Abstract
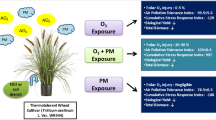
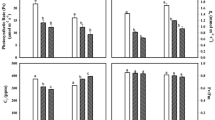
In the present study wheat (Triticum aestivum) cultivar HD 2967 was exposed to ambient and elevated levels of O3 and PM deposition, with and without exogenous application of ascorbic acid (AA). Cultivar HD 2967 exposed to eight treatments in free air O3 enrichment facility and the assessed results showed that wheat cultivar, growth, biochemical, physiological and yield attributes were variably but adversely affected by combined exposure to O3 and PM deposition. PM deposition clogged stomata and enhanced leaf temperature. However, plants exposed to O3 and PM deposition and treated with AA exhibited less reduction in yield as compared to plants exposed to O3 and PM deposition without AA treatment. The decline in grain yield of HD 2967 due to combined exposure of O3 and PM deposition were in the range of 4%–17%. AA spray partially mitigated ozone and PM deposition adverse impact and enhanced wheat yield by 16%.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal M, Singh B, Rajput M, Marshall F, Bell JN (2003) Effect of air pollution on peri-urban agriculture: a case study. Environ Pollut 126(3):323–329
Ainsworth EA (2008) Rice production in a changing climate: a meta-analysis of responses to elevated carbon dioxide and elevated ozone concentration. Global Change Biol 14(7):1642–1650
Ainsworth EA, Serbin SP, Skoneczka JA, Townsend PA (2014) Using leaf optical properties to detect ozone effects on foliar biochemistry. Photosynth Res 119(1–2):65–76
Auerbach NA, Walker MD, Walker DA (1997) Effects of roadside disturbance on substrate and vegetation properties in Arctic Tundra. Ecol Appl 7:218–235
Bernacchi CJ, Leakey AD, Hepmy LE, Morgan PB, Dohleman FG, McGrath JM, Ort DR (2006) Hourly and seasonal variation in photosynthesis and stomatal conductance of soybean grown at future CO2 and ozone concentrations for 3 years under fully open-air field conditions. Plant Cell Environ 29(11):2077–2090
Burney J, Ramanathan V (2014) Recent climate and air pollution impacts on Indian agriculture. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(46):16319–16324
Burkhardt J, Pariyar S (2014) Particulate pollutants are capable to ‘degrade’epicuticular waxes and to decrease the drought tolerance of Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.). Environ Pollut 184:659–667
Burkhardt J, Basi S, Pariyar S, Hunsche M (2012) Stomatal penetration by aqueous solutions–an update involving leaf surface particles. New Phytol 196(3):774–787
Castillo FJ, Greppin H (1988) Extracellular ascorbic acid and enzyme activities related to ascorbic acid metabolism in Sedum album L. leaves after ozone exposure. Environ Exp Bot 28(3):231–238
Daripa A, Bhatia A, Ojha S, Tomer R, Chatterjee S, Singh KP, Singh SD (2016) Chemical and natural plant extract in ameliorating negative impact of tropospheric ozone on wheat crop: a case study in a part of semiarid north west India. Aerosol Air Qual Res 16(7):1742–1756
Didyk NP, Blum OB (2011) Natural antioxidants of plant origin against ozone damage of sensitive crops. Acta Physiol Plant 33(1):25–34
Evans LS, Ting IP (1974) Ozone sensitivity of leaves: relationship to leaf water content, gas transfer resistance, and anatomical characteristics. Am J Bot 61:592–597
Fatima S, Sehgal A, Mishra SK, Mina U, Goel V, Vijayan N, Tawale JS, Kothari R, Ahlawat A, Sharma C (2021) Particle composition and morphology over urban environment (New Delhi): plausible effects on wheat leaves. Environ Res 202:111552
Farmer AM (1993) The effect of dust on vegetation-a review. Environ Pollut 538(79):63–75
Feng Z, Kobayashi K, Ainsworth EA (2008) Impact of elevated ozone concentration on growth, physiology, and yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): a meta-analysis. Glob Change Biol 14(11):2696–2708
Feng Z, Calatayud V, Zhu J, Kobayashi K (2018) Ozone exposure- and flux-based response relationships with photosynthesis of winter wheat under fully open air condition. Sci Total Environ 619–620:1538–1544
Frei M, Wissuwa M, Pariasca-Tanaka J, Chen CP, Südekum KH, Kohno Y (2012) Leaf ascorbic acid level–is it really important for ozone tolerance in rice? Plant Physiol Biochem 59:63–70
Genga A, Baglivi F, Siciliano M, Siciliano T, Tepore M, Micocci G, Tortorella C, Aiello D (2012) SEM-EDS investigation on PM10 data collected in Central Italy: principal component analysis and hierarchical cluster analysis. Chem Cent J 6(2):S3
Ghude SD, Jain SL, Arya BC, Beig G, Ahammed YN, Kumar A, Tyagi B (2008) Ozone in ambient air at a tropical megacity, Delhi: characteristics, trends and cumulative ozone exposure indices. J Atmos Chem 60(3):237–252
Ghude SD, Jena C, Chate DM, Beig G, Pfister GG, Kumar R, Ramanathan V (2014) Reductions in India’s crop yield due to ozone. Geophys Res Lett 41(15):5685–5691
Grantz DA, Zinsmeister D, Burkhardt J (2018) Ambient aerosl increases minimum leaf conductance and alters the aperture–flux relationship as stomata respond to vapor pressure deficit (VPD). New Phytol 219(1):275–286
