Abstract
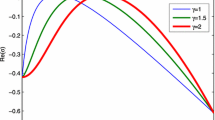
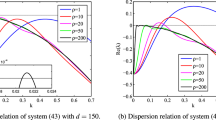
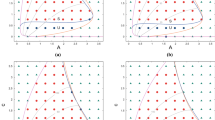
This paper is devoted to a mathematical model with diffusion and cross-diffusion to describe the interaction between vegetation and soil water. First, the existence of Hopf bifurcation and cross-diffusion-driven Turing instability are discussed. Then, based on the nonlinear analysis, we obtain the exact parameters range for stationary patterns and show the dynamical behavior near Turing bifurcation point. It is found that the model has the properties of gap, strip and spot patterns. Moreover, the small water-uptake ability of vegetation roots promotes the growth of vegetation and the transitions of vegetation pattern. But with the continuous increase of the water-uptake ability of vegetation roots, the local vegetation biomass density increases and the isolation between vegetation patches also increases, which may induce the emergence of desertification. In addition, our results reveal that the water consumption rate induces the transitions of vegetation pattern and prohibits the increase of vegetation biomass density.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gilad, E., von Hardenberg, J., Provenzale, A., et al.: Ecosystem engineers: from pattern formation to habitat creation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93(9), 098105 (2004)
Tarnita, C.E., Bonachela, J.A., Sheffer, E., et al.: A theoretical foundation for multi-scale regular vegetation patterns. Nature 541(7637), 398–401 (2017)
Liu, Q., Herman, P.M.J., Mooij, W.M., et al.: Pattern formation at multiple spatial scales drives the resilience of mussel bed ecosystems. Nat. Commun. 5(1), 5234 (2014)
Meron, E.: Pattern-formation approach to modelling spatially extended ecosystems. Ecol. Model. 234, 70–82 (2012)
Reynolds, J.F., Stafford Smith, D.M., Lambin, E.F., et al.: Global desertification: building a science for dryland development. Science 316(5826), 847–851 (2007)
Zhang, J., Guan, Q., Qinqin, D., et al.: Spatial and temporal dynamics of desertification and its driving mechanism in Hexi region. Land Degrad. Dev. 33(17), 3539–3556 (2022)
Yue, Y., Geng, L., Li, M.: The impact of climate change on aeolian desertification: a case of the agro-pastoral ecotone in northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 859, 160126 (2023)
Xu, X., Liu, L., Han, P., et al.: Accuracy of vegetation indices in assessing different grades of grassland desertification from UAV. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19(24), 16793 (2022)
Guo, G., Zhao, S., Wang, J., et al.: Positive steady-state solutions for a water-vegetation model with the infiltration feedback effect. Discrete Continuous Dyn. Syst. B 29, 426–458 (2023)
Gowda, K., Riecke, H., Silber, M.: Transitions between patterned states in vegetation models for semiarid ecosystems. Phys. Rev. E 89(2), 022701 (2014)
Rietkerk, M., Bastiaansen, R., et al.: Evasion of tipping in complex systems through spatial pattern formation. Science 374(6564), 169-+ (2021)
Sun, G., Zhang, H., et al.: Mathematical modeling and mechanisms of pattern formation in ecological systems: a review. Nonlinear Dyn. 104(2), 1677–1696 (2021)
Klausmeier: Regular and irregular patterns in semiarid vegetation. Science 284(5421), 1826–1828 (1999)
Sun, G., Wang, C., Chang, L., et al.: Effects of feedback regulation on vegetation patterns in semi-arid environments. Appl. Math. Model. 61, 200–215 (2018)
Sun, G., Zhang, H., Song, Y., et al.: Dynamic analysis of a plant-water model with spatial diffusion. J. Differ. Equ. 329, 395–430 (2022)
Sherratt, J.A., Synodinos, A.D.: Vegetation patterns and desertification waves in semi-arid environments: mathematical models based on local facilitation in plants. Discrete Continuous Dyn. Syst. Ser. B 17(8), 2815–2827 (2012)
HilleRisLambers, R., Rietkerk, M., van den Bosch, F., et al.: Vegetation pattern formation in semi-arid grazing systems. Ecology 82(1), 50–61 (2001)
Shnerb, N.M., Sarah, P., Lavee, H., et al.: Reactive glass and vegetation patterns. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90(3), 038101 (2003)
