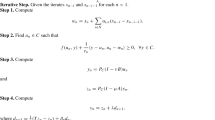Abstract
The aim of this article is to develop and analyze the matrix iterative method for computing the Moore–Penrose inverse of a given complex matrix. The theoretical analysis of the presented method is established, which indicates that the method achieves at least ninth order of convergence. The effectiveness of the developed method is tested via computational efficiency index, and the number of iterations required for convergence. Besides it, numerical reports are provided on a variety of problems arising from different fields of science and engineering. In particular, we study the linear system of equations originated from the statically determinate truss problems, elliptic partial differential equations, and balancing chemical equations. It is demonstrated that the performance of the presented method is significantly better than its existing counterparts.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben-Israel, A., Greville, T.N.: Generalized Inverses: Theory and Applications. Springer, New York (2003)
Codevico, G., Pan, V.Y., Van Barel, M.: Newton-like iteration based on a cubic polynomial for structured matrices. Numer. Algorithms 36(4), 365–380 (2004)
Grosz, L.: Preconditioning by incomplete block elimination. Numer. Linear Algebra Appl. 7(7–8), 527–541 (2000)
Horn, R.A., Johnson, C.R.: Matrix Analysis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2012)
Krishnamurthy, E.V., Sen, S.K.: Numerical Algorithms: Computations in Science and Engineering. Affiliated East-West Press, New Delhi (1986)
Li, H.B., Huang, T.Z., Zhang, Y., Liu, X.P., Gu, T.X.: Chebyshev-type methods and preconditioning techniques. Appl. Math. Comput. 218(2), 260–270 (2011)
Moore, E.H.: On the reciprocal of the general algebraic matrix. Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 26, 394–395 (1920)
Pan, V., Schreiber, R.: An improved Newton iteration for the generalized inverse of a matrix, with applications. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput. 12(5), 1109–1130 (1991)
Penrose, R.: A generalized inverse for matrices. Math. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 51(3), 406–413 (1955)
Penrose, R.: On best approximate solutions of linear matrix equations. Math. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 52(1), 17–19 (1956)
Schulz, G.: Iterative berechung der reziproken matrix. ZAMM Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 13(1), 57–59 (1933)
Söderström, T., Stewart, G.W.: On the numerical properties of an iterative method for computing the Moore-Penrose generalized inverse. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 11(1), 61–74 (1974)
Soleimani, F., Soleymani, F.: Some matrix iterations for computing generalized inverses and balancing chemical equations. Algorithms 8(4), 982–998 (2015)
Soleymani F.: A rapid numerical algorithm to compute matrix inversion. Int. J. Math. Math. Sci. Article ID 134653 (2012)
Soleymani, F.: On finding robust approximate inverses for large sparse matrices. Linear Multilinear Algebra 62(10), 1314–1334 (2014)
Soleymani, F., Stanimirović, P.S., Ullah, M.Z.: An accelerated iterative method for computing weighted Moore–Penrose inverse. Appl. Math. Comput. 222, 365–371 (2013)
Stanimirović, P.S., Cvetković-Ilić, D.S.: Successive matrix squaring algorithm for computing outer inverses. Appl. Math. Comput. 203(1), 19–29 (2008)
Toutounian, F., Soleymani, F.: An iterative method for computing the approximate inverse of a square matrix and the Moore–Penrose inverse of a non-square matrix. Appl. Math. Comput. 224, 671–680 (2013)
Traub, J.F.: Iterative Methods for the Solution of Equations. American Mathematical Society, New York (1982)
Trott, M.: The Mathematica GuideBook for Programming. Springer, New York (2013)
Weiguo, L., Juan, L., Tiantian, Q.: A family of iterative methods for computing Moore–Penrose inverse of a matrix. Linear Algebra Appl. 438(1), 47–56 (2013)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, M., Kansal, M. & Kumar, S. An Efficient Matrix Iterative Method for Computing Moore–Penrose Inverse. Mediterr. J. Math. 18, 42 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00009-020-01675-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00009-020-01675-4
Keywords
- Moore–Penrose inverse
- iterative method
- matrix multiplications
- computational efficiency index
- rank-deficiency matrix