Abstract
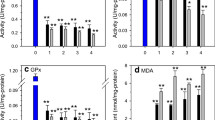
Cadmium-induced oxidative stress in the bivalve Modiolus modiolus is studied from the standpoint of the universality of the mechanism of free-radical oxidation. The kinetics of cadmium accumulation by the bivalve was revealed in a laboratory experiment. The gills accumulated higher Cd levels than the digestive gland. In the process of cadmium accumulation, there was an increase in lipid peroxidation products (malondialdehyde and lipofuscin) and a reduction in the total oxiradical scavenging capacity (TOSC). Cadmium induces oxidative stress in molluscan tissues through damage to the antioxidation system. Thus, TOSC can provide a useful biochemical indicator of early pathological changes in the cell or the organism, as well as of the environmental effects of heavy metal pollution.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Dovzhenko, N.V., Kavun V.Ya., Bel'cheva, N.N., and Chelomin, V.P., Biochemical Parameters of Oxidative Stress as Indicators of Anthropogenic Pollution of Water Ecosystems, Sb. statei konferentsii molodyh uchenyh TOI DVO RAN (Coll. Pap., Conf. Young Scientists, Pacific Institute of Oceanology, FEB RAS), Vladivostok: Dal'nauka, 2002, pp. 290–296.
Chelomin, V.P., Belcheva, N.N., and Zakhartsev, M.V., Biochemical Mechanisms of Adaptation to Cadmium and Copper Ions in the Mussel Mytilus trossulus, Biol. Morya, 1998, vol. 24, no.5, pp. 319–325.
Buege, J.A., and Aust, S.D., Microsomal Lipid Peroxidation, Methods in enzymology, New York: Academic Press, 1978, pp. 302–310.
Canesi, L., Ciacci, C., Piccoli, G., et al., In vitro and in vivo Effects of Heavy Metals on Mussel Digestive Gland Hexokinase Activity: The Role of Glutathione, Comp. Biochem. Physiol., ser. C, 1998, vol. 120, pp. 261–268.
Chelomin, V.P., Bobkova, E.A., Luk'yanova, O.N., and Chekmasova, N.M. Cadmium-Induced Alterations in Essential Trace Element Homeostasis in the Tissues of Scallop Mizuhopecten yessoensis, Comp. Biochem. Physiol., ser. C, 1995, vol. 110, no.3, pp. 329–335.
Depledge, M.N., Aagaard, A., and Gyorkos P., Assessment of Trace Metal Toxicity Using Molecular, Physiological and Behavioural Biomarkers, Mar. Biol. Bull., 1995, vol. 31, pp. 19–27.
Frenzilli, G., Nigro, M., Scarcelli, V.,et al., DNA Integrity and Total Oxyradical Scavenging Capacity in the Mediterranean Mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis: A Field Study in a Highly Eutrophicated Coastal Lagoon, Aquat. Toxicol., 2001, vol. 53, pp. 19–32.
Greenberg, C.S. and Gaddock, P.R., Rapid Single-Step Membrane Protein Assay, Clin. Chem., 1982, vol. 28, no.7, pp. 1725–1726.
Kiningham, K. and Kasarskis, E., Antioxidant Function of Metallothioneins, J. Trace Elem. Exp. Med., 1998, vol. 11, pp. 219–226.
Klein, D., Sato, S., and Summer, K.H., Quantification of Oxidized Metallothionein in Biological Material by a Cd Saturation method, Anal. Biochem., 1994, vol. 221, pp. 405–409.
Nasci, C., Da Ros L., Campesan, G., et al., Clam Transplantation and Stress-Related Biomarkers as Useful Tools for Assessing Water Quality in Coastal Environments, Mar. Pollut. Bull., 1999, vol. 39, nos.1–12, pp. 255–260.
Regoli, F., Total Oxyradical Scavenging Capacity (TOSC) in Polluted and Translocated Mussels: A Predictive Biomarker of Oxidative Stress, Aquat. Toxicol., 2000, vol. 50, pp. 351–361.
