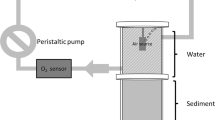
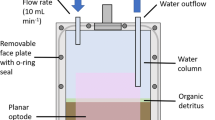
Abstract
This study investigates the potential of bioturbating Tubificidae to alter biogeochemical processes by sediment aeration in order to enhance ecosystem development in eco-engineering projects. We introduced Tubificidae in three different densities (5000, 15,000, and 30,000 individuals m−2) in clay-rich sediment from lake Markermeer (The Netherlands). Redox potential, nutrients and major elements were measured from the water column and porewater at different depths. Mineral phase and redox transfers were chemically modelled and oxygen concentrations in bioturbated sediments for each density were mathematically predicted. The measured results of this experiment showed that Tubificidae oxygenated the upper 15 mm of the sediment. This resulted in decomposition of sedimentary organic matter with an associated sixfold increase in NH4 and NOx concentrations in the porewater and the water column. However, phosphorus concentrations were declining in the upper 16 mm, likely as a result of immobilization by pyrite oxidation and production of iron oxides. These bioturbation effects were highest in the treatment with an intermediate density of Tubificidae (15,000 worms m−2) as aeration effects in the treatment with the highest density of Tubificidae (30,000 worms m−2) was impeded by high respiration rates. Furthermore, with a two dimensional diffusion model, simulated effects of respiration and aeration on the oxygen concentration in the sediment suggest that the bioturbation effect is strongest at a density of 12,000 worms m−2. In ecological engineering projects where fast ecosystem development is important, introducing Tubificidae to aquatic sediments to optimal densities might enhance initial ecosystem development due to improved availability of nitrogen as nutrient.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anschutz P, Ciutat A, Lecroart P, Gérino M, Boudou A (2012) Effects of Tubificid worm bioturbation on freshwater sediment biogeochemistry. Aquat Geochem 18:475–497
Callender E, Hammond DE (1982) Nutrient exchange across the sediment–water interface in the Potomac River estuary. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 15:395–413
De Lucas Pardo MA (2014) Effect of biota on fine sediment transport processes. A study of lake Markermeer. Ph.D. dissertation, Delft University
De Lucas Pardo MA, Bakker M, Van Kessel T, Cozzoli F, Winterwerp JC (2013) Erodibility of soft freshwater sediments in Markermeer: the role of bioturbation by meiobenthic fauna. Ocean Dyn 63:1137–1150
Egozcue JJ, Pawlowsky GV, Mateu Figueras F, Barceló Vidal C (2003) Isometric logratio transformations for compositional data analysis. Math Geol 35:279–300
Fillos J, Swanson WR (1975) The release rate of nutrients from river and lake sediments. Water Pollut Control Fed J 47:1032–1042
Filzmoser P, Hron K, Reimann C, Garret RG (2009) Robust factor analysis for compositional data. Comput Geosci 35:1854–1861
Fisher B, Lick WJ, McCall PL, Robbins JA (1980) Vertical mixing of lake sediments by tubificid oligochaetes. J Geophys Res 85:3997–4006
Fowler DJ, Goodnight CJ (1965) The effect of environmental factors on the respiration of Tubifex. Am Midl Nat 74:418–428
Griffioen J (2006) Extent of immobilization of phosphate during aeration of nutrient-rich, anoxic groundwater. J Hydrol 320:359–369
Han P, Bartels DM (1996) Temperature dependence of oxygen diffusion in H2O and D2O. J Phys Chem 100:5597–5602
Hansen K, Kristensen E (1997) Impact of macrofaunal recolonization on benthic metabolism and nutrient fluxes in a shallow marine sediment previously overgrown with macroalgal mats. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 45:613–628
Helder W, De Vries RTP (1979) An automatic phenol-hypochlorite method for the determination of ammonia in sea- and brackish waters. Neth J Sea Res 13:154–160
Iversen N, Jørgensen BB (1993) Diffusion coefficients of sulfate and methane in marine sediments: influence of porosity. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 57:571–578