Wang, X., Shi, J., Zhang, G.: Interaction between water and plants: rich dynamics in a simple model. Discrete Continuous Dyn. Syst. Ser. B 22(7), 2971–3006 (2017)
Song, D., Li, C., Song, Y.: Stability and cross-diffusion-driven instability in a diffusive predator-prey system with hunting cooperation functional response. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 54, 103106 (2020)
Lv, Y.: Turing–Hopf bifurcation in the predator-prey model with cross-diffusion considering two different prey behaviours transition. Nonlinear Dyn. 107(1), 1357–1381 (2022)
Zhang, F., Li, Y., Zhao, Y., et al.: Vegetation pattern formation and transition caused by cross-diffusion in a modified vegetation-sand model. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 32(05), 2250069 (2022)
Kerner, E.H.: A statistical mechanics of interacting biological species. Bull. Math. Biophys. 19(2), 121–146 (1957)
von Hardenberg, J., Meron, E., Shachak, M., et al.: Diversity of vegetation patterns and desertification. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87(19), 198101 (2001)
Su, R., Zhang, C.: Pattern dynamical behaviors of one type of tree-grass model with cross-diffusion. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 32(04), 2250051 (2022)
Wang, X., Wang, W., Zhang, G.: Vegetation pattern formation of a water-biomass model. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 42, 571–584 (2017)
Gilad, E., Shachak, M., Meron, E.: Dynamics and spatial organization of plant communities in water-limited systems. Theor. Popul. Biol. 72(2), 214–230 (2007)
Liu, Q., Jin, Z., Li, B.: Numerical investigation of spatial pattern in a vegetation model with feedback function. J. Theor. Biol. 254(2), 350–360 (2008)
Liu, C., Li, L., Wang, Z., et al.: Pattern transitions in a vegetation system with cross-diffusion. Appl. Math. Comput. 342, 255–262 (2019)
Djilali, S.: Spatiotemporal patterns induced by cross-diffusion in predator-prey model with prey herd shape effect. Int. J. Biomath. 13(4), 1–19 (2020)
Sherratt, J.A.: Pattern solutions of the Klausmeier model for banded vegetation in semiarid environments IV: slowly moving patterns and their stability. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 73(1), 330–350 (2013)
Tzou, J.C., Tzou, L.: Analysis of spot patterns on a coordinate-invariant model for vegetation on a curved terrain. SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst. 19(4), 2500–2529 (2020)
Xue, Q., Liu, C., Li, L., et al.: Interactions of diffusion and nonlocal delay give rise to vegetation patterns in semi-arid environments. Appl. Math. Comput. 399, 126038 (2021)
Sun, G., Wang, C., Chang, L., et al.: Effects of feedback regulation on vegetation patterns in semi-arid environments. Appl. Math. Model. 61, 200–215 (2018)
Gowda, K., Chen, Y., Iams, S., Silber, M.: Assessing the robustness of spatial pattern sequences in a dryland vegetation model. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 472(2187), 20150893 (2016)
Sun, G., Zeyan, W., Wang, Z., et al.: Influence of isolation degree of spatial patterns on persistence of populations. Nonlinear Dyn. 83(1–2), 811–819 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (12301634, 12061081, 61872227, 12126420). The authors wish to express grateful thanks to the anonymous referees for their careful reading and some valuable comments and suggestions which greatly improved this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally to the research and manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent for publication
It is not under consideration for publication elsewhere. And its publication has been approved by all authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (12301634, 12061081, 61872227, 12126420).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, G., Zhao, S., Pang, D. et al. Stability and cross-diffusion-driven instability for a water-vegetation model with the infiltration feedback effect. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 75, 33 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00033-023-02167-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00033-023-02167-7