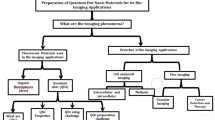
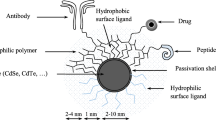
Abstract
Recent years have witnessed a giant leap in the synthesis and studies of Quantum dots (QDs). With their remarkable photophysical properties, QDs have emerged as an essential material in material science research. QDs are multifaceted, with their applications ranging from optical to next-generation theranostics. In Biomedical research, visual analysis of cellular parameters plays a crucial role in understanding the mechanisms and cellular transport. Due to their high photostability and fluorescence intensity, they are inevitable in imaging applications. QDs can be used for long time imaging when compared to their conventional organic dyes. Moreover, they can be easily used for multiplex imaging that regular fluorescent dyes cannot achieve. QDs are extensively used for cellular and biomolecular imaging, tissue staining, and binding assays in vitro and tumor imaging and Deep tissue imaging in vivo. Various types of QDs with different elemental compositions are studied for their imaging applications. However, a lack of detailed understanding of their toxicity is still a significant concern. Hence, this chapter focuses on the various imaging applications of QDs and their potential safety issues.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banerjee A, Pons T, Lequeux N, Dubertret B (2016) Quantum dots–DNA bioconjugates: synthesis to applications. Interface Focus 6(6):20160064
Burda C, Chen X, Narayanan R, El-Sayed MA (2005) Chemistry and properties of nanocrystals of different shapes. Chem Rev 105(4):1025–1102
Cai W, Shin D-W, Chen K, Gheysens O, Cao Q, Wang SX, Gambhir SS, Chen X (2006) Peptide-labeled near-infrared quantum dots for imaging tumor vasculature in living subjects. Nano Lett 6(4):669–676
Chen G, Zhang Y, Peng Z, Huang D, Li C, Wang Q (2019) Glutathione-capped quantum dots for plasma membrane labeling and membrane potential imaging. Nano Res 12(6):1321–1326
Cho SJ, Maysinger D, Jain M, Röder B, Hackbarth S, Winnik FM (2007) Long-term exposure to CdTe quantum dots causes functional impairments in live cells. Langmuir 23(4):1974–1980
Choi AO, Cho SJ, Desbarats J, Lovrić J, Maysinger D (2007) Quantum dot-induced cell death involves Fas upregulation and lipid peroxidation in human neuroblastoma cells. J Nanobiotechnol 5(1):1–13
Choy JC, Granville DJ, Hunt DWC, McManus BM (2001) Endothelial cell apoptosis: biochemical characteristics and potential implications for atherosclerosis. J Mol Cell Cardiol 33(9):1673–1690
Dabbousi BO, Rodriguez-Viejo J, Mikulec FV, Heine JR, Mattoussi H, Ober R, Jensen KF, Bawendi MG (1997) (CdSe) ZnS core–shell quantum dots: synthesis and characterization of a size series of highly luminescent nanocrystallites. J Phys Chem B 101(46):9463–9475
Dennis AM, Rhee WJ, Sotto D, Dublin SN, Bao G (2012) Quantum dot–fluorescent protein FRET probes for sensing intracellular pH. ACS Nano 6(4):2917–2924
Derfus AM, Chan WCW, Bhatia SN (2004) Probing the cytotoxicity of semiconductor quantum dots. Nano Lett 4(1):11–18
Di J, Xia J, Ji M, Wang B, Yin S, Huang Y, Chen Z, Li H (2016) New insight of Ag quantum dots with the improved molecular oxygen activation ability for photocatalytic applications. Appl Catal B Environ 188:376–387
Du Y, Bing X, Tao F, Cai M, Li F, Zhang Y, Wang Q (2010) Near-infrared photoluminescent Ag2S quantum dots from a single source precursor. J Am Chem Soc 132(5):1470–1471
Farahani JN, Pohl DW, Eisler H-J, Hecht B (2005) Single quantum dot coupled to a scanning optical antenna: a tunable superemitter. Phys Rev Lett 95(1):017402
Fouladi-Oskouei J, Shojaei S, Liu Z (2018) Robust tunable excitonic features in monolayer transition metal dichalcogenide quantum dots. J Phys Condens Matter 30(14):145301
Fountaine TJ, Wincovitch SM, Geho DH, Garfield SH, Pittaluga S (2006) Multispectral imaging of clinically relevant cellular targets in tonsil and lymphoid tissue using semiconductor quantum dots. Mod Pathol 19(9):1181–1191
Frangioni JV, Kim S-W, Ohnishi S, Kim S, Bawendi MG (2007) Sentinel lymph node mapping with type-II quantum dots. In: Quantum dots. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, pp 147–159
