Abstract
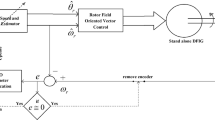
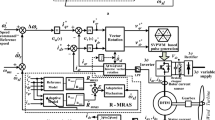
This chapter handles the investigation of various proposed sensorless schemes of rotor position observer for brushless doubly-fed induction generator (BDFIG) systems based on both schemes of the model reference adaptive system (MRAS) and the high-frequency signal (HFS) injection methodology. The algorithm of MRAS is implemented with the functional quantity of CW reactive power (Q-MRAS) which can eliminate the integration process for the flux estimation and reduce the required sensors used to achieve the effective estimation of rotor position signal for BDFIGs. On the other side, the proposed methodology of CW-HFS injection approach is realized through the injection of HFS into the CW side while the resulted induced signal detected from the PW side will observe the information of rotor position. The proposed new position observer of CW-HFS injection offers a high-performance operation with a good tracking for the actual rotor position during various states of operation with any need for the machine parameters which would assure its reliability and strong robustness.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- L 1 r :
-
Inductance of coupling between the rotor side and the PW
- L 2 r :
-
Inductance of coupling between the rotor side and the CW
- L 1 :
-
Self-inductance of the PW
- L 2 :
-
Self-inductance of the CW
- L r :
-
Self-inductance of the rotor-side
- ω 1 :
-
Angular frequency of the PW
- ω 2 :
-
Angular frequency of the CW
- R 1 :
-
Resistance of the PW
- R 2 :
-
Resistance of the CW
- R r :
-
Resistance of the rotor side
- Ψ1dq:
-
Flux linkages of the dq-axis for the PW
- Ψ2dq:
-
Flux linkages of the dq-axis for the CW
- Ψrdq:
-
Flux linkages of the dq-axis for the rotor side
- i 1 dq :
-
dq-axis components of the PW
- i 2 dq :
-
dq-axis components of the CW
- i rdq :
-
dq-axis components of the rotor side
- s :
-
The differential operator, d/dt
- u 1 dq :
-
dq-axis voltages of PW
- u 2 dq :
-
dq-axis voltages of CW
- \(\omega _{hf}\) :
-
The frequency of the injected HFS
- \(U_{2_{hf}}\) :
-
The magnitude of the injected HFS
- \(k_{p_{MRAS} }\) :
-
Proportion parameter of the PI controller for the proposed observer
- \(k_{i_{MRAS}}\) :
-
Integration parameter of the PI controller for the proposed observer
- BDFIG:
-
Brushless doubly-fed induction generator
- PW:
-
Power winding
- CW:
-
Cower winding
- DVC:
-
Direct voltage control
- MRAS:
-
Model reference adaptive system
- HFS:
-
High-frequency signal
- PMSMs:
-
Permanent-magnet synchronous machines
- IMs:
-
Induction machines
- DFIGs:
-
Doubly-fed induction generators
- PLL:
-
Phase-locked-loop
References
Y. Liu, W. Xu, J. Zhu, F. Blaabjerg, Sensorless control of standalone brushless doubly fed induction generator feeding unbalanced loads in a ship shaft power generation system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 66(1), 739–749 (2019)
F. Xiong, X. Wang, Design of a low-harmonic-content wound rotor for the brushless doubly fed generator. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 29(1), 158–168 (2014)
J. Chen, W. Zhang, B. Chen, Y. Ma, Improved vector control of brushless doubly fed induction generator under unbalanced grid conditions for offshore wind power generation. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 31(1), 293–302 (2016)
M.G. Hussien, Y. Liu, W. Xu, M. Dong, in Sensorless Position Control Based on Active Power MRAS for Ship Shaft Stand-Alone BDFIGs. 2020 International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Gothenburg, Sweden, pp. 2209–2215 (2020)
S. Shao, E. Abdi, F. Barati, R.A. McMahon, Stator-flux-oriented vector control for brushless doubly-fed induction generator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 56(10), 4220–4228 (2009)
Y. Liu, W. Ai, B. Chen, K. Chen, G. Luo, Control design and experimental verification of the brushless doubly-fed machine for stand-alone power generation applications. IET Elect. Power Appl. 10(1), 25–35 (2016)