Kitson RE, Mellon MG (1944) Colorimetric determination of phosphorus as molybdivanadophosphoric acid. Ind Eng Chem Anal Ed 16:379–383
Krantzberg G (1985) The influence of bioturbation on physical, chemical and biological parameters in aquatic environments: a review. Environ Pollut 39:99–122
Kristensen E (2000) Organic matter diagenesis at the oxic/anoxic interface in coastal marine sediments, with emphasis on the role of burrowing animals. Hydrobiologia 426:1–24
Kristensen E, Penha-Lopes G, Delefosse M, Valdemarsen T, Quintana CO, Banta GT (2012) What is bioturbation? The need for a precise definition for fauna in aquatic sciences. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 446:285–302
Lagauzère S, Moreira S, Koschorreck M (2011) Influence of bioturbation on the biogeochemistry of littoral sediments of an acidic post-mining pit lake. Biogeosciences 8:339–352
Lobet G, Pagès L, Draye X (2011) A novel image analysis toolbox enabling quantitative analysis of root system architecture. Plant Physiol 157:29–39
Lou J, Cao Y, Sun P, Zeng P (2013) The effects of operational conditions on the respiration rate of Tubificidae. PLoS One 8:1–9
Luedecke C, Hermanewicz SW, Jenkins D (1989) Precipitation of ferric phosphate in activated sludge: a chemical model and its verification. Water Sci Technol 21:325–337
Martin P, Boes X, Goddeeris B, Fagel N (2005) A qualitative assessment of the influence of bioturbation in Lake Baikal sediments. Glob Planet Change 46:87–99
Mermillod-Blondin F, Rosenberg R (2006) Ecosystem engineering: the impact of bioturbation on biogeochemical processes in marine and freshwater benthic habitats. Aquat Sci 68:434–442
Ministry of Infrastructure and the Environment (2017) Watergegevens Rijkswaterstaat. http://watergegevens.rws.nl/. Accessed 11 Oct 2017
Mitsch WJ (1998) Ecological engineering—the 7-year itch. Ecol Eng 10:119–130
Nepf HM (2012) Flow and transport in regions with aquatic vegetation. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 44:123–142
Nogaro G, Mermillod-Blondin F, Valett MH, François-Carcaillet F, Gaudet JP, Lafont M, Gibert J (2009) Ecosystem engineering at the sediment–water interface: bioturbation and consumer–substrate interaction. Oecologia 161:125–138
Noordhuis R, Groot S, Dionisio Pires M, Maarse M (2014) Wetenschappelijk eindadvies ANT-IJsselmeergebied. Vijf jaar studie naar kansen voor het ecosysteem van het IJsselmeer, Markermeer en IJmeer met het oog op de Natura-2000 doelen. Deltares report 1207767-000
Oates BR (1985) Photosynthesis and amelioration of desiccation in the intertidal saccate alga Colpomenia peregrina. Mar Biol 89:109–119
Odum HT, Odum B (2003) Concepts and methods of ecological engineering. Ecol Eng 20:339–361
Parkhurst DL, Appelo CAJ (2013) Description of input and examples for PHREEQC version 3-A computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. U.S. Geological Survey, Denver
Pelegri SP, Blackburn TH (1995) Effects of Tubifex tubifex (Oligochaeta: Tubificidae) on N-mineralization in freshwater sediments, measured with 15N isotopes. Aquat Microbiol Ecol 9:289–294
Rogaar H (1980) The morphology of burrow structures made by Tubificids. Hydrobiologia 71:107–124
Ruginis T, Bartoli M, Petkuviene J, Zilius M, Lubiene I, Laini A, Rainkovas-Baziukas A (2014) Benthic respiration and stoichiometry of regenerated nutrients in lake sediments with Dreissena polymorpha. Aquat Sci 76:405–417
Saaltink RM, Dekker SC, Griffioen J, Wassen MJ (2016) Wetland eco-engineering: measuring and modeling feedbacks of oxidation processes between plants and clay-rich material. Biogeosciences 13:4945–4957
Saaltink RM, Dekker SC, Eppinga MB, Griffioen J, Wassen MJ (2017) Plant-specific effects of iron toxicity in wetlands. Plant Soil 416:83–96
Saaltink RM, Dekker SC, Griffioen J, Wassen MJ (2018) Vegetation growth and sediment dynamics in a created freshwater wetland. Ecol Eng 111:11–21
Sanford LP (2008) Modeling a dynamically varying mixed sediment bed with erosion, deposition, bioturbation, consolidation, and armoring. Comput Geosci 34:1263–1283
