Abstract
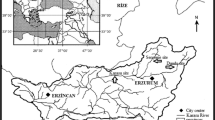
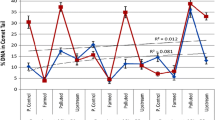
This study evaluated the incidence of nuclear abnormalities (NA) in four fish species from an impacted river in Northeastern Brazil, characterized by accumulation of heavy metals and organic sewage. Two carnivores (Serrasalmus brandtii and Hoplias malabaricus) and two omnivore species (Oreochromis niloticus and Geophagus brasiliensis), used as food sources by local populations, were collected during the dry and the rainy season along Contas River basin. Nuclear abnormalities (bulbs, binuclei, lobes, micronuclei, notches, and vacuoles) were reported in all fish samples, with high occurrence in S. brandtii and H. malabaricus, species commonly found in local fish markets. This result agrees with previous analyses of accumulation of trace metals in both species, suggesting an association of genotoxic effects and biomagnification. Moreover, native specimens collected near urban areas presented higher frequencies of NA while O. niloticus seems to be more tolerant to environmental contamination. Therefore, effective policies are required to reduce the contamination of Contas River, since pollution by xenobiotics are potential threats to both local biodiversity and human population.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arkhipchuk VV, Garanko NN (2005) Using the nucleolar biomarker and the micronucleus test on in vivo fish fin cells. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 62:42–52
Ayllón F, Garcia-Vazquez E (2001) Micronuclei and other nuclear lesions as genotoxicity indicators in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 49:221–225
Ayllón F, Suciu R, Gephard S, Juanes F, Garcia-Vazquez E (2000) Conventional armament wastes induce micronuclei in wild brown trout Salmo trutta. Mutat Res 470:169–176
Ayres M, Ayres Júnior M, Ayres DL, Santos AA (2007) BIOESTAT –Aplicações estatísticas nas áreas das ciências bio-médicas. Ong Mamiraua, Belém
Barbosa JS, Cabral TM, Ferreira DN, Agnez-Lima LF, Medeiros SRB (2010) Genotoxicity assessment in aquatic environment impacted by the presence of heavy metals. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:320–325
Baršienė J, Butrimavičienė L, Michailovas A, Grygiel W (2015) Assessing the environmental genotoxicity risk in the Baltic Sea: frequencies of nuclear buds in blood erythrocytes of three native fish species. Environ Monit Assess 187:4078. doi:10.1007/s10661-014-4078-x
Benicá C, Ramsdorf W, Vicari T, Ribeiro CAO, Almeida MI, Assis HCS, Cestari MM (2012) Chronic genetic damages in Geophagus brasiliensis exposed to anthropic impact in Estuarine Lakes at Santa Catarina Coast-Southern of Brazil. Environ Monit Assess 184:2045–2056
Blessing JJ, Marshall JC, Balcombe SR (2010) Humane killing of fishes for scientific research: a comparison of two methods. J Fish Biol 76:2571–2577
Carvalho LN, Arruda R, Raizer J, Del-Claro K (2007) Feeding habits and habitat use of three sympatric piranha species in the Pantanal wetland of Brazil. Ichthyol Explor Freshwat 18:109–116
Çavas T, Ergene-Gozukara S (2003) Micronuclei, nuclear lesions and interphase silver-stained nucleolar organizer regions (AgNORs) as cyto-genotoxicity indicators in Oreochromis niloticus exposed to textile mill effluent. Mutat Res 538:81–91
Correia LO, Siqueira S Jr., Carneiro PLS, Bezerra MA (2014) Evaluation of the use of Leptodactylus ocellatus (Anura: Leptodactylidae) frog tissues as bioindicator of metal contamination in Contas River, Northeastern Brazil. An Acad Bras Ciênc 86:1549–1561
Duarte ID, Dias MC, David JAO, Matsumoto ST (2012) A qualidade da água da Lagoa Jacuném (Espírito Santo, Brasil) em relação a aspectos genotóxicos e mutagênicos, mensurados respectivamente pelo ensaio do cometa e teste do micronúcleo em peixes da espécie Oreochromis niloticus. Rev Bras Biocienc 10:211–219
Ergene S, Çavas T, Çelik A, Köleli N, Aymak C (2007) Evaluation of river water genotoxicity Using the piscine micronucleus test. Environ Mol Mutagen 48:421–429
Grisolia CK, Rivero CLG, Starling FLRM, Silva ICR, Barbosa AC, Dorea JG (2009) Profile of micronucleus frequencies and DNA damage in different species of fish in a eutrophic tropical lake. Genet Mol Biol 32:138–143
