Abstract
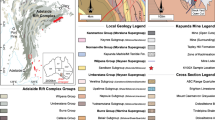
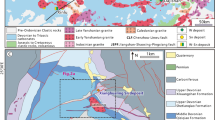
The Huangshui’an deposit located in East Qinling (China) is an unusual case of a Si-rich carbonatite hosting economic Mo and minor Pb and REE mineralization. The role of mantle-sourced carbonatite melts and fluids in the formation of the Mo mineralization remains poorly understood. Our integrated study based on field geology, petrography, microthermometry, and LA-ICP-MS analysis of single fluid inclusions, and noble gas isotopes of pyrite permits to reconstruct the source characteristics, the magmatic-hydrothermal evolution of the carbonatitic fluids, and their controls on Mo mineralization. Fluid inclusions hosted in calcite in the carbonatite dikes have the highest concentrations of Mo (9.9–62 ppm), Ce (820–9700 ppm), Pb (1800–19500 ppm), and Zn (570–5800 ppm) and represent the least modified hydrothermal fluid derived from the carbonatite melt. Fluid inclusions hosted in calcite (Cal) and quartz (Qz2 and Qz3) of the stage I carbonatite dikes have different metal concentrations, suggesting that they formed from two distinct end member fluids. The FIA in calcite represent fluid A evolved from carbonatite melt with relatively high-ore metal concentrations, and those in quartz characterize fluid B having a crustal signature due to metasomatic reactions with the wall rocks. The FIA in quartz (Qz1) within the altered wall rock have overlapping elemental concentrations with those of massive quartz (Qz2) and vuggy quartz (Qz3) in carbonatite. This suggests that the volumetrically significant quartz in the Huangshui’an carbonatite has been formed by the introduction of Si by fluid B. The positive correlations between Rb, B, Al, Cl, and Sr in stage II fluid inclusions in late fluorite + quartz + calcite veins indicate that this late mineralization formed from the mixing of primary hydrothermal fluid B with meteoric water. The He–Ar isotope data, in combination with available C–O–Sr–Nd–Pb isotope data, constrain the carbonatite source as an enriched mantle source modified by contributions from crustal material which was probably the fertile lower crust in the region. This distinct source facilitated the enrichment in Mo, REE, and Pb in the primary carbonatite magma. The carbonatite magmatism and Mo mineralization at 209.5–207 Ma occurred in the regional-scale extensional setting at the postcollision stage of the Qinling Orogenic Belt.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amsellem E, Moynier F, Bertrand H, Bouyon A, Mata J, Tappe S, Day JM (2020) Calcium isotopic evidence for the mantle sources of carbonatites. Sci Adv 5:eaba3269
Anenburg M (2019) Molybdenum and rhenium disulfide synthesis via high-pressure carbonate melt. CrystEngComm 21:4513–4518
Anenburg M, Mavrogenes JA (2018) Carbonatitic versus hydrothermal origin for fluorapatite REE-Th deposits: experimental study of REE transport and crustal "antiskarn" metasomatism. Am J Sci 318:335–366
Anenburg M, Mavrogenes JA, Bennett VC (2020a) The fluorapatite P–REE–Th vein deposit at Nolans Bore: genesis by carbonatite metasomatism. J Petrol 61. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egaa003
Anenburg M, Mavrogenes JA, Frigo C, Wall F (2020b) Rare earth element mobility in and around carbonatites controlled by sodium, potassium, and silica. Sci Adv 6. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abb6570
Aquilina L, Pauwels H, Genter A, Fouillac C (1997) Water-rock interaction processes in the Triassic sandstone and the granitic basement of the Rhine Graben: geochemical investigation of a geothermal reservoir. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 61:4281–4295
