Abstract
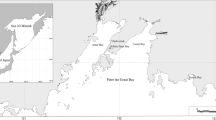
We examined the effects of environmental remediation on the heavy metal concentration and lipid peroxidation activity in the digestive gland and gills of the marine mussel Crenomytilus grayanus. Changes in heavy metal concentrations and lipid peroxidation biomarkers in the tissues of mussels collected at a contaminated site were compared with those obtained from a reference site. Prior to remediation the concentration of Pb, Cu, Cd, Fe and Zn and the levels of malondialdehyde, conjugated dienes and lipofuscin in mussels collected from the contaminated site were significantly increased compared with those obtained from the reference site. Three years after remediation, these parameters did not significantly exceed the reference site parameters, except Pb, whose concentration, though markedly decreased, yet was much higher than in tissues of mussels from the reference site.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akberali HB, Marriott KRM, Trueman ER (1977) Calcium utilisation during anaerobiosis induced by osmotic shock in a bivalve mollusc. Nature 266:852–853
Banni M, Bouraoui Z, Ghedira J, Clearandeau C, Jebali J, Boussetta H (2009) Seasonal variation of oxidative stress biomarkers in clams Ruditapes decussatus sampled from Tunisian coastal areas. Environ Monit Assess 55:119–128
Belcheva NN, Zakhartsev MV, Dovzhenco NV, Zhukovskaya AF, Kavun VY, Chelomin VP (2011) Anthropogenic pollution stimulates oxidative stress in soft tissues of mussel Crenomytilus grayanus. Ocean Sci J 46:85–94
Bourgoin BP (1990) Mytilus edulis shell as a bioindicator of lead pollution: considerations on bioavailability and variability. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 61:253–262
Buege JA, Aust SD (1978) Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 52:302–310
CCME (2001) Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment. Canadian sediment quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life: summary tables. https://www.elaw.org/system/files/sediment_summary_table.pdf. Accessed 20 July 2013
Depledge MH, Aagaard A, Györkös P (1995) Assessment of trace metal toxicity using molecular, physiological and behavioural biomarkers. Mar Pollut Bull 31:19–27
Di Giulio RT, Washburn PC, Wenning RJ, Winston GW, Jewell CS (1989) Biochemical responses in aquatic animals: a review of determinants of oxidative stress. Environ Toxicol Chem 8:1103–1123
Dillard CJ, Tappel AL (1984) Fluorescent damage products of lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 105:337–341
Dovzhenko NV, Kurilenko AV, Belcheva NN, Chelomin VP (2005) Cadmium-induced oxidative stress in the bivalve mollusk Modiolus modiolus. Russ J Mar Biol 31:309–313
Fisher NS, Jean-Louis T, Fowler SW, Wang WX (1996) Accumulation and retention of metals in mussels from food and water: a comparison under field and laboratory conditions. Environ Sci Technol 30:3232–3242
Folch J, Lees M, Stanley J (1957) A simple method for isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
Frazier JM (1976) The dynamics of metals in the American oyster, Crassostrea virginica. 11. Environmental effects. Chesap Sci 17:188–197
Kavun VY, Shulkin VM (2005) Changes in the microelement composition in organs and tissues of the bivalve Crenomytilus grayanus acclimatized in a biotope with long-term heavy metal contamination. Russ J Mar Biol 31:109–114
Koukouzika N, Raftopoulou EK, Dimitriadis VK (2009) Seasonal differences of lisosomal, lipid and lipofuscin parameters in the digestive gland of the mussel Mutilus galloprovincialis. J Molluscan Stud 75:261–267
Kovekovdova LT, Simokon MV (2004) Tendencies of change in the chemoecological situation in coastal area of Primorye. Toxic elements in bottom sediments and aquatic organisms. Izv TINRO 137:310–320 (In Russian)
