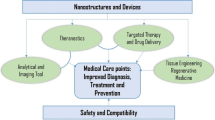
Abstract
Medicinal plants and their products have been utilized ever since prehistoric era for health and medicinal assessment and are exploited thus far. Undoubtedly, robust utilization of medicinal wealth has resulted progressive exhaustion. Additionally, these plant by-products face tribulations such as inadequate absorption at specific sites. To overcome proper accumulation problems, nanotechnology is playing a significant role. This chapter aims to highlight novel drug delivery systems, their challenges and potential in innovative nanomedicines. In present times, it has been well recognized that nanocarrier systems encompass multifaceted relevances than conservative formulations. Currently, imperative thoughtfulness is being given to synthesis of therapeutic formations comprising biocompatible nanocomposites, e.g., micellar, liposomes, nanocapsules as well nanofibers, etc. These aforesaid delivery arrangements usually are polymeric in nature and possess nanostructured morphology and consequently are used to offer targeted delivery of drugs and to improve bioavailability. Certainly, nanomedicine and nano-delivery systems are moderately new, however, swiftly emerging discipline possessing supplies in nanoscale dimensions are engaged to deliver purposes such as diagnostic apparatus or to carry therapeutic drugs to desired locations in an organized mode. Nanotechnology proffers manifold applications in curing persistent sicknesses in human beings by targeted delivery of accurate medicines. Currently, a plethora of uses of nanomedicine are there; for instance, chemotherapeutic drugs, biological materials, immunotherapeutic agents, etc. for cure of a range of ailments. Accordingly, present chapter portrays rationalized synopsis of current progress in area of nano-oriented drug carriers and nanomedicines. These nano-based drug delivery systems have improved effectiveness of old as well as new drugs, eventually, accurate diagnosis via novel indicators. In addition, the limitations and benefits of nanomedicine have also been discussed in brief.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldakheel RK, Rehman S, Almessiere MA, Khan FA, Gondal MA, Mostafa A, Baykal A (2020) Bactericidal and in vitro cytotoxicity of Moringa oleifera seed extract and its elemental analysis using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Pharmaceuticals 13(8):193
Altunbas A, Lee SJ, Rajasekaran SA, Schneider JP, Pochan DJ (2011) Encapsulation of curcumin in self-assembling peptide hydrogels as injectable drug delivery vehicles. Biomaterials 32(25):5906–5914
Amna T, Hassan MS, Nam K-T, Bing YY, Barakat NA, Khil M-S, Kim HY (2012) Preparation, characterization, and cytotoxicity of CPT/Fe2O3-embedded PLGA ultrafine composite fibers: a synergistic approach to develop promising anticancer material. Int J Nanomedicine 7:1659
Amna T, Barakat NA, Hassan MS, Khil M-S, Kim HY (2013) Camptothecin loaded poly (ε-caprolactone) nanofibers via one-step electrospinning and their cytotoxicity impact. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 431:1–8
Amna T, Hassan MS, Sheikh FA (2020) Nanocamptothecins as new generation pharmaceuticals for the treatment of diverse cancers: overview on a natural product to nanomedicine. In: Application of nanotechnology in biomedical sciences. Springer, Cham, pp 39–49
Attari E, Nosrati H, Danafar H, Kheiri Manjili H (2019) Methotrexate anticancer drug delivery to breast cancer cell lines by iron oxide magnetic based nanocarrier. J Biomed Mater Res A 107(11):2492–2500
Bamrungsap S, Zhao Z, Chen T, Wang L, Li C, Fu T, Tan W (2012) Nanotechnology in therapeutics: a focus on nanoparticles as a drug delivery system. Nanomedicine 7(8):1253–1271
Banker GS, Lieberman HA, Rieger MM (1996) Pharmaceutical dosage forms: disperse systems. M. Dekker, New York
Bawarski WE, Chidlowsky E, Bharali DJ, Mousa SA (2008) Emerging nanopharmaceuticals. Nanomedicine 4(4):273–282
Choradiya BR, Patil SB (2021) A comprehensive review on nanoemulsion as an ophthalmic drug delivery system. J Mol Liq 339(116751.10):1016
Chyzy A, Tomczykowa M, Plonska-Brzezinska ME (2020) Hydrogels as potential nano-, micro- and macro-scale systems for controlled drug delivery. Materials 13(1):188
