Abstract
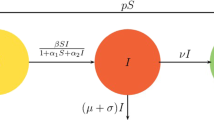
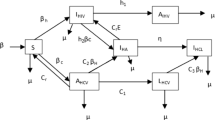
Mathematical models play a crucial role in controlling and preventing the spread of diseases. Based on the communication characteristics of diseases, it is necessary to take into account some essential epidemiological factors such as the time delay that takes an individual to progress from being latent to become infectious, the infectious age which refers to the duration since the initial infection and the occurrence of reinfection after a period of improvement known as relapse, etc. Moreover, age-structured models serve as a powerful tool that allows us to incorporate age variables into the modeling process to better understand the effect of these factors on the transmission mechanism of diseases. In this paper, motivated by the above fact, we reformulate an SEIR model with relapse and age structure in both latent and infected classes. Then, we investigate the asymptotic behavior of the model by using the stability theory of differential equations. For this purpose, we introduce the basic reproduction number \(\mathcal {R}_0\) of the model and show that this threshold parameter completely governs the stability of each equilibrium of the model. Our approach to show global attractivity is based on the fluctuation lemma and Lyapunov functionals method with some results on the persistence theory. The conclusion is that the system has a disease-free equilibrium which is globally asymptotically stable if \(\mathcal {R}_0<1\), while it has only a unique positive endemic equilibrium which is globally asymptotically stable whenever \(\mathcal {R}_0>1\). Our results imply that early diagnosis of latent infection with decrease in both transmission and relapse rates may lead to control and restrict the spread of disease. The theoretical results are illustrated with numerical simulations, which indicate that the age variable is an essential factor affecting the spread of the epidemic.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Castillo-Chávez, C., Song, B.: Dynamical models of tuberculosis and their applications. Math. Biosci. Eng. 1(2), 361–40 (2004)
Capasso, V.: Mathematical structures of epidemic systems. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-70514-7
Diekmann, O., Heesterbeek, J.A., Metz, J.A.: On the definition and the computation of the basic reproduction ratio \(\cal{R} _0\) in models for infectious diseases in heterogeneous populations. J. Math. Biol. 28, 365–382 (1990)
Kermack, W.O., McKendrick, A.G.: A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics. Proc. Royal Soc. London A 115(772), 700–721 (1927)
Xu, R., Ma, Z.: Global stability of a SIR epidemic model with nonlinear incidence rate and time delay. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 10(5), 3175–3189 (2009)
Zaman, G., Han Kang, Y., Jung, I.H.: Stability analysis and optimal vaccination of an SIR epidemic model. Biosystems 93(3), 240–249 (2008)
Yuan, X., Wang, F., Xue, Y., Liu, M.: Global stability of an SIR model with differential infectivity on complex networks. Phys. A 499, 443–456 (2018)
Hu, Z., Teng, Z., Zhang, L.: Stability and bifurcation analysis in a discrete SIR epidemic model. Math. Comput. Simul. 97, 80–93 (2014)
Tahir, H., Khan, A., Din, A., Khan, A., Zaman, G.: Optimal control strategy for an age-structured SIR endemic model. Discret. Contin. Dynamic. Syst.-S 14(7), 2535–2555 (2021)
Brookmeyer, R.: Incubation period of infectious diseases. In Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118445112.stat05241.pub2
Wang, L., Xu, R.: Global stability of an SEIR epidemic model with vaccination. Int. J. Biomath. 09(06), 1650082 (2016)
McCluskey, C.C.: Global stability for an SEIR epidemiological model with varying infectivity and infinite delay. Math. Biosci. Eng. 6(3), 603–610 (2009)
Xue, C.: Study on the global stability for a generalized SEIR epidemic model. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8215214
Wang, J., Shu, H.: Global analysis on a class of multi-group SEIR model with latency and relapse. Math. Biosci. Eng. 13(1), 209–225 (2016)
Bernoussi, A.: Stability analysis of an SIR epidemic model with homestead-isolation on the susceptible and infectious, immunity, relapse and general incidence rate. Int. J. Biomath. 16(05), 2250102 (2023)
Pradeep, B.G.S.A., Ma, W., Wang, W.: Stability and Hopf bifurcation analysis of an SEIR model with nonlinear incidence rate and relapse. J. Stat. Manag. Syst. 20(3), 483–497 (2017)
Tudor, D.: A deterministic model for herpes infections in human and animal populations. SIAM Rev. 32(1), 136–139 (1990)
Wang, J., Pang, J., Liu, X.: Modelling diseases with relapse and nonlinear incidence of infection: a multi-group epidemic model. J. Biol. Dyn. 8(1), 99–116 (2014)
Guo, Z.K., Xiang, H., Huo, H.F.: Analysis of an age-structured tuberculosis model with treatment and relapse. J. Math. Biol. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-021-01595-1
