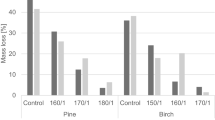
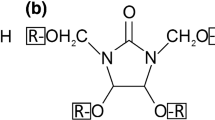
Abstract
Environmental pressures in France and in most European countries during the last decade have considerably changed the practises for wood protection. In this context, legislation and regulations, among which the Biocidal Products Directive (BPD) and Biocidal Products Regulations (BPR), are more and more constraining leading to the development of more environmentally acceptable preservation formulations and to an increasing interest in non-biocidal alternatives like thermal or chemical modifications. Wood heat treatment has been one of the most investigated alternative methods during the last years. However, even if some of the wood properties, like its decay resistance or and dimensional stability, are improved, the overall durability of the material is not sufficient to envisage use class 3 and 4 applications, where the wood is in direct contact with soil and termites. Impregnation of borax associated to polyglycerolmethacrylate (PGMA) before thermal treatment could be an attractive alternative to improve the performance of thermally modified wood in ground contact and especially its resistance to termites taking advantage of thermal treatment to initiate polymerization of PGMA within the wood structure to limit boron mobility. Thermo-modification with or without combination of boron impregnation and PGMA improved the durability of all wood samples. Thermal treatment alone or after boron impregnation and leaching was unable to effectively protect wood blocks against termites after leaching, while bocks treated with boron and PGMA were shown to be fully resistant to termites. More surprisingly, association of thermal treatment and PGMA impregnation without boron impregnation also produced protection against termite attack. Such treatments may be valuable alternatives to extend the scope of utilization of thermally modified wood in outdoor conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baysal E, Ozaki SK, Yalinkilic MK (2004) Dimensional stabilization of wood treated with furfuryl alcohol catalysed by borates. Wood Sci Technol 38:405–415
Candelier K, Dumarçay S, Pétrissans A, Gérardin P, Pétrissans M (2013) Comparison of mechanical properties of heat treated beech wood cured under nitrogen or vacuum. Polym Degrad Stab 98(9):1762–1765
EN 113 (1986) Wood preservatives—determination of toxic values of wood preservatives against wood destroying basidiomycetes cultured on agar medium. European committee for standardization, NF EN 113
EN 117 (1990) Wood preservatives—determination of toxic values against Reticulitermes santonensis de Feytaud (laboratory method). European committee for standardization, NF EN 117
EN 335-2 (2007) Durability of wood and wood-based products—definition of use classes—part 2: application to solid wood. European committee for standardization, EN 335-2
Esteves BM, Pereira HM (2009) Wood modification by heat treatment—A review. Bioresources 4(1):370–404
European Committee for Standardization (1994) Wood preservatives—methods for measuring losses of active ingredients and other preservative ingredients from treated timber—part 2: laboratory method for obtaining samples for analysis to measure losses by leaching into water or synthetic sea water. ENV 1250-2
Gezer ED, Michael JH, Morrell JJ (1999) Effects of glycol on leachability and efficacy of boron wood preservatives. Wood Fiber Sci 31:136–142
Kartal SN (2006) Combined effect of boron compounds and heat treatments on wood properties: boron release and decay and termite resistance. Holzforschung 60(4):455–458
Kartal SN, Green F (2003) Leachability of boron from wood treated with natural and semi-synthetic polymers and calcium precipitating agent. Holz Roh Werkst 61:388–389
Kartal SN, Imamura Y (2004) Effects of N’-N-(1, 8-naphthalyl) hydroxylamine (NHA-Na) and hydroxyl naphthalimide (NHA-H) on boron leachability and biological degradation of wood. Holz Roh Werkst 62:378–385
Kartal SN, Yoshimura T, Imamura Y (2004) Decay and termite resistance of boron-treated and chemically modified wood by in situ co-polymerisation of allyl glycidyl ether (AGE) with methyl methacrylate (MMA). Int Biodeter Biodegr 53:111–117
Kartal SN, Hwang WJ, Imamura Y (2008) Combined effect of boron compounds and heat treatments on wood properties: chemical and strength properties of wood. J Mat Process Tech 198:234–240
Kikuchi S, Maeda S (2007) Effects of fire retardant chemicals and retention on heat release rate of wood. Mokuzai Gakkaishi 53(5):276–282
Korkut S, Mehmet A, Turker D (2008) The effects of heat treatment on some technological properties of Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) wood. Bioresour Technol 99:1861–1868