Heddle JA (1973) A rapid in vivo test for chromosomal damage. Mutat Res 18:187–190
IBGE—Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (2010) Censo Demográfico 2010. http://censo2010.ibge.gov.br/. Accessed Mar 2015
Jesus TB, Carvalho CEV, Ferreira AG, Siqueira EM, Machado ALS (2012) Mercury distribution in muscular tissues of a tropical carnivorous fish (Hoplias malabaricus) from four lakes in the North of Rio de Janeiro State, SE Brazil. J Braz Soc Ecotoxicol 7:37–42
Jesus IS, Medeiros RLS, Cestari MM, Bezerra MA, Affonso PRAM (2014) Analysis of metal contamination and bioindicator potential of predatory fish species along Contas River basin in northeastern Brazil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 52:551–556
Korfali SI, Davies BE (2004) Speciation of metals in sediment and water in a river underlain by limestone: role of carbonate species for purification capacity of rivers. Adv Environ Res 8:599–612
Lemos CT, Rödel PM, Terra NR, Oliveira NCD, Erdtmann B (2007) River water genotoxicity evaluation using micronucleus assay in fish erythrocytes. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 66:391–401
Loureiro VE, Hahn NS (1996) Dieta e atividade alimentar da traíra Hoplias malabaricus (BLOCH, 1794) (Osteichthyes, Erythrinidae), nos primeiros anos de formação do reservatório de Segredo—PR. Acta Limnol Bras 8:195–205
Osman A, Ali E, Hashem M, Mostafa M, Mekkawy I (2010) Genotoxicity of two pathogenic strains of zoosporic fungi (Achlyak lebsiana and Aphanomyces laevis) on erythrocytes of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus niloticus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:24–31
Palacio-Betancur I, Palacio-Baena JA, Camargo-Guerrero M (2009) Micronuclei test application to wild tropical ichthyic species common in two lentic environments of the low zones in Colombia. Actual Biol 31:67–77
Pantaleão SM, Alcântara AV, Alves JPH, Spanó MA (2006) The piscine micronucleus test to assess the impact of pollution on the Japaratuba River in Brazil. Environ Mol Mutagen 47:219–224
Rivero CLG, Barbosa AC, Ferreira MFN, Dorea JG, Grisolia CK (2008) Evaluation of genotoxicity and effects on reproduction of nonylphenol in Oreochromis niloticus (Pisces: Cichlidae). Ecotoxicology 17:732–737
Rocha PS, Luvizotto GL, Kosmehl T, Böttcher M, Storch V, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2009) Sediment genotoxicity in the Tietê River (São Paulo, Brazil): in vitro comet assay versus in situ micronucleus assay studies. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:1842–1848
Sá TRBT, Sá MT (2004) Os processos espaciais presentes no espaço urbano de Jequié—Bahia. Estud Geogr Rev Eletron Geogr 2:1–13
Santos JS, Santos MJS, Santos MLP (2012) Influence of the rainfall regime on the mobility of Zn, Cd, Ni, Cu, Mn and Fe in the surface sediments of the Contas River located in the Brazilian semi-arid region. J Braz Chem Soc 23:718–726
Schmid W (1975) The micronucleus test. Mutat Res 31:9–15
Silva GS, Neto FF, Assis HCS, Bastos WR, Ribeiro CAO (2012) Potential risks of natural mercury levels to wild predator fish in an Amazon reservoir. Environ Monit Assess 184:4815–4827
SRH—Secretaria de Recursos Hídricos (2007) Resolução nº 20, de 23 de agosto de 2007. http://www.semarh.ba.gov.br. Accessed July 2012
Udroiu I (2006) The micronucleus test in piscine erythrocytes. Aquat Toxicol 79:201–204
Vicari T, Ferraro MVM, Ramsdorf WA, Mela M, Ribeiro CAO, Cestari MM (2012) Genotoxic evaluation of different doses of methylmercury (CH3Hg+) in Hoplias malabaricus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 82:47–55
Acknowledgments
The authors thank UESB for the financial support, ICMBio/SISBIO for authorizing fish collection (License Number 26752-1) and local fisherman Valdemir for the assistance in collecting samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Jesus, I.S., Cestari, M.M., Bezerra, M.A. et al. Genotoxicity Effects in Freshwater Fish from a Brazilian Impacted River. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 96, 490–495 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1755-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1755-1