Bai T, Chen W, Jiang SY (2019) Evolution of the carbonatite Mo-HREE deposits in the Lesser Qinling Orogen: insights from in situ geochemical investigation of calcite and sulfate. Ore Geol Rev 113:103069
Bakker RJ (1997) Clathrates: Computer programs to calculate fluid inclusion V-X properties using clathrate melting temperatures. Comput Geosci 23:1–18
Bakker RJ (1999) Optimal interpretation of microthermometrical data from fluid inclusions: thermodynamic modelling and computer programming. Ruprecht-Karls-University, Habilitation
Bakker RJ (2003) Package FLUIDS 1. Computer programs for analysis of fluid inclusion data and for modelling bulk fluid properties. Chem Geol 194:3–23
Ballentine CJ, Burgess R, Marty B (2002) Tracing fluid origin, transport and interaction in the crust. Rev Mineral Geochem 47:539–614
Bell K, Tilton GR (2001) Nd, Pb and Sr isotopic compositions of East African carbonatites: evidence for mantle mixing and plume inhomogeneity. J Petrol 42:1927–1945
Bühn B, Rankin AH (1999) Composition of natural, volatile-rich Na–Ca–REE−Sr carbonatitic fluids trapped in fluid inclusions. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63:3781–3797
Cao J (2019) Mineralization of the Huangshui’an carbonatite Mo deposit in East Qinling. PhD dissertation, China University of Geosciences, Beijing pp. 1-113 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Cao J, Ye HS, Li H, Li Z, Zhang XK, He W, Li C (2014) Geological characteristics and molybdenite Re-Os isotopic dating of Huangshuian carbonatite vein-type Mo(Pb) deposit in Songxian County, Henan Province. Mineral Deposita 33:53–69 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Cao HW, Zhang ST, Santosh M, Zheng L, Tang L, Li D, Zhang X, Zhang YH (2015) The Luanchuan Mo–W–Pb–Zn–Ag magmatic–hydrothermal system in the East Qinling metallogenic belt, China: constrains on metallogenesis from C–H–O–S–Pb isotope compositions and Rb–Sr isochron ages. J Asian Earth Sci 111:751–780
Chaussidon M, Lorand JP (1990) Sulphur isotope composition of orogenic spinel lherzolite massifs from Ariege (North-Eastern Pyrenees, France): an ion microprobe study. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 54:2835–2846
Chen YJ, Santosh M (2014) Triassic tectonics and mineral systems in the Qinling Orogen, central China. Geol J 49:338–358
Chen YJ, Pirajno F, Qi JP, Li J, Wang HH (2006) Ore geology, fluid geochemistry and genesis of the Shanggong gold deposit, eastern Qinling Orogen, China. Resour Geol 56:99–116
Chen YJ, Pirajno F, Qi JP (2008) The Shanggong gold deposit, Eastern Qinling Orogen, China: isotope geochemistry and implications for ore genesis. J Asian Earth Sci 33:252–266
Çimen O, Kuebler C, Simonetti SS, Corcoran L, Mitchell R, Simonetti A (2019) Combined boron, radiogenic (Nd, Pb, Sr), stable (C, O) isotopic and geochemical investigations of carbonatites from the Blue River Region, British Columbia (Canada): implications for mantle sources and recycling of crustal carbon. Chem Geol 529:119240
Dong YP, Santosh M (2016) Tectonic architecture and multiple orogeny of the Qinling Orogenic Belt, Central China. Gondwana Res 29:1–40
Dong YP, Yang Z, Liu X, Zhang X, He D, Li W, Zhang F, Sun S, Zhang H, Zhang G (2014) Neoproterozoic amalgamation of the Northern Qinling terrain to the North China Craton: constraints from geochronology and geochemistry of the Kuanping ophiolite. Precambrian Res 255:77–95
Dong YP, Yang Z, Liu X, Sun S, Li W, Cheng B, Zhang F, Zhang X, He D, Zhang G (2016) Mesozoic intracontinental orogeny in the Qinling Mountains, central China. Gondwana Res 30:144–158