Gan C, Zhang Y, Battaglia D, Peng X, Xiao M (2008) Fluorescence lifetime of Mn-doped ZnSe quantum dots with size dependence. Appl Phys Lett 92(24):241111
Grützmacher D, Fromherz T, Dais C, Stangl J, Müller E, Ekinci Y, Solak HH et al (2007) Three-dimensional Si/Ge quantum dot crystals. Nano Lett 7(10):3150–3156
Guo Y, Li J (2020) MoS2 quantum dots: synthesis, properties and biological applications. Mater Sci Eng C 109:110511
Haustein E, Schwille P (2007) Trends in fluorescence imaging and related techniques to unravel biological information. HFSP J 1(3):169–180
Holleitner AW, Decker CR, Qin H, Eberl K, Blick RH (2001) Coherent coupling of two quantum dots embedded in an Aharonov-Bohm interferometer. Phys Rev Lett 87(25):256802
Jain PK, Huang X, El-Sayed IH, El-Sayed MA (2008) Noble metals on the nanoscale: optical and photothermal properties and some applications in imaging, sensing, biology, and medicine. Acc Chem Res 41(12):1578–1586
Jamieson T, Bakhshi R, Petrova D, Pocock R, Imani M, Seifalian AM (2007) Biological applications of quantum dots. Biomaterials 28(31):4717–4732
Jeong S, Jung Y, Bok S, Ryu Y-M, Lee S, Kim Y-E, Song J et al (2018) Multiplexed in vivo imaging using size-controlled quantum dots in the second near-infrared window. Adv Healthc Mater 7(24):1800695
Juette MF, Terry DS, Wasserman MR, Zhou Z, Altman RB, Zheng Q, Blanchard SC (2014) The bright future of single-molecule fluorescence imaging. Curr Opin Chem Biol 20:103–111
Kolahalam LA, Viswanath IVK, Diwakar BS, Govindh B, Reddy V, Murthy YLN (2019) Review on nanomaterials: synthesis and applications. Mater Today Proc 18:2182–2190
Kouwenhoven L, Marcus C (1998) Quantum dots. Phys World 11(6):35
Leatherdale CA, Woo W-K, Mikulec FV, Bawendi MG (2002) On the absorption cross section of CdSenanocrystal quantum dots. J Phys Chem B 106(31):7619–7622
Lee HU, Park SY, Lee SC, Choi S, Seo S, Kim H, Won J et al (2016) Black phosphorus (BP) nanodots for potential biomedical applications. Small 12(2):214–219
Li H, Li Y, Cheng J (2010) Molecularly imprinted silica nanospheres embedded CdSe quantum dots for highly selective and sensitive optosensing of pyrethroids. Chem Mater 22(8):2451–2457
Li Y, Li Z, Wang X, Liu F, Cheng Y, Zhang B, Shi D (2012) In vivo cancer targeting and imaging-guided surgery with near infrared-emitting quantum dot bioconjugates. Theranostics 2(8):769
Lin K-F, Cheng H-M, Hsu H-C, Lin L-J, Hsieh W-F (2005) Band gap variation of size-controlled ZnO quantum dots synthesized by sol–gel method. Chem Phys Lett 409(4–6):208–211
Liu X, Rui H, Lian H, Liu Y, Liu J, Liu J, Lin G et al (2015) Dual-color immunofluorescent labeling with quantum dots of the diabetes-associated proteins aldose reductase and Toll-like receptor 4 in the kidneys of diabetic rats. Int J Nanomedicine 10:3651
Long Z, Zhang W, Tian J, Chen G, Liu Y, Liu R (2021) Recent research on the luminous mechanism, synthetic strategies, and applications of CuInS2 quantum dots. Inorg Chem Front 8(4):880–897
Lovrić J, Cho SJ, Winnik FM, Maysinger D (2005) Unmodified cadmium telluride quantum dots induce reactive oxygen species formation leading to multiple organelle damage and cell death. Chem Biol 12(11):1227–1234
Ma Q, Su X (2010) Near-infrared quantum dots: synthesis, functionalization and analytical applications. Analyst 135(8):1867–1877
Montón H, Nogués C, Rossinyol E, Castell O, Roldán M (2009) QDs versus Alexa: reality of promising tools for immunocytochemistry. J Nanobiotechnol 7(1):1–10
Murray CB, Norris DJ, Bawendi MG (1993) Synthesis and characterization of nearly monodisperse CdE (E = sulfur, selenium, tellurium) semiconductor nanocrystallites. J Am Chem Soc 115(19):8706–8715
Ramasamy P, Kim N, Kang Y-S, Ramirez O, Lee J-S (2017) Tunable, bright, and narrow-band luminescence from colloidal indium phosphide quantum dots. Chem Mater 29(16):6893–6899
Resch-Genger U, Grabolle M, Cavaliere-Jaricot S, Nitschke R, Nann T (2008) Quantum dots versus organic dyes as fluorescent labels. Nat Methods 5(9):763–775
Rezaei G, Tanhaei MH (2016) Optical absorption coefficients and refractive index changes of an on-centerhydrogenic impurity in a multi-layered spherical quantum dot: Effects of external fields and geometrical size. Opt Quant Electron 48(1):73
