Abstract
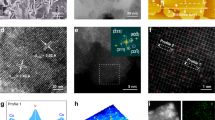
The development of efficient and durable bifunctional electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction (OER), still poses huge challenges. Herein, we utilize a facile hydrothermal method to synthesize a novel IrNi nanocrystals. In particular, the electronic structure is altered when a portion of the iridium atom is replaced by a Ni atom, which causes the center of the d band to shift downward, favoring the catalytic reaction. The overpotentials for OER of 273 mV at a current density of 10 mA cm−2, exceed the capabilities of commercial Ir catalysts. The alloying of Ir with Ni reduces the adsorption energy of oxygen intermediates to achieve a fast oxygen evolution reaction. This work highlights a potentially powerful strategy toward the general synthesis of novel, Ir-based alloy as highly active and durable bifunctional electrocatalysts for high-performance electrochemical overall-water-splitting devices.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
She, Z.W., Kibsgaard, J., Dickens, C.F., Chorkendorff, I., Nørskov, J.K., Jaramillo, T.F.: Combining theory and experiment in electrocatalysis: insights into materials design. Science 355, eaad4998 (2017)
Schuler, T., Kimura, T., Schmidt, T.J., Büchi, F.N.: Towards a generic understanding of oxygen evolution reaction kinetics in polymer electrolyte water electrolysis. Energy Environ. Sci. 13, 2153–2166 (2020)
Wang, S., Lv, H., Tang, F., Sun, Y., Ji, W., Zhou, W., et al.: Defect engineering assisted support effect:IrO2/N defective g-C3N4 composite as highly efficient anode catalyst in PEM water electrolysis. Chem. Eng. J. 419, 129455 (2021)
Dang, N.K., Tiwari, J.N., Sultan, S., Meena, A., Kim, K.S.: Multi-site catalyst derived from Cr atoms-substituted CoFe nanoparticles for high-performance oxygen evolution activity. Chem. Eng. J. 404, 126513 (2021)
Liu, S., Liu, B., Gong, C., Li, Z.: Finely prepared and optimized Co/Fe double hydroxide nanofilms at an ionic layer level on rough Cu substrates for efficient oxygen evolution reaction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 478, 615–622 (2019)
Shi, Z., Li, J., Jiang, J., Wang, Y., Wang, X., Li, Y., et al.: Enhanced acidic water oxidation by dynamic migration of oxygen species at the Ir/Nb2O5−x catalyst/support interfaces. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 61, e202212341 (2022)
Mazúr, P., Polonský, J., Paidar, M., Bouzek, K.: Non-conductive TiO2 as the anode catalyst support for PEM water electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 37, 12081–12088 (2012)
Wang, X., Habte, B.T., Zhang, S., Yang, H., Zhao, J., Jiang, F., et al.: Localized electrochemical impedance measurements on Nafion membranes: observation and analysis of spatially diverse proton transport using atomic force microscopy. Anal. Chem. 91, 11678–11686 (2019)
Wang, Y., Chu, F., Zeng, J., Wang, Q., Naren, T., Li, Y., et al.: Single atom catalysts for fuel cells and rechargeable batteries: principles, advances, and opportunities. ACS Nano 15, 210–239 (2021)
Ruiz Esquius, J., Morgan, D.J., Algara Siller, G., Gianolio, D., Aramini, M., Lahn, L., et al.: Lithium-directed transformation of amorphous iridium (Oxy)hydroxides to produce active water oxidation catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 6398–6409 (2023)
Zhu, J., Wei, M., Meng, Q., Chen, Z., Fan, Y., Hasan, S.W., et al.: Ultrathin-shell IrCo hollow nanospheres as highly efficient electrocatalysts towards the oxygen evolution reaction in acidic media. Nanoscale 12, 24070–24078 (2020)
Daiane Ferreira da Silva, C., Claudel, F., Martin, V., Chattot, R., Abbou, S., Kumar, K., et al.: Oxygen evolution reaction activity and stability benchmarks for supported and unsupported IrOx electrocatalysts. ACS Catal. 11, 4107–4116 (2021)
Mom, R.V., Falling, L.J., Kasian, O., Algara-Siller, G., Teschner, D., Crabtree, R.H., et al.: Operando structure–activity–stability relationship of iridium oxides during the oxygen evolution reaction. ACS Catal. 12, 5174–5184 (2022)
Kwon, T., Hwang, H., Sa, Y.J., Park, J., Baik, H., Joo, S.H., et al.: Cobalt assisted synthesis of IrCu hollow octahedral nanocages as highly active electrocatalysts toward oxygen evolution reaction. Adv. Func. Mater. 27, 1604688 (2017)