Dalwadi C, Patel G (2015) Application of nanohydrogels in drug delivery systems: recent patents review. Recent Pat Nanotechnol 9(1):17–25
El-Aswar EI, Ramadan H, Elkik H, Taha AG (2022) A comprehensive review on preparation, functionalization and recent applications of nanofiber membranes in wastewater treatment. J Environ Manag 301:113908
Gao W, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Zhang L (2016) Nanoparticle-hydrogel: a hybrid biomaterial system for localized drug delivery. Ann Biomed Eng 44(6):2049–2061
Garg U, Chauhan S, Nagaich U, Jain N (2019) Current advances in chitosan nanoparticles based drug delivery and targeting. Adv Pharm Bull 9(2):195
Granata G, Petralia S, Forte G, Conoci S, Consoli GML (2020) Injectable supramolecular nanohydrogel from a micellar self-assembling calix[4]arene derivative and curcumin for a sustained drug release. Mater Sci Eng C 111:110842
Haggag YA, Faheem AM, Tambuwala MM, Osman MA, El-Gizawy SA, O’Hagan B, Irwin N, McCarron PA (2018) Effect of poly (ethylene glycol) content and formulation parameters on particulate properties and intraperitoneal delivery of insulin from PLGA nanoparticles prepared using the double-emulsion evaporation procedure. Pharm Dev Technol 23(4):370–381
Hani U, Shivakumar H, Anjum H, Pasha MY (2014) Preparation and optimization of curcumin-hydroxy propyl cyclodextrin bioadhesive vaginal films for human papilloma virus-induced cervical cancer. J Biomater Tissue Eng 4(10):796–803
Huang ZM, He CL, Yang A, Zhang Y, Han XJ, Yin J, Wu Q (2006) Encapsulating drugs in biodegradable ultrafine fibers through co-axial electrospinning. J Biomed Mater Res A 77(1):169–179
Joshi D, Garg T, Goyal AK, Rath G (2015) Development and characterization of novel medicated nanofibers against periodontitis. Curr Drug Deliv 12(5):564–577
Kamsani NH, Haris MS, Pandey M, Taher M, Rullah K (2021) Biomedical application of responsive ‘smart’ electrospun nanofibers in drug delivery system: a minireview. Arab J Chem 2021:103199
Liu D, Yang F, Xiong F, Gu N (2016) The smart drug delivery system and its clinical potential. Theranostics 6(9):1306
Ma P, Mumper RJ (2013) Paclitaxel nano-delivery systems: a comprehensive review. J Nanomed Nanotechnol 4(2):1000164
Mahanta AK, Senapati S, Paliwal P, Krishnamurthy S, Hemalatha S, Maiti P (2018) Nanoparticle-induced controlled drug delivery using chitosan-based hydrogel and scaffold: application to bone regeneration. Mol Pharm 16(1):327–338
Mahinroosta M, Farsangi ZJ, Allahverdi A, Shakoori Z (2018) Hydrogels as intelligent materials: a brief review of synthesis, properties and applications. Mater Today Chem 8:42–55
Nahvi I, Belkahla S, Asiri SM, Rehman S (2021) Overview and prospectus of algal biogenesis of nanoparticles. In: Microbial nanotechnology: green synthesis and applications. Springer, Singapore, pp 121–134
Narayanaswamy R, Torchilin VP (2019) Hydrogels and their applications in targeted drug delivery. Molecules 24(3):603
Nayak D, Minz AP, Ashe S, Rauta PR, Kumari M, Chopra P, Nayak B (2016) Synergistic combination of antioxidants, silver nanoparticles and chitosan in a nanoparticle based formulation: characterization and cytotoxic effect on MCF-7 breast cancer cell lines. J Colloid Interface Sci 470:142–152
Olerile LD, Liu Y, Zhang B, Wang T, Mu S, Zhang J, Selotlegeng L, Zhang N (2017) Near-infrared mediated quantum dots and paclitaxel co-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for cancer theragnostic. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 150:121–130
Otto A, Du Plessis J, Wiechers J (2009) Formulation effects of topical emulsions on transdermal and dermal delivery. Int J Cosmet Sci 31(1):1–19
Patel GC, Yadav BK (2018) Polymeric nanofibers for controlled drug delivery applications. In: Organic materials as smart nanocarriers for drug delivery. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 147–175
Patra JK, Das G, Fraceto LF, Campos EVR, del Pilar Rodriguez-Torres M, Acosta-Torres LS, Diaz-Torres LA, Grillo R, Swamy MK, Sharma S (2018) Nano based drug delivery systems: recent developments and future prospects. J Nanobiotechnol 16(1):1–33
Pierard G, Lachapelle J, Frentz G, Schopf E, Stolz E (1996) Hydrocortisone 17-butyrate topical emulsion (Locoid Crelo®) in psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 6(1):11–14