M.G. Hussien, Y. Liu, W. Xu, A.K. Junejo, S. Allam, Improved MRAS rotor position observer based on control winding power factor for stand-alone brushless doubly-fed induction generators. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TEC.2021.3110776
Y. Liu, W. Xu, G. Zhi, J. Zhang, Performance analysis of a stand-alone brushless doubly-fed induction generator using a new T-type steady-state model. J. Power Electron. 17(4), 1027–1036 (2017)
W. Xu, M.G. Hussien, Y. Liu, M.R. Islam, S.M. Allam, Sensorless voltage control schemes for brushless doubly-fed induction generators in stand-alone and grid-connected applications. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 35(4), 1781–1795 (2020)
M.G. Hussien, Y. Liu, W. Xu, Robust position observer for sensorless direct voltage control of stand-alone ship shaft brushless doubly-fed induction generators. CES Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 3(4), 363–376 (2019)
Y. Liu, W. Xu, T. Long, F. Blaabjerg, An improved rotor speed observer for standalone brushless doubly-fed induction generator under unbalanced and nonlinear loads. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 35(1), 775–788 (2020)
M.G. Hussien, Y. Liu, W. Xu, J. Rodriguez, in Fictitious Power Based MRAS Observer for Sensorless Control of Stand-Alone Brushless Doubly-Fed Induction Generators. 2020 IEEE 9th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC2020-ECCE Asia), Nanjing, China, pp. 3511–3518 (2020)
M.G. Hussien, W. Xu, Y. Liu, S.M. Allam, Rotor speed observer with extended current estimator for sensorless control of induction motor drive systems. Energies 12, 3613 (2019)
W. Xu, M.G. Hussien, Y. Liu, S.M. Allam, Sensorless control of ship shaft stand-alone BDFIGs based on reactive-power MRAS observer. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Topics Power Electron. 9(2), 1518–1531 (2021)
C. Caruana, G.M. Asher, M. Sumner, Performance of HF signal injection techniques for zero-low-frequency vector control of induction machines under sensorless conditions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 53(1), 225–238 (2006)
P.P. Acarnely, J.F. Watson, Review of position-sensorless operation of brushless permanent-magnet machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 53(2), 352–362 (2006)
Y. Liu, M.G. Hussien, W. Xu, S. Shao, E.M. Rashad, Recent advances of control technologies for brushless doubly-fed generators. IEEE Access 9, 123324–123347 (2021)
D.D. Reigosa, F. Briz, C. Blanco, J.M. Guerrero, Sensorless control of doubly fed induction generators based on stator high-frequency signal injection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 50(5), 3382–3391 (2014)
M.G. Hussien, Y. Liu, W. Xu, in A New Rotor Position Observer of Brushless Doubly-Fed Induction Generators Based on Control-Winding High-Frequency Signal Injection. 2021 IEEE 4th International Electrical and Energy Conference (CIEEC2021), China, pp. 1–6 (2021)
Y.D. Landau, Adaptive control: The model reference approach. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern. 14(1), 169–170 (1984)
I. Boldea et al., Fractional kVA rating PWM converter doubly fed variable speed electric generator systems: An overview in 2020. IEEE Access 9, pp. 117957–117968 (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Liu, Y., Hussien, M.G., Xu, W. (2022). Sensorless Control Technologies for Stand-Alone and Grid-Connected Operation of Brushless Doubly-Fed Induction Generators in Smart Grid. In: Das, S.K., Islam, M.R., Xu, W. (eds) Advances in Control Techniques for Smart Grid Applications. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-9856-9_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-9856-9_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-9855-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-9856-9
eBook Packages: EnergyEnergy (R0)