González, D., Sodupe, M., Rodríguez-Santiago, L., Solans-Monfort, X.: Metal coordination determines the catalytic activity of IrO2 nanoparticles for the oxygen evolution reaction. J. Catal. 412, 78–86 (2022)
Xue, Y., Fang, J., Wang, X., Xu, Z., Zhang, Y., Lv, Q., et al.: Sulfate-functionalized RuFeOx as highly efficient oxygen evolution reaction electrocatalyst in acid. Adv. Func. Mater. 31, 2101405 (2021)
Duan, Z., Zhang, M., Mao, Q., Deng, K., Yu, H., Wang, Z., et al.: Synergistic coupling of IrNi/Ni(OH)2 nanosheets with polypyrrole and iron oxyhydroxide layers for efficient electrochemical overall water splitting. Nanotechnology 34, 275401 (2023)
Liu, S., Hu, Z., Wu, Y., Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., Cui, B., et al.: Dislocation-strained IrNi alloy nanoparticles driven by thermal shock for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv. Mater. 32, 2006034 (2020)
Pi, Y., Shao, Q., Wang, P., Guo, J., Huang, X.: General formation of monodisperse IrM (M = Ni Co, Fe) bimetallic nanoclusters as bifunctional electrocatalysts for acidic overall water splitting. Adv. Func. Mater. 27, 1700886 (2017)
Wang, Y., Zhang, L., Yin, K., Zhang, J., Gao, H., Liu, N., et al.: Nanoporous iridium-based alloy nanowires as highly efficient electrocatalysts toward acidic oxygen evolution reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 39728–39736 (2019)
Lv, F., Zhang, W., Yang, W., Feng, J., Wang, K., Zhou, J., et al.: Ir-based alloy nanoflowers with optimized hydrogen binding energy as bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Small Methods 4, 1900129 (2020)
Jin, H., Hong, Y., Yoon, J., Oh, A., Chaudhari, N.K., Baik, H., et al.: Lanthanide metal-assisted synthesis of rhombic dodecahedral MNi (M = Ir and Pt) nanoframes toward efficient oxygen evolution catalysis. Nano Energy 42, 17–25 (2017)
Harzandi, A.M., Shadman, S., Nissimagoudar, A.S., Kim, D.Y., Lim, H.-D., Lee, J.H., et al.: Ruthenium core-shell engineering with nickel single atoms for selective oxygen evolution via nondestructive mechanism. Adv. Energy Mater. 11, 2003448 (2021)
Su, R., Hsain, A.L., Wu, M., Zhang, D.W., Hu, X.H., Wang, Z.P., et al.: Nano-ferroelectric for high efficiency overall water splitting under ultrasonic vibration. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 15076–15081 (2019)
Liao, J., Ding, W., Tao, S., Nie, Y., Li, W., Wu, G., et al.: Carbon supported IrM (M = Fe, Ni, Co) alloy nanoparticles for the catalysis of hydrogen oxidation in acidic and alkaline medium. Chin. J. Catal. 37, 1142–1148 (2016)
Moriau, L., Smiljanić, M., Lončar, A., Hodnik, N.: Supported iridium-based oxygen evolution reaction electrocatalysts—recent developments. ChemCatChem 14, e202200586 (2022)
Islam, J., Kim, S.-K., Thien, P.T., Kim, M.-J., Cho, H.-S., Cho, W.-C., et al.: Enhancing the activity and durability of iridium electrocatalyst supported on boron carbide by tuning the chemical state of iridium for oxygen evolution reaction. J. Power. Sources 512, 230506 (2021)
Park, S., Shviro, M., Hartmann, H., Besmehn, A., Mayer, J., Stolten, D., et al.: Nickel structures as a template strategy to create shaped iridium electrocatalysts for electrochemical water splitting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13, 13576–13585 (2021)
Feng, J., Lv, F., Zhang, W., Li, P., Wang, K., Yang, C., et al.: Iridium-based multimetallic porous hollow nanocrystals for efficient overall-water-splitting catalysis. Adv. Mater. 29, 1703798 (2017)
Kuttiyiel, K.A., Choi, Y., Sasaki, K., Su, D., Hwang, S.-M., Yim, S.-D., et al.: Tuning electrocatalytic activity of Pt monolayer shell by bimetallic Ir-M (M=Fe Co, Ni or Cu) cores for the oxygen reduction reaction. Nano Energy 29, 261–267 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sun, Y., Lv, H., Gao, D., Zhang, C. (2024). IrNi Nanoparticles as Highly Efficient Electrocatalysts Towards the Oxygen Evolution Reaction in an Acidic Medium. In: Sun, H., Pei, W., Dong, Y., Yu, H., You, S. (eds) Proceedings of the 10th Hydrogen Technology Convention, Volume 3. WHTC 2023. Springer Proceedings in Physics, vol 395. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8581-4_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8581-4_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-8580-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-8581-4
eBook Packages: Physics and AstronomyPhysics and Astronomy (R0)