Feng JY, Tang L, Santosh M, Zhang ST, Sheng YM, Hu XK, Wang L (2021) Genesis of hydrothermal gold mineralization in the Qianhe deposit, central China: constraints from in situ sulfur isotope and trace elements of pyrite. Geol J, https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.4099
Fusswinkel T, Wagner T, Wenzel T, Wälle M, Lorenz J (2014) Red bed and basement sourced fluids recorded in hydrothermal Mn–Fe–As veins, Sailauf (Germany): a LA-ICPMS fluid inclusion study. Chem Geol 363:22–39
Fusswinkel T, Wagner T, Sakellaris G (2017) Fluid evolution of the Neoarchean Pampalo orogenic gold deposit (E Finland): constraints from LA-ICPMS fluid inclusion microanalysis. Chem Geol 450:96–121
Fusswinkel T, Giehl C, Beermann O, Fredriksson JR, Garbe-Schönberg D, Scholten L, Wagner T (2018) Combined LA-ICP-MS microanalysis of iodine, bromine and chlorine in fluid inclusions. J Anal At Spectrom 33:768–783
Gao S, Luo TC, Zhang BR, Zhang HF, Han YW, Zhao ZD, Hu YK (1998a) Chemical composition of the continental crust as revealed by studies in East China. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 62:1959–1975
Gao S, Zhang BR, Jin ZM, Kern H, Luo TC, Zhao ZD (1998b) How mafic is the lower continental crust? Earth Planet Sci Lett 161:101–117
Guillong M, Pettke T (2012) Depth dependent element ratios in fluid inclusion analysis by laser ablation ICP-MS. J Anal At Spectrom 27:505–508
Guillong M, Meier DL, Allan MM, Heinrich CA, Yardley BW (2008) Appendix A6: SILLS: a MATLAB-based program for the reduction of laser ablation ICP-MS data of homogeneous materials and inclusions. Mineral Assoc Canada Short Course 40:328–333
Günther D, Audétat A, Frischknecht R, Heinrich CA (1998) Quantitative analysis of major, minor and trace elements in fluid inclusions using laser ablation–inductively coupled plasmamass spectrometry. J Anal At Spectrom 13:263–270
Hall DL, Sterner SM, Bodnar RJ (1988) Freezing point depression of NaCl-KCl-H2O solutions. Econ Geol 83:197–202
He H, Zhu R, Saxton J (2011) Noble gas isotopes in corundum and peridotite xenoliths from the eastern North China Craton: implication for comprehensive refertilization of lithospheric mantle. Phys Earth Planet Inter 189:185–191
He X, Wang J, Wang C, Carranza EJM, Chen L, Wu B (2016) Petrogenesis, zircon U–Pb age, and geochemistry of the A-type Mogou syenite, western Henan Province: implications for Mesozoic tectono-magmatic evolution of the Qinling Orogen. J Earth Syst Sci 125:585–603
Horton F, Nielsen S, Shu Y, Gagnon A, Blusztajn J (2021) Thallium isotopes reveal brine activity during carbonatite magmatism. Geochem Geophys Geosyst, e2020GC009472
Hou ZQ, Tian S, Yuan Z, Xie Y, Yin S, Yi L, Fei H, Yang Z (2006) The Himalayan collision zone carbonatites in western Sichuan, SW China: petrogenesis, mantle source and tectonic implication. Earth Planet Sci Lett 244:234–250
Hou ZQ, Liu Y, Tian S, Yang Z, Xie Y (2015) Formation of carbonatite-related giant rare-earth-element deposits by the recycling of marine sediments. Sci Rep 5:10231
Hu XK, Tang L, Zhang ST, Santosh M, Spencer CJ, Zhao Y, Cao HW, Pei QM (2019) In situ trace element and sulfur isotope of pyrite constrain ore genesis in the Shapoling molybdenum deposit, East Qinling Orogen, China. Ore Geol Rev 105:123–136
Hu XK, Tang L, Zhang ST, Santosh M, Sun L, Spencer CJ, Jeon H, Zhao Y, Huang DF (2020) Geochemistry, zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf-O isotopes of the Late Mesozoic granitoids from the Xiong'ershan area, East Qinling Orogen, China: implications for petrogenesis and molybdenum metallogeny. Ore Geol Rev 124:103653