Sangeetha VP, Smriti S, Solanki PR, Mohanan PV (2021) Mechanism of action and cellular responses of HEK293 cells on challenge with zwitterionic carbon dots. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 202:111698
Shin YC, Song S-J, Lee YB, Kang MS, Lee HU, Jin-Woo O, Han D-W (2018) Application of black phosphorus nanodots to live cell imaging. Biomater Res 22(1):1–8
Sun Y-P, Zhou B, Lin Y, Wang W, Fernando KAS, Pathak P, Meziani MJ et al (2006) Quantum-sized carbon dots for bright and colorful photoluminescence. J Am Chem Soc 128(24):7756–7757
Valizadeh A, Mikaeili H, Samiei M, Farkhani SM, Zarghami N, Akbarzadeh A, Davaran S (2012) Quantum dots: synthesis, bioapplications, and toxicity. Nanoscale Res Lett 7(1):1–14
Warner JH, Hoshino A, Yamamoto K, Tilley RD (2005) Water-soluble photoluminescent silicon quantum dots. Angew Chem Int Ed 44(29):4550–4554
Wilkinson JM (2003) Nanotechnology applications in medicine. Med Device Technol 14(5):29–31
Xu H, Jing X, Wang X, Daqing W, Chen ZG, Wang AY (2013) Quantum dot-based, quantitative, and multiplexed assay for tissue staining. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5(8):2901–2907
Xu Q, Pu P, Zhao J, Dong C, Gao C, Chen Y, Chen J, Liu Y, Zhou H (2015a) Preparation of highly photoluminescent sulfur-doped carbon dots for Fe (III) detection. J Mater Chem A 3(2):542–546
Xu S, Li D, Peiyi W (2015b) One-pot, facile, and versatile synthesis of monolayer MoS2/WS2 quantum dots as bioimaging probes and efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv Funct Mater 25(7):1127–1136
Xu G, Zeng S, Zhang B, Swihart MT, Yong K-T, Prasad PN (2016) New generation cadmium-free quantum dots for biophotonics and nanomedicine. Chem Rev 116(19):12234–12327
Xu Q, Li W, Ding L, Yang W, Xiao H, Ong W-J (2019) Function-driven engineering of 1D carbon nanotubes and 0D carbon dots: mechanism, properties and applications. Nanoscale 11(4):1475–1504
Xue Q, Zhang H, Zhu M, Pei Z, Li H, Wang Z, Huang Y et al (2017) Photoluminescent Ti3C2 MXene quantum dots for multicolor cellular imaging. Adv Mater 29(15):1604847
Yan M, Zhang Y, Xu K, Fu T, Qin H, Zheng X (2011) An in vitro study of vascular endothelial toxicity of CdTe quantum dots. Toxicology 282(3):94–103
Zhang F, Yi D, Sun H, Zhang H (2014) Cadmium-based quantum dots: preparation, surface modification, and applications. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 14(2):1409–1424
Zhang X, Lai Z, Liu Z, Tan C, Huang Y, Li B, Zhao M, Xie L, Huang W, Zhang H (2015) A facile and universal top-down method for preparation of monodisperse transition-metal dichalcogenide nanodots. Angew Chem Int Ed 54(18):5425–5428
Zhao J, Zhong D, Zhou S (2018) NIR-I-to-NIR-II fluorescent nanomaterials for biomedical imaging and cancer therapy. J Mater Chem B 6(3):349–365
Zhou J, Booker C, Li R, Zhou X, Sham T-K, Sun X, Ding Z (2007) An electrochemical avenue to blue luminescent nanocrystals from multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs). J Am Chem Soc 129(4):744–745
Zhu H, Wang X, Li Y, Wang Z, Yang F, Yang X (2009) Microwave synthesis of fluorescent carbon nanoparticles with electrochemiluminescence properties. Chem Commun 34:5118–5120
Zhu C-N, Jiang P, Zhang Z-L, Zhu D-L, Tian Z-Q, Pang D-W (2013) Ag2Se quantum dots with tunable emission in the second near-infrared window. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5(4):1186–1189
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express their sincere thanks to the Director and Head, Biomedical Technology Wing, Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology (Govt. of India), Trivandrum, for their support and for providing the infrastructure to carry out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Akhil, Arathi, Megha, K.B., Joseph, X., Sangeetha, V.P., Mohanan, P.V. (2023). Quantum Dots for Imaging and Its Safety. In: Mohanan, P.V., Kappalli, S. (eds) Biomedical Applications and Toxicity of Nanomaterials. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-7834-0_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-7834-0_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-7833-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-7834-0
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)