Jamir C (2011) Assessing Ozone impacts on arable crops in South Asia: identification of suitable risk assessment methods to improve crop biotechnology (Doctoral dissertation, University of York
Kameswaran S, Gunavathi Y, Gopi Krishna P (2019) Dust pollution and its influence on vegetation–a critical analysis. Life Science Informatics Publication, Pune
Lal DM, Ghude SD, Patil SD, Kulkarni SH, Jena C, Tiwari S, Srivastava MK (2012) Tropospheric ozone and aerosol long-term trends over the Indo-Gangetic Plain (IGP), India. Atmos Res 116:82–92
Liu YJ, Ding H (2008) Variation in air pollution tolerance index of plants near a steel factory: implications for landscape-plant species selection for industrial areas. WSEAS Trans Environ Dev 4:24–32
Maddison J, Lyons T, Plöchl M, Barnes J (2002) Hydroponically cultivated radish fed L-galactono-1, 4-lactone exhibit increased tolerance to ozone. Planta 214(3):383–391
Malik S, Ashraf M (2012) Exogenous application of ascorbic acid stimulates growth and photosynthesis of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under drought. Soil Environ 31(1):72
Mina U, Fuloria A, Aggarwal R (2016) Effect of ozone and antioxidants on wheat and its pathogen—Bipolaris sorokininana. Cereal Res Comm 44(4):594–604
Mina U, Chandrashekara T, Kumar SN, Meena M, Yadav S, Tiwari S, Singh D, Kumar P, Kumar R (2018) Impact of particulate matter on basmati rice varieties grown in Indo-Gangetic Plains of India: growth, biochemical, physiological and yield attributes. Atmos Environ 188:174–184
Mina U, Smiti K, Yadav P (2021) Thermotolerant wheat cultivar (Triticum aestivum L. var. WR544) response to ozone, EDU, and particulate matter interactive exposure. Environ Monit Assess 193(6):1–16
Nanos GD, Ilias IF (2007) Effects of inert dust on olive (Olea europaea L.) leaf physiological parameters. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 14(3):212–214
Rai PK (2016) Impacts of particulate matter pollution on plants: implications for environmental biomonitoring. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 129:120–136
Rai PK, Panda LL, Chutia BM, Singh MM (2013) Comparative assessment of air pollution tolerance index (APTI) in the industrial (Rourkela) and non-industrial area (Aizawl) of India: an eco-management approach. Afr J Environ Sci Technol 7(10):944–948
Rahul J, Jain MK (2014) An investigation in to the impact of particulate matter on vegetation along the National Highway: review. Res J Environ Sci 8:356–372
Roy SD, Beig G, Ghude SD (2009) Exposure-plant response of ambient ozone over the tropical Indian region. Atmos Chem Phys 9:5253–5260
Sarkar A, Agrawal SB (2010) Elevated ozone and two modern wheat cultivars: an assessment of dose dependent sensitivity with respect to growth, reproductive and yield parameters. Environ Exp Bot 69(3):328–337
Sarkar A, Agrawal SB (2012) Evaluating the response of two high yielding Indian rice cultivars against ambient and elevated levels of ozone by using open top chambers. J Environ Manage 95:S19–S24
Song Y, Maher BA, Li F, Wang X, Sun X, Zhang H (2015) Particulate matter deposited on leaf of five evergreen species in Beijing, China: source identification and size distribution. Atmos Environ 105:53–60
Tiwari S, Agrawal M, Marshall FM (2006) Evaluation of ambient air pollution impact on carrot plants at a suburban site using open-top chambers. Environ Monit Assess 119(1):15–30
Tiwari S, Chate DM, Pragya P, Ali K, Bisht DS (2012) Variations in mass of the PM10, PM2.5 and PM1 during the monsoon and the winter at New Delhi. Aerosol Air Qual Res 12(1):20–29
Tomer R, Bhatia A, Kumar V, Kumar A, Singh R, Singh B, Singh SD (2015) Impact of elevated ozone on growth, yield and nutritional quality of two wheat species in Northern India. Aerosol Air Qual Res 15(1):329–340
Turk R, Wirth V (1975) The pH dependence of SO2 damage to lichens. Oecologia 811(19):285–291
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (2016) Integrated science assessment for ozone and related photochemical oxidants [EPA Report - EPA/600/R-10/076F]. Research Triangle Park, NC
Zheng Y, Cheng D, Simmons M (2014) Ozone pollution effects on gas exchange, growth and biomass yield of salinity-treated winter wheat cultivars. Sci Total Environ 499:18–26
Acknowledgements
Financial support from the Indian Council for Agricultural Research to Indian Agriculture Research Institute for conducting the study and critical comments received from the reviewers for improving the manuscript are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mina, U., Kandpal, A., Bhatia, A. et al. Wheat Cultivar Growth, Biochemical, Physiological and Yield Attributes Response to Combined Exposure to Tropospheric Ozone, Particulate Matter Deposition and Ascorbic Acid Application. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 107, 938–945 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03373-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03373-7