Huang DH, Wu CY, Du AD, He HL (1995) Re-Os Isotope ages of molybdenum deposits in East Qinling and their significance. Chin J Geochem 14:313–322 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Huang DH, Hou ZQ, Yang ZM, Li ZQ, Xu DX (2009) Geological and geochemical characteristics, metallogenetic mechanism and tectonic setting of carbonatite dyke type Mo (Pb) deposits in East Qinling molybdenum ore belt. Acta Geol Sin 83:1968–1984 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Huang XL, Wilde SA, Yang QJ, Zhong JW (2012) Geochronology and petrogenesis of gray gneisses from the Taihua Complex at Xiong'er in the southern segment of the Trans-North China Orogen: implications for tectonic transformation in the Early Paleoproterozoic. Lithos 134:236–252
Ionov DA, Qi YH, Kang JT, Golovin AV, Oleinikov OB, Zheng W, Anbar A, Zhang Z, Huang F (2019) Calcium isotopic signatures of carbonatite and silicate metasomatism, melt percolation and crustal recycling in the lithospheric mantle. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 248:1–13
Kynicky J, Smith MP, Xu C (2012) Diversity of rare earth deposits: the key example of China. Elements 8:361–367
Li N, Chen YJ, Santosh M, Pirajno F (2015) Compositional polarity of Triassic granitoids in the Qinling Orogen, China: implication for termination of the northernmost Paleo-Tethys. Gondwana Res 27:244–257
Liu Y, Hou Z (2017) A synthesis of mineralization styles with an integrated genetic model of carbonatite-syenite-hosted REE deposits in the Cenozoic Mianning-Dechang REE metallogenic belt, the eastern Tibetan Plateau, southwestern China. J Asian Earth Sci 137:35–79
Liu Y, Chakhmouradian AR, Hou Z, Song W, Kynický J (2019) Development of REE mineralization in the giant Maoniuping deposit (Sichuan, China): insights from mineralogy, fluid inclusions, and trace-element geochemistry. Mineral Deposita 54:701–718
Mamyrin BA, Tolstikhin IN (1984) Helium Isotopes in Nature. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1–273
Mao JW, Xie G, Pirajno F, Ye H, Wang Y, Li Y, Xiang J, Zhao H (2010) Late Jurassic–Early Cretaceous granitoid magmatism in Eastern Qinling, central-eastern China: SHRIMP zircon U–Pb ages and tectonic implications. Aust J Earth Sci 57:51–78
Mark DF, Stuart FM, De PM (2011) New high-precision measurements of the isotopic composition of atmospheric argon. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 75:7494–7501
Meng QR, Zhang GW (1999) Timing of collision of the North and South China blocks: controversy and reconciliation. Geology 27:123–126
Palmer DA, Williams-Jones AE (1996) Genesis of the carbonatite-hosted fluorite deposit at Amba Dongar, India; evidence from fluid inclusions, stability isotopes, and whole rock-mineral geochemistry. Econ Geol 91:934–950
Pettke T, Oberli F, Audétat A, Guillong M, Simon AC, Hanley JJ, Klemm LM (2012) Recent developments in element concentration and isotope ratio analysis of individual fluid inclusions by laser ablation single and multiple collector ICP-MS. Ore Geol Rev 44:10–38
Qiu KF, Yu HC, Gou ZY, Liang ZL, Zhang JL, Zhu R (2018) Nature and origin of Triassic igneous activity in the Western Qinling Orogen: the Wenquan composite pluton example. Int Geol Rev 60:242–266
Reyes AG, Trompetter WJ (2012) Hydrothermal water–rock interaction and the redistribution of Li, B and Cl in the Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand. Chem Geol 314–317:96–112
Rudnick RL, Fountain DM (1995) Nature and composition of the continental crust: a lower crustal perspective. Rev Geophys 33:267–309
Seo JH, Guillong M, Aerts M, Zajacz Z, Heinrich CA (2011) Microanalysis of S, Cl and Br in fluid inclusions by LA–ICP-MS. Chem Geol 284:35–44
Smith MP, Henderson P (2000) Preliminary fluid inclusion constraints on fluid evolution in the Bayan Obo Fe-REE-Nb deposit, Inner Mongolia, China. Econ Geol 95:1371–1388