Regoli, F. and Principato, G., Glutathione, Glutathione-Depended and Antioxidant Enzymes in Mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis, Exposed to Metals under Field and Laboratory Conditions: Implications for the Use of Biochemical Biomarkers, Aquat. Toxicol., 1995, vol. 31, pp. 143–164.
Regoli, F. and Winston, G.W., Applications of a New Method for Measuring the Total Oxyradical Scavenging Capacity in Marine Invertebrates, Mar. Environ. Res., 1998, vol. 46, nos.1–5, pp. 439–442.
Regoli, F., Winston, G.W., Mastrangelo, V., et al., Total Oxyradical Scavenging Capacity in Mussel Mytilus sp. as a New Index of Biological Resistance to Oxidative Stress, Chemosphere, 1998, vol. 37, nos.14–15, pp. 2773–2783.
Regoli, F., Nigro, M., Bompadre, S., and Winston, G.W., Total Oxidant Scavenging Capacity (TOSC) of Microsomal and Cytosolic Fraction from Antarctic, Arctic and Mediterranean Scallops: Differentiation Between Three Potent Oxidants, Aquat. Toxicol., 2000, vol. 49, pp. 13–25.
Regoli, F., Gorbi S., Frenzilli, G., et al., Oxidative Stress in Ecotoxicology: From the Analysis of Individual Antioxidants to a More Integrated Approach, Mar. Environ. Res., 2002, vol. 54, pp. 419–423.
Shen, Y., Sangiah, S. Na+, K+-ATPase, Glutathione, and Hydroxyl Free Radicals in Cadmium Chloride-Induced Testicular Toxicity in Mice, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 1995, vol. 29, pp. 174–179.
Shimasaki, H., Hirai, N., and Ueta, N., Comparison of Fluorescence Characteristics of Products of Peroxidation of Membrane Phospholipids with Those of Products Derived from Reaction of Malonaldehyde with Glycine as a Model of Lipofuscin Fluorescent Substances, Biochem., 1988, vol. 104, pp. 761–766.
Sies, H., Oxidative Stress: Oxidants and Antioxidants, London: Academic Press, 1991.
Stohs, S.J. and Bagchi, D., Oxidative Mechanisms in the Toxicity of Metal Ions, Free Rad. Biol. Med., 1995, vol. 18, no.2, pp. 312–336.
Storey, K.B., Oxidative Stress: Animal Adaptations in Nature, Brazil. J. Med. Biol. Res., 1996, vol. 29, pp. 1715–1733.
Torres, M.A., Testa, C.P., Gaspari, C., et al. Oxidative Stress in Mussel Mytella guyanensis from Polluted Mangroves on Santa Catarina Island, Brazil, Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2002, vol. 44, pp. 923–932.
Viarengo, A. Heavy Metals in Marine Invertebrates: Mechanisms of Regulation and Toxicity at the Cellular Level, CRC Crit. Rev. Aquat. Sci., 1989, vol. 1, pp. 295–317.
Viarengo, A., Burlando, B., Ceratto, N., and Panfoli, I., Antioxidant Role of Metallothioneins: A Comparative Overview, Cell. Mol. Biol., 2000, vol. 46, no.2, pp. 407–417.
Wayner, D.D. M., Burton, G.W., and Ingold, K.U., The Antioxidant Efficiency of Vitamin E is Concentration-Dependent, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1986, vol. 884, pp. 119–123.
Winston, G.W., Regoli, F., Dugas, A.J. Jr., et al., A Rapid Gas Chromatographic Assay for Determining Oxyradical Scavenging Capacity of Antioxidants and Biological Fluids, Free Rad. Biol. Med., 1998, vol. 24, no.3, pp. 480–493.
Wright, D.A., Trace Metal and Major Ion Interactions in Aquatic Animals, Mar. Pollut. Bull., 1995, vol. 31, nos.1–3, pp. 8–18.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text Copyright © 2005 by Biologiya Morya, Dovzhenko, Kurilenko, Bel'cheva, Chelomin.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dovzhenko, N.V., Kurilenko, A.V., Bel'cheva, N.N. et al. Cadmium-Induced Oxidative Stress in the Bivalve Mollusk Modiolus modiolus . Russ J Mar Biol 31, 309–313 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11179-005-0093-7
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11179-005-0093-7