Liu, L., Ren, X., Jin, Z.: Threshold dynamical analysis on a class of age-structured tuberculosis model with immigration of population. Adv. Difference Equ. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13662-017-1295-y
Huang, G., Liu, X., Takeuchi, Y.: Lyapunov functions and global stability for age-structured HIV infection model. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 72(1), 25–38 (2012)
Xu, J., Geng, Y., Zhou, Y.: Global dynamics for an age-structured HIV virus infection model with cellular infection and antiretroviral therapy. Appl. Math. Comput., Elsevier 305(C), 62–83 (2017)
Shi, L., Wang, L., Zhu, L., Din, A., Qi, X., WuL, P.: Dynamics of an infection-age HIV diffusive model with latent infected cell and Beddington–DeAngelis infection incidence. Eur. Phy. J. Plus (2022). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-02428-w
Zou, L., Ruan, S., Zhang, W.: An age-structured model for the transmission dynamics of hepatitis B. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 70(8), 3121–3139 (2010)
Thieme, H.R., Castillo-Chávez, C.: How may infection-age-dependent infectivity affectthe dynamics of HIV/AIDS? SIAM J. Appl. Math. 53(5), 1447–1479 (1993)
Webb, G.F.: Theory of Nonlinear Age-Dependent Population Dynamics. Marcel Dekker, New York (1985)
Magal, P., McCluskey, C.C., Webb, G.: Lyapunov functional and global asymptotic stability for an infection-age model. Appl. Anal. 89(7), 1109–1140 (2010)
McCluskey, C.C.: Delay versus age-of-infection-global stability. Appl. Math. Comput. 217(7), 3046–3049 (2010)
Melnik, V.A., Korobeinikov, A.: Lyapunov functions and global stability for SIR and SEIR models withage-dependent susceptibility. Math. Biosci. Eng. 10(2), 369–378 (2013)
Liu, W.M., Levin, S.A., Iwasa, Y.: Influence of nonlinear incidence rates upon the behaviour of SIRS epidemiological models. J. Math. Biol. 23, 187–204 (1986)
Henshaw, S., McCluskey, C.C.: Global stability of a vaccination model with immigration. Electron. J. Differ. Equ. 2015(92), 1–10 (2015)
Yang, Y., Li, J., Zhou, Y.: Global stability of two tuberculosis models with treatment and self-cure. Rocky Mt. J. Math. 42(4), 1367–1386 (2012)
McCluskey, C.C.: Global stability for an SEI epidemiological model with continuous age-structure in the exposed and infectious classes. Math. Biosci. Eng. 9(4), 819–841 (2012)
Yang, Y., Li, J., Ma, Z., Liu, L.: Global stability of two models with incomplete treatment for tuberculosis. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals 43(1), 79–85 (2010)
Hu, R., Liu, L., Ren, X., Liu, X.: Global stability of an information-related epidemic model with age-dependent latency and relapse. Ecol. Complex. 36, 30–47 (2018)
Xu, R.: Global dynamics of an epidemiological model with age of infection and disease relapse. J. Biol. Dyn. 12(1), 118–145 (2018)
Din, A., Li, Y.: Controlling heroin addiction via age-structured modeling. Adv. Difference Equ. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13662-020-02983-5
Iannelli, M.: Mathematical Theory of Age-Structured Population Dynamics, In : Applied Mathematics Monographs. Vol. 7, comitato Nazionale per le Scienze Matematiche, Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (C.N.R.), Giardini, Pisa (1995)
Magal, P.: Compact attractors for time-periodic age-structured population models. Electron. J. Differ. Equ. 65, 1–35 (2001)
Hale, J.K.: Asymptotic Behavior of Dissipative Systems. American Mathematical Society, Providence (1988)
Yosida, K.: Functional Analysis, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (1968)
Smith, H. L., Thieme, H. R.: Dynamical Systems and Population Persistence, American Mathematical Society, Providence, 118 (2011)
Hirsch, W.M., Hanisch, H., Gabriel, P.: Differential equation models of some parasitic infections: Methods for the study of asymptotic behavior. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 38(6), 733–753 (1985)
Hale, J.K.: Dynamical systems and stability. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 26(1), 39–59 (1969)
Walker, J.A.: Dynamical Systems and Evolution Equations: Theory and Applications. Plenum Press, New York (1980)
Goh, B.S.: Global stability in many species systems. Am. Nat. 111(977), 135–142 (1977)
Foss, A.M., Vickerman, P.T., Chalabi, Z., Mayaud, P., Alary, M., Watts, C.H.: Dynamic modelling of herpes simplex virus type-2 (HSV-2) transmission: issue in structure uncertainty. Bull. Math. Biol. 71(3), 720–749 (2009)
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank the anonymous referees for their comments which contributed to improve this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
NABTi, A. Dynamical analysis of an age-structured SEIR model with relapse. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 75, 84 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00033-024-02227-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00033-024-02227-6