Smith M, Kynicky J, Xu C, Song W, Spratt J, Jeffries T, Brtnicky M, Kopriva A, Cangelosi D (2018) The origin of secondary heavy rare earth element enrichment in carbonatites: constraints from the evolution of the Huanglongpu district, China. Lithos 308:65–82
Song WL, Xu C, Qi L, Zhou L, Wang L, Kynicky J (2015) Genesis of Si-rich carbonatites in Huanglongpu Mo deposit, Lesser Qinling orogen, China and significance for Mo mineralization. Ore Geol Rev 64:756–765
Song WL, Xu C, Smith MP, Kynicky J, Huang K, Wei C, Zhou L, Shu Q (2016a) Origin of unusual HREE-Mo-rich carbonatites in the Qinling orogen, China. Sci Rep 6:37377
Song WL, Xu C, Veksler IV, Kynicky J (2016b) Experimental study of REE, Ba, Sr, Mo and W partitioning between carbonatitic melt and aqueous fluid with implications for rare metal mineralization. Contrib Mineral Petrol 171:1–12
Stein HJ, Markey RJ, Morgan JW, Du A, Sun Y (1997) Highly precise and accurate Re-Os ages for molybdenite from the East Qinling molybdenum belt, Shaanxi Province, China. Econ Geol 92:827–835
Sun SS, McDonough WF (1989) Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes. Geol Soc Lond, Spec Publ 42:313–345
Tang L, Santosh M, Dong YP (2015) Tectonic evolution of a complex orogenic system: evidence from the northern Qinling belt, central China. J Asian Earth Sci 113:544–559
Tang L, Santosh M, Dong YP, Tsunogae T, Zhang S, Cao H (2016) Early Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the North Qinling orogenic belt: evidence from geochemistry, phase equilibrium modeling and geochronology of metamorphosed mafic rocks from the Songshugou ophiolite. Gondwana Res 30:48–64
Tang L, Zhang ST, Yang F, Santosh M, Li JJ, Kim SW, Hu XK, Zhao Y, Cao HW (2019a) Triassic alkaline magmatism and mineralization in the Xiong'ershan area, East Qinling, China. Geol J 54:143–156
Tang L, Hu XK, Santosh M, Zhang ST, Spencer CJ, Jeon H, Zhao Y, Cao HW (2019b) Multistage processes linked to tectonic transition in the genesis of orogenic gold deposit: a case study from the Shanggong lode deposit, East Qinling, China. Ore Geol Rev 111:102998
Tang L, Zhao Y, Zhang ST, Sun L, Hu XK, Sheng YM, Zeng T (2021) Origin and evolution of a porphyry-breccia system: Evidence from zircon U-Pb, molybdenite Re-Os geochronology, in situ sulfur isotope and trace elements of the Qiyugou deposit, China. Gondwana Res 89:88–104
Taylor SR, McLennan SM (1995) The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Rev Geophys 33:241–265
Walter BF, Giebel RJ, Steele-MacInnis M, Marks MA, Kolb J, Markl G (2021) Fluids associated with carbonatitic magmatism: a critical review and implications for carbonatite magma ascent. Earth-Science Reviews, 103509
Wang CM, He X, Carranza EJM, Cui C (2019) Paleoproterozoic volcanic rocks in the southern margin of the North China Craton, central China: implications for the Columbia supercontinent. Geosci Front 10:1543–1560
Wedepohl KH (1995) The composition of the continental crust. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:1217–1232
Wei CW, Xu C, Chakhmouradian AR, Brenna M, Kynicky J, Song WL (2020) Carbon–strontium isotope decoupling in carbonatites from Caotan (Qinling, China): implications for the origin of calcite carbonatite in orogenic settings. J Petrol 61:egaa024
Weidendorfer D, Schmidt MW, Mattsson HB (2017) A common origin of carbonatite magmas. Geology 45:507–510
Weng Z, Jowitt SM, Mudd GM, Haque N (2015) A detailed assessment of global rare earth element resources: opportunities and challenges. Econ Geol 110:1925–1952
Westra G, Keith SB (1981) Classification and genesis of stockwork molybdenum deposits. Econ Geol 76:844–873
Williams-Jones AE, Palmer DAS (2002) The evolution of aqueous–carbonic fluids in the Amba Dongar carbonatite, India: implications for fenitisation. Chem Geol 185:283–301