Kovekovdova LT, Kiky DP, Blokhin MG (2012) Heavy metals in bottom sediments of Peter the Great Bay, Sea of Japan. In: Khristoforova NK (ed) Sovremennoe ekologicheskoe sostoyanie zaliva Petra Velikogo Yaponskogo morya (Current Ecological State of Peter the Great Bay, Sea of Japan). Far Eastern Federal University Press, Vladivostok, pp 312–333 (In Russian)
Livingstone DR (2001) Contaminant-stimulated reactive oxygen species production and oxidative damage in aquatic organisms. Mar Pollut Bull 42:656–666
Markwell M, Haas S, Bieber L, Tolbert N (1978) A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem 87:206–210
PHEMA (2000, 2002, 2011, 2012, 2014) Yearbook on sea water quality, evaluated from hydrochemical parameters (Sea of Japan) for 1999, 2001, 2010, 2011, 2013. Primorye Hydrometeorological and environmental monitoring agency, Vladivostok, 2000, 2002, 2011, 2012, 2014 (In Russian)
Podorvanova NF, Ivashinnikova TS, Petrenko VS, Khomichuk LS (1989) Osnovnye cherty gidrokhimii zaligva Petra Velikogo, Yaponskoe more [The main hydrochemical features of peter the great bay (the Japan Sea)]. Far East Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Vladivostok (In Russian)
Rai L, Gaur JP, Kumar HD (1981) Physiology and heavy metal pollution. Biol Rev 56:99–151
Regoli F (2000) Total oxyradical scavenging capacity (TOSC) in polluted and translocated mussels: a predictive biomarker of oxidative stress. Aquat Toxicol 50:351–361
Sericano JL, Wade TL, Brooks JM (1996) Accumulation and depuration of organic contaminants by the American oyster (Crassostrea virginica). Sci Total Environ 179:149–160
Sevastyanov AV, Lishavskaya TS, Chatkina TV (2014) Monitoring of self-purification of seawater and bottom sediment of Ussuriysky Bay in the area of the former municipal dumping site (Gornostai Bay), Trudy DVNIGMI (Transactions of Far Eastern Regional Hydrometeorological Research Institute), vol. 155. Dalnauka Press, Vladivostok, pp. 160–175 (In Russian)
Shulkin VM (2004) Metally v ekosistemakh morskikh melkovodii (Heavy metals in marine shallow-water ecosystems). Dalnauka, Vladivostok (In Russian)
Sturesson U (1976) Lead enrichment in shells of Mytilus edulis. AMBIO J Hum Environ 5:253–256
Tkalin AV, Lishavskaya TS, Shulkin VM (1998) Radionuclides and trace metals in mussels and bottom sediments around Vladivostok, Russia. Mar Pollut Bull 36:511–554
Tkalin AV, Samsonov DP, Lishavskaya TS, Chernik GV (2000) New data on organochlorine distributions in the marine environment near Vladivostok. Mar Pollut Bull 40:879–881
Valavanidis A, Vlahogianni T, Dassenakis M, Scoullos M (2006) Molecular biomarkers of oxidative stress in aquatic organisms in relation to toxic environmental pollutants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 64:178–189
Viarengo A, Canesi L, Pertica M, Poli G, Moore MN, Orunesu M (1990) Heavy metal effects on lipid peroxidation in the tissues of Mytilus galloprovincialis Lam. Comp Biochem Physiol C 97:37–42
Yutsuk AV (2010) Water area pollution monitoring of the Gulf of Ussuriysky in the zone of influence city dump of Vladivostok. In: Materials all-russian scientific youth conference-school “environmental problems of marine shelf”. Far Eastern Federal University Press, Vladivostok, pp 201–203 (In Russian)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belcheva, N., Istomina, A., Dovzhenko, N. et al. Using Heavy Metal Content and Lipid Peroxidation Indicators in the Tissues of the Mussel Crenomytilus grayanus for Pollution Assessment After Marine Environmental Remediation. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 95, 481–487 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1624-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1624-3