Abstract
Background
Allergic inflammation is primarily mediated by immune effector cells such as mast cells and basophils that release proinflammatory cytokines. Both mast cells and basophils are activated via their high affinity IgE receptor (FcεRI) which initiates the release of proinflammatory mediators such as histamine and tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Considerable effort has been focused on finding an effective basophil stabilizer that inhibits the activation of FcεRI-activated mediator release. Recently, eremophilane lactones, a novel family of sesquiterpene compound originally isolated from Petasites japonicas (Sieb. et Zucc.), have been described, and it has been postulated that they may have anti-inflammatory activity, particularly in allergic disease.
Objective
Our objective was to determine the effect of two eremophilane lactones derived from 6β-angeloyloxy-3β,8-dihydroxyeremophil-7(11)-en-12,8β-olide (F-1) on immunoglobulin E (IgE)-dependent release of pro-inflammatory mediators by a basophil cell line, RBL-2H3, a model system for FcεRI-mediated activation of pro-inflammatory mediator release.
Methods
The parent compound (F-1) was chemically modified to produce F-1a [6β-angeloyloxy-3β-benzoyloxy-8-hydroxyeremophil-7(11)-en-12,8β-olide] and F-1b [6β-angeloyloxy-3β,8-diacetoxyeremophil-7(11)-en-12,8β-olide]. RBL-2H3 cells were sensitized with DNP-specific IgE and then activated with DNP-BSA. The effect of these compounds on IgE-dependent basophil degranulation was assessed by measuring the release of β-hexosaminidase (b-hex). In addition, TNF release was measured via ELISA.
Results
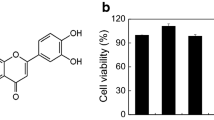
The phenylacetyl reaction modified C-8 and produced F-1a whereas acetylation of F-1 produced F-1b. F-1a was not cytotoxic to RBL-2H3 cells even at 50 μM, but F-1b was slightly cytotoxic at 50 μM, reducing viability of the cells by approximately 15 %. Neither F-1a nor F-1b inhibited FcεRI-dependent activation of RBL-2H3 cells when the cells were pretreated for only 30 min with the compounds. However, 24 h pretreatment with F-1a inhibited antigen-dependent degranulation by as much as 60 % and TNF production by as much as 90 %. F-1b had no effect on RBL-2H3 activation via FcεRI.
Conclusions
These results indicate that F-1a inhibits degranulation of RBL-2H3 cells activated via the high affinity IgE receptor, FcεRI, and that this effect is dependent upon hydroxylation of the third carbon.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ghantous A, et al. Parthenolide: from plant shoots to cancer roots. Drug Discov Today. 2013;18(17):894–905.
Galli SJ, Tsai M, Piliponsky AM. The development of allergic inflammation. Nature. 2008;454(7203):445–54.
Zheng Q, Kong P, Wu X, Li H, Li Y. Experimental study of anti-allergy effects of bioactive fraction of Petasites japonicas. J Shanghai Univ Tradit Chin Med. 2011;25(4):79–82.
Lee T, et al. Effects of magnolialide isolated from the leaves of Laurus nobilis L. (Lauraceae) on immunoglobulin E-mediated type I hypersensitivity in vitro. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013;149(2):550–6.
Kim TJ, et al. Inhibitory effects of costunolide isolated from Laurus nobilis on IgE-induced degranulation of mast cell-like RBL-2H3 cells and the growth of Y16 pro-B cells. Phytother Res. 2011;25(9):1392–7.
Zhang N, Park DK, Park HJ. The inhibitory activity of atractylenolide Ш, a sesquiterpenoid, on IgE-mediated mast cell activation and passive cutaneous anaphylaxis (PCA). J Ethnopharmacol. 2013;145(1):278–85.
Lan B, et al. Parthenolide induces autophagy via the depletion of 4E-BP1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;456(1):434–9.
Carlisi D, et al. The synergistic effect of SAHA and parthenolide in MDA-MB231 breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 2015;230(6):1276–89.
Hamzeloo-Moghadam M, et al. Britannin, a sesquiterpene lactone, inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis through the mitochondrial signaling pathway in human breast cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 2015;36(2):1191–8.
Kuchtey J, Fewtrell C. Subcloning the RBL-2H3 mucosal mast cell line reduces Ca2+ response heterogeneity at the single-cell level. J Cell Physiol. 1996;166(3):643–52.
Liu Y, et al. Single-cell measurements of IgE-mediated FcεRI signaling using an integrated microfluidic platform. PloS one. 2013;8(3):e60159.
Passante E, et al. RBL-2H3 cells are an imprecise model for mast cell mediator release. Inflamm Res. 2009;58(9):611–8.
Passante E, Frankish N. The RBL-2H3 cell line: its provenance and suitability as a model for the mast cell. Inflamm Res. 2009;58(11):737–45.
Urata C, Siraganian RP. Pharmacologic modulation of the IgE or Ca2+ ionophore A23187 mediated Ca2+ influx, phospholipase activation, and histamine release in rat basophilic leukemia cells. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1985;78(1):92–100.
Onose J, et al. Inhibitory effects of vialinin A and its analog on tumor necrosis factor-α release and production from RBL-2H3 cells. Cell Immunol. 2012;279(2):140–4.
Yoo J-M, Sok D-E, Kim MR. Effect of endocannabinoids on IgE-mediated allergic response in RBL-2H3 cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013;17(1):123–31.
Tang F, Chen F, Ling X, Huagn Y, Zheng X, Tang Q, Tan X. Inhibitory Effect of methyleugenol on IgE-mediated allergic inflammation in RBL-2H3 cells. Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:463530.
Shimoda H, et al. Anti type I allergic property of Japanese butterbur extract and its mast cell degranulation inhibitory ingredients. J Agric Food Chem. 2006;54(8):2915–20.
Lee J-S, et al. Suppressive effect of Petasites japonicus extract on ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation in an asthmatic mouse model. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011;133(2):551–7.
Eccleston ENID, et al. Basophilic leukaemia in the albino rat and a demonstration of the basopoietin. Nature. 1973;244(133):73–6.
Moon TC, Befus AD, Kulka M. Mast cell mediators: their differential release and the secretory pathways involved. Front Immunol. 2015;214(14):569.
Kimata M, Shichijo M, Miura T, Serizawa I, Inagaki N, Nagai H. Ca2+ and protein kinase C signaling for histamine and sulfidoleukotrienes released from human cultured mast cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;259(2):503–4.
Choi OH, Adelstein RS, Beaven MA. Secretion from rat basophilic RBL-2H3 cells is associated with diphosphorylation of myosin light chains by myosin light chain kinase as well as phosphorylation by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1994;269(1):536–41.
Acknowledgments
We thank Priyanka Pundir and Clayton MacDonald for technical assistance and helpful discussions during the course of this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: John Di Battista.
This work was supported by Canadian Institutes of Health Research and National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, F., Guo, G., Li, Y. et al. A novel eremophilane lactone inhibits FcεRI-dependent release of pro-inflammatory mediators: structure-dependent bioactivity. Inflamm. Res. 65, 303–311 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-016-0917-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-016-0917-2