, Tanekhy M, Wassif E, Abdel-Tawab HS (2020) Lake Edku pollutants induced biochemical and histopathological alterations in muscle tissues of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Toxicol Environ Health Sci 12:247–255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-020-00042-w
Iavicoli I, Fontana L, Bergamaschi A (2009) The effects of metals as endocrine disruptors. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev 12(3):206–223. https://doi.org/10.1080/10937400902902062
Islam FU, Jalali S, Shafqat MN, Shah STA (2017) Endosulfan is toxic to the reproductive health of male freshwater fish Cyprinion Watsoni. Sci Nat 104:104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-017-1526-9
Javed M, Ahmad MI, Usmani N, Ahmad M (2017) Multiple biomarker responses (serum biochemistry, oxidative stress, genotoxicity and histopathology) in Channa punctatus exposed to heavy metal loaded waste water. Sci Rep 7:1675–1685. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-01749-6
Jozefczak M, Remans T, Vangronsveld J, Cuypers A (2012) Glutathione is a key player in metal-induced oxidative stress defenses. Int J Mol Sci 13(3):3145–3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13033145
Kaptaner B, Kankaya E, Dogan A, Durmuş A (2016) Alterations in histology and antioxidant defense system in the testes of the lake Van fish (Alburnus tarichi Güldenstädt, 1814). Environ Monit Assess 188(8):474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5476-z
Karadag H, Fırat Ö, Fırat Ö (2014) Use of oxidative stress biomarkers in Cyprinus carpio l. for the evaluation of water pollution in Ataturk Dam Lake (Adiyaman, Turkey). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 92:289–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-013-1187-0
Marentette J, Corkum L (2008) Does the reproductive status of male round gobies (Neogobius melanostomus) influence their response to conspecific odours? Environ Biol Fish 81(4):447–455. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-007-9240-7
Martyniuk CJ, Mehinto AC, Denslow ND (2020) Organochlorine pesticides: agrochemicals with potent endocrine-disrupting properties in fish. Mol Cell Endocrinol 507:110764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2020.110764
Neugebauer EA, Sans Cartier GL, Wakeford BJ (2000) Methods for the determination of metals in wildlife tissues using various atomic absorption spectrophotometry techniques. Canadian wildlife service, Headquarters, Hull, Québec, Canada. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.578.2937&rep=rep1&type=pdf
Nishikimi M, Appaji Rao N, Yagi K (1972) The occurrence of superoxide anion in the reaction of reduced phenazine methosulfate and molecular oxygen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 46:849–854. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-291X(72)80218-3
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3
Ramamoorthi RV, Rossano MG, Paneth N, Gardiner JC, Diamond MP, Puscheck E, Daly DC, Potter RC, Wirth JJ (2008) An application of multivariate ranks to assess effects from combining factors: metal exposures and semen analysis outcomes. Stat Med 27(18):3503–3514. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.3236
Sainath SB, Meena R, Supriya C, Reddy KP, Reddy PS (2011) Protective role of Centella asiatica on lead-induced oxidative stress and suppressed reproductive health in male rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 32(2):146–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2011.04.005
Samanta P, Im H, Yoo J, Lee H, Kim NY, Kim W, Hwang SJ, Kim WK, Jung J (2018) Comparative assessment of the adverse outcome of wastewater effluents by integrating oxidative stress and histopathological alterations in endemic fish. J Hazard Mater 344:81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.10.016
Sun J, Wang C, Peng H, Zheng G, Zhang S, Hu J (2016) p, p’-DDE induces gonadal intersex in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) at environmentally relevant concentrations: comparison with o, p’-DDT. Environ Sci Technol 50:462–469. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b05042
Tyor AK, Pahwa K (2018) Testicular oxidative stress and cellular deformities in Clarias gariepinus (burchell) from river Yamuna in Delhi region, India. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 100:659–664. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2286-8
Vergilio CS, Moreira RV, Carvalho CEV, Melo EJT (2015) Evolution of cadmium effects in the testis and sperm of the tropical fish Gymnotus carapo. Tissue Cell 47(2):132–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tice.2015.02.001
Zaghloul KH, Omar WA, Abdel-Khalek AA, Abo-Hegab S (2011) Ecological monitoring of Mediterranean Solea aegyptiaca transplanted into Lake Qaroun. Egypt Aust J Basic Appl Sci 5(7):851–862
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP-2021/25), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by [AAA-K], [SA-Q], and [RA-G]. The first draft of the manuscript was written by [AAA-K] and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
This manuscript complies with the ethical rules applicable for this journal.
Consent to Participate
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel-Khalek, A.A., Al-Quraishy, S. & Abdel-Gaber, R. Long-Term Exposure to the Water of Wadi El-Rayan Lakes Induced Testicular Damage and Endocrine Disruption in Mugil cephalus. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 108, 663–671 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03406-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03406-1