Mburu F, Dumarçay S, Huber F, Pétrissans M, Gérardin P (2007) Evaluation of thermally modified Grevillea robusta heartwood as an alternative to shortage of wood resource in Kenya: characterisation of physicochemical properties and improvement of bio-resistance. Bioresour Technol 98:3478–3486
Mburu F, Dumarçay S, Bocquet JF, Pétrissans M, Gérardin P (2008) Effect of chemical modifications caused by heat treatment on mechanical properties of Grevillea robusta wood. Polym Degrad Stab 93:401–405
Militz H (2002) Thermal treatment of wood: European processes and their background, The international research group on wood preservation. IRG/WP 02-40241
Mohareb A, Thévenon MF, Wozniak E, Gérardin P (2010) Effects of monoglycerides on leachability and efficacy of boron wood preservatives against decay and termites. Int Biodeter Biodegr 64:135–138
Mohareb A, Thévenon MF, Wozniak E, Gérardin P (2011) Effects of polyvinyl alcohol on leachability and efficacy of boron wood preservatives against fungal decay and termites attack. Wood Sci Technol 45(2):369–382
Mourant D, Yang DQ, Lu X, Riedl B, Roy C (2009) Copper and boron fixation in wood by pyrolytic resins. Bioresour Technol 100:1442–1449
Obanda DN, Shupe FT, Barnes HM (2008) Reducing leaching of boron based wood preservatives—a review of research. Bioresour Technol 99:7312–7322
Obounou Akong F, Pasc A, Mutlu M, Cosgun S, Gérardin P, Gérardin-Charbonnier C (2013) Hydrogels obtained from an original catanionic system for efficient formulation of boron wood-preservatives. Int Biodeter Biodegr 77:123–126
Patzelt M, Stingl R, Teischinger A (2002) Thermische Modifikation von Holz und deren Einfluss auf ausgewählte Holzeigenschaften (Thermal modification of wood and ist influence on selected wood properties), In Lignovisionen volume 3, Modifiziertes Holz Eigenschaften und Märkte., ISSN 1681–2808, 101–49 (In German)
Raberg U, Daniel G, Terziev N (2012) Loss of strength in biologically degraded thermally modified wood. Bioressources 7(4):4658–4671
Salman S, Pétrissans A, Thévenon MF, Dumarçay S, Perrin D, Pollier B, Gérardin P (2014) Development of new wood treatments combining boron impregnation and thermo modification—effect of additives on boron leachability. Eur J Wood Prod 72:355–365
Soulounganga P, Marion C, Huber F, Gérardin P (2003) Synthesis of polyglycerol methacrylate and its application to wood dimensional stabilization. J Appl Polym Sci 88:743–749
Soulounganga P, Loubinoux B, Wozniak E, Lemor A, Gérardin P (2004) Improvement of wood properties by impregnation with polyglycerol methacrylate. Holz Roh Werkst 62:281–285
Surini T, Charrier F, Malvestio J, Charrier B, Moubarik A, Castéra P, Grelier S (2012) Physical properties and termite durability of maritime pine Pinus pinaster Ait heat-treated under vacuum pressure. Wood Sci Technol 46:487–501
Temiz A, Alfredsen G, Eikenes M, Terziev N (2008) Decay resistance of wood treated with boric acid and tall oil derivates. Bioresour Technol 99:2102–2106
Thévenon MF, Pizzi A (2003) Polyborate ions influence on the durability of wood treated with non-toxic protein borate preservatives. Holz Roh Werkst 61:457–464
Thévenon MF, Pizzi A, Haluk JP (1997) Non-toxic albumin and soja protein borates as ground-contact wood preservatives. Holz Roh Werkst 55:293–296
Thévenon MF, Pizzi A, Haluk JP (1998) Protein borates as non-toxic, long-term, wide-spectrum, ground- contact wood preservatives. Holzforschung 52:241–248
Tomak ED, Hughes M, Yildiz UC, Viitanen H (2011) The combined effects of boron and oil heat treatment on beech and Scots pine wood properties. Part 1: boron leaching, thermogravimetric analysis and chemical composition. J Mater Sci 46(3):598–607
Toussaint-Dauvergne E, Soulounganga P, Gérardin P, Loubinoux B (2000) Glycerol/glyoxal: a new boron fixation system for wood preservation and dimensional stabilization. Holzforschung 54:123–126
Vernois M (2001) Heat treatment of wood in France—state of art, Proceedings of special seminar review on heat treatment of wood, Antibes, France february 9. BFH the federal research centre for forestry and forest products, Hamburg, 39–46
Yildiz S, Gezerb D, Yildiz C (2006) Mechanical and chemical behavior of spruce wood modified by heat. Build Environ 41:1762–1766
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the CPER 2007-2013 “Structuration du Pôle de Compétitivité Fibres Grand’Est” (Competitiveness Fibers Cluster). LERMAB is supported by a grant overseen by the French National Research Agency (ANR) as part of the “Investissements d’Avenir” program (ANR-11-LABX-0002-01, Lab of Excellence ARBRE).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salman, S., Pétrissans, A., Thévenon, M.F. et al. Decay and termite resistance of pine blocks impregnated with different additives and subjected to heat treatment. Eur. J. Wood Prod. 74, 37–42 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-015-0972-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-015-0972-3