Xu C, Wang L, Song W, Wu M (2010a) Carbonatites in China: a review for genesis and mineralization. Geosci Front 1:105–114
Xu C, Kynicky J, Chakhmouradian AR, Qi L, Song W (2010b) A unique Mo deposit associated with carbonatites in the Qinling orogenic belt, central China. Lithos 118:50–60
Xu C, Taylor RN, Kynicky J, Chakhmouradian AR, Song W, Wang L (2011) The origin of enriched mantle beneath North China block: evidence from young carbonatites. Lithos 127:1–9
Xu C, Chakhmouradian AR, Taylor RN, Kynicky J, Li W, Song W, Fletcher IR (2014) Origin of carbonatites in the South Qinling orogen: implications for crustal recycling and timing of collision between the South and North China Blocks. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 143:189–206
Yang F, Xue F, Santosh M, Wang G, Kim SW, Shen Z, Jia W, Zhang X (2019) Late Mesozoic magmatism in the East Qinling Orogen, China and its tectonic implications. Geosci Front 10:1803–1821
Ying Y, Chen W, Lu J, Jiang SY, Yang Y (2017) In situ U–Th–Pb ages of the Miaoya carbonatite complex in the South Qinling orogenic belt, central China. Lithos 290:159–171
Zhang L, Audétat A, Dolejš D (2012) Solubility of molybdenite (MoS2) in aqueous fluids at 600-800°C, 200MPa: a synthetic fluid inclusion study. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 77:175–185
Zhang Y, Cao H, Xu M, Zhang S, Tang L, Wang S, Pei Q, Cai G, Shen T (2018) Petrogenesis of the late Mesozoic highly fractionated I-type granites in the Luanchuan district: implications for the tectono-magmatic evolution of eastern Qinling. Geosci J 22:253–272
Zhang W, Chen WT, Gao JF, Chen HK, Li JH (2019a) Two episodes of REE mineralization in the Qinling Orogenic Belt, Central China: in-situ U-Th-Pb dating of bastnäsite and monazite. Mineral Deposita 54:1265–1280
Zhang D, Liu Y, Pan J, Dai T, Bayless RC (2019b) Mineralogical and geochemical characteristics of the Miaoya REE prospect, Qinling orogenic Belt, China: Insights from Sr-Nd-C-O isotopes and LA-ICP-MS mineral chemistry. Ore Geol Rev 110:102932
Zheng H, Chen H, Li D, Wu C, Chen X, Lai CK (2020) Timing of carbonatite-hosted U-polymetallic mineralization in the supergiant Huayangchuan deposit, Qinling Orogen: constraints from titanite U–Pb and molybdenite Re–Os dating. Geosci Front 5:1581–1592
Bell K, Blenkinsop J (1987) Nd and Sr isotopic compositions of East African carbonatites: implications for mantle heterogeneity. Geology 15:99–102
Acknowledgements
This study was jointly supported through the Open Research Project from the State Key Laboratory of Geological Processes and Mineral Resources, China University of Geosciences (GPMR201825), and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0600504). The analytical work of this project was supported by an infrastructure grant from the German Research Foundation (DFG), grant number INST222/1235-1. The authors thank Yu Zhao, Roman Klinghardt, Xiao-Guang Li, Jiang-Yan Yuan, Dan-Feng Huang, and Yuan-Ming Sheng for their help in the field and analytical work. We thank Rolf L. Romer, Georges Beaudoin, Michael Anenburg, and two anonymous referees for their valuable editorial efforts and constructive comments that greatly improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial handling: R. L. Romer
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, L., Wagner, T., Fusswinkel, T. et al. Magmatic-hydrothermal evolution of an unusual Mo-rich carbonatite: a case study using LA-ICP-MS fluid inclusion microanalysis and He–Ar isotopes from the Huangshui’an deposit, Qinling, China. Miner Deposita 56, 1133–1150 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-021-01055-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-021-01055-2