Schaller J (2014) Bioturbation/bioirrigation by Chironomus plumosus as main factor controlling elemental remobilization from aquatic sediments? Chemosphere 107:336–343
Scicluna TR, Woodland RJ, Zhu Y, Grace MR, Cook PLM (2015) Deep dynamic pools of phosphorus in the sediment of a temperate lagoon with recurring blooms of diazotrophic cyanobacteria. Limnol Oceanogr 60:2185–2196
Svensson JM, Leonardsson L (1996) Effects of bioturbation by tube-dwelling chironomid larvae on oxygen uptake and denitrification in eutrophic lake sediments. Freshw Biol 35:289–300
Svensson JM, Enrich-Prast A, Leonardson L (2001) Nitrification and denitrification in a Eutrophic Lake sediment bioturbated by oligochaetes. Aquat Microb Ecol 23:177–186
Temmerman S, Meire P, Bouma TJ, Herman PMJ, Ysebaert T, de Vriend HJ (2013) Ecosystem-based coastal defence in the face of global change. Nature 504:79–83
Turner CB (2010) Influence of zebra (Dreissena polymorpha) and quagga (Dreissena rostriformis) mussel invasions on benthic nutrient and oxygen dynamics. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 67:1899–1908
Ullman WJ, RC Aller (1981) Diffusion coefficients in nearshore marine sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 27:552–556
Van Kessel T, De Boer G, Boderie P (2008) Calibration suspended sediment model Markermeer. Open File Rep 4612:107 pp
Van Riel MC, Verdonschot PFM, Dekkers DD (2018) De bodemfauna van het Markermeer. Markermeer bodemfaunakartering 2016 en MWTL-analyse. https://doi.org/10.18174/442521
Van de Velde S, Meysman FJR (2016) The influence of bioturbation on iron and sulphur cycling in marine sediments: a model analysis. Aquat Geochem 22:469–504
Van der Grift B, Behrends T, Osté LA, Schot PP, Wassen MJ, Griffioen J (2016) Fe hydroxyphosphate precipitation and Fe(II) oxidation kinetics upon aeration of Fe(II) and phosphate-containing synthetic and natural solutions. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 186:71–90
Vepraskas MJ, Polizzotto M, Faulkner SP (2001) Redox chemistry of hydric soils in wetland soils: genesis, hydrology, landscapes, and classification. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Vijverberg T, Winterwerp JC, Aarninkhof SGJ, Drost H (2011) Fine sediment dynamics in a shallow lake and implication for design of hydraulic works. Ocean Dyn 61:187–202
Vink JPM (2002) Measurement of heavy metal speciation over redox gradients in natural water–sediment interfaces and implications for uptake by benthic organisms. Environ Sci Technol 36:5130–5138
Vink JPM (2009) The origin of speciation: trace metal kinetics and bioaccumulation by oligochaetes and chironomids in undisturbed water–sediment interfaces. Environ Pollut 157:519–527
Volkenborn N, Polerecky L, Hedtkamp SIC, van Beusekom JEE, de Beer D (2007) Bioturbation and bioirrigation extend the open exchange regions in permeable sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 52:1898–1909
Walker RA, Hallock P, Torres JJ, Vargo GA (2011) Photosynthesis and respiration in five species of benthic Foraminifera that host algal endosymbionts. J Foramin Res 41:314–325
Zhu Y, Hipsey MR, McCowan A, Beardall J, Cook PLM (2016) The role of bioirrigation in sediment phosphorus dynamics and blooms of toxic cyanobacteria in a temperate lagoon. Environ Model Softw 86:277–304
Acknowledgements
This study was supported with funding from Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (NWO), Stichting voor de Technische Wetenschappen (project no. 850.13.032) and the companies Deltares, Boskalis and Van Oord. This manuscript was produced with unrestricted freedom to report all results. We would also like to express our thanks to Thom Claessen and John Visser for their help, support and advice during the experiment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saaltink, R.M., Honingh, E., Dekker, S.C. et al. Respiration and aeration by bioturbating Tubificidae alter biogeochemical processes in aquatic sediment. Aquat Sci 81, 13 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-018-0610-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-018-0610-3