Qureshi A, Blaisi NI, Abbas AA, Khan NA, Rehman S (2021) Prospectus and development of microbes mediated synthesis of nanoparticles. In: Microbial nanotechnology: green synthesis and applications. Springer, Singapore, pp 1–15
Rehman S (2016) Endophytes: the producers of important functional metabolites. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 5(5):377–391
Rehman S, Al Salem Z, Al Jindan R, Hameed S (2019) Microbial natural products: exploiting microbes against drug-resistant bugs. In: Pathogenicity and drug resistance of human pathogens. Springer, Singapore, pp 393–404
Rehman S, Asiri SM, Khan FA, Jermy BR, Ravinayagam V, Alsalem Z, Al Jindan R, Qurashi A (2020a) Anticandidal and in vitro anti-proliferative activity of sonochemically synthesized indium tin oxide nanoparticles. Sci Rep 10(1):1–9
Rehman S, Farooq R, Jermy R, Mousa Asiri S, Ravinayagam V, Al Jindan R, Alsalem Z, Shah MA, Reshi Z, Sabit H, Alam Khan F (2020b) A wild fomes fomentarius for biomediation of one pot synthesis of titanium oxide and silver nanoparticles for antibacterial and anticancer application. Biomol Ther 10(4):622
Rehman S, Jermy R, Asiri SM, Shah MA, Farooq R, Ravinayagam V, Ansari MA, Alsalem Z, Al Jindan R, Reshi Z, Khan FA (2020c) Using Fomitopsis pinicola for bioinspired synthesis of titanium dioxide and silver nanoparticles, targeting biomedical applications. RSC Adv 10(53):32137–32147
Rehman S, Almessiere MA, Al-Suhaimi AE, Hussain M, Yousuf Bari M, Mehmood Ali S, Al-Jameel SS, Slimani Y, Khan FA, Baykal A (2021a) Ultrasonic synthesis and biomedical application of Mn0.5Zn0.5ErxYxFe2− 2xO4 nanoparticles. Biomolecules 11(5):703
Rehman S, Almessiere MA, Al-Jameel SS, Ali U, Slimani Y, Tashkandi N, Al-Saleh NS, Manikandan A, Khan FA, Al-Suhaimi EA, Baykal A (2021b) Designing of Co0.5Ni0.5GaxFe2− xO4 (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 1.0) microspheres via hydrothermal approach and their selective inhibition on the growth of cancerous and fungal cells. Pharmaceutics 13(7):962
Sábio RM, Meneguin AB, Ribeiro TC, Silva RR, Chorilli M (2019) New insights towards mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a technological platform for chemotherapeutic drugs delivery. Int J Pharm 564:379–409
Shakeel F, Baboota S, Ahuja A, Ali J, Faisal M, Shafiq S (2008) Stability evaluation of celecoxib nanoemulsion containing Tween 80. Thai J Pharm Sci 32:4–9
Sosnik A, Seremeta KP (2017) Polymeric hydrogels as technology platform for drug delivery applications. Gels 3(3):25
Tiwari S, Amiji M (2006) Nanoemulsion formulations for tumor-targeted delivery. In: Nanotechnology for cancer therapy. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Valdivia FJG, Dachs AC, Perdiguer NC (1997) Nanoemulsion of the oil water type, useful as an ophthalmic vehicle and process for the preparation thereof. Google Patents
Verderio P, Bonetti P, Colombo M, Pandolfi L, Prosperi D (2013) Intracellular drug release from curcumin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles induces G2/M block in breast cancer cells. Biomacromolecules 14(3):672–682
Webber MJ, Dankers PY (2019) Supramolecular hydrogels for biomedical applications. Macromol Biosci 19:1800452
Xiao S, Zhou D, Luan P, Gu B, Feng L, Fan S, Liao W, Fang W, Yang L, Tao E (2016) Graphene quantum dots conjugated neuroprotective peptide improve learning and memory capability. Biomaterials 106:98–110
Zhao T, Liu X, Li Y, Zhang M, He J, Zhang X, Liu H, Wang X, Gu H (2017) Fluorescence and drug loading properties of ZnSe:Mn/ZnS-Paclitaxel/SiO2 nanocapsules templated by F127 micelles. J Colloid Interface Sci 490:436–443
Zhou J, Deng W, Wang Y, Cao X, Chen J, Wang Q, Xu W, Du P, Yu Q, Chen J (2016) Cationic carbon quantum dots derived from alginate for gene delivery: one-step synthesis and cellular uptake. Acta Biomater 42:209–219
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Amna, T., Hassan, M.S., Gharsan, F.N., Rehman, S., Sheikh, F.A. (2022). Nanotechnology in Drug Delivery Systems: Ways to Boost Bioavailability of Drugs. In: Hameed, S., Rehman, S. (eds) Nanotechnology for Infectious Diseases. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-9190-4_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-9190-4_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-9189-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-9190-4
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)