Abstract
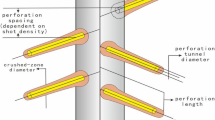
A considerable number of experimental work on the influence of flux ration on wellbore pressure drop in perforated completed horizontal wells has been published by many scholars, but the effects of the wall inflow on the main stream have not been studied systematically. The RNG k-ε turbulence model in computational fluid dynamics software FLUENT was used to simulate the influence of wall inflow on the main stream in perforation completion. Under the condition of different injection ratio (0.1%–80%) the pressure and variation regularity along the wellbore and perforation section with 90° phase angle spiral perforation format is studied. The influence of different wall injection ratio and different viscosity of crude oil on wall total pressure drop is also analyzed. The results of the study show that: Under different injection ratio, the total pressure drop of wellbore increases with the increase of wall injection ratio. The speed of the main stream is less than that of the outlet and the inlet velocity decreases with the increase of wall injection ratio and the exit velocity increases gradually. Moreover, the outlet streamline is more and more densely, and the influx is significantly affected. The inflow velocity increases with the increase of injection ratio, and the wall pressure drop gradually increases. Under the same injection ratio, the pressure drop of high viscosity crude oil well is higher than that of low viscosity crude oil. When the viscosity is 132 cp, the pressure drop in the wellbore section is about 2 times the viscosity of 19 cp crude oil. The flow chart of high viscosity crude is lower than that of viscous crude oil, and the influx is significantly affected by inflow. It can be seen from the pressure cloud map of well bore and perforation section, velocity cloud map and streamline map (whole, entrance and exit) that the pressure drop in the wellbore changes obviously corresponding to the injection ratio of 5%, the main flow velocity is obviously changed corresponding to the injection ratio of 25%. The effects of perforation parameters and injection ratio on the total pressure drop of the wellbore wall are studied in this paper, which provides a scientific basis for the establishment of a well bore pressure drop model in perforated well completion.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ouyang, L.B., Arbabi, S., Aziz, K.: General wellbore flow model for horizontal, vertical, and slanted wells completions. SPE J. 3(2), 124–133 (1998)
Su, Z., Gudmundsson, J.S.: Friction factor of perforation roughness in pipes. In: Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, 3–6 October 1993, Houston, Texas, pp. 151–163. SPE (1993)
Wang, Z., Zhang, S., Xue, L., et al.: Pressure drop of variable mass flow in perforation completion of horizontal wellbore. Oil
Wang, Z., Xiao, J., Wang, X., et al.: Experimental study for pressure drop of variable mass flow in horizontal well. J. Exp. Fluid Mechan. 255, 26–29 (2011)
Sun, Y., Hu, S., Zhao, J., et al.: Numerical study on flow characteristics of 90° bend pipe under different Reynolds number. Univ. Shanghai Sci. Technol., 32(6) , 525–529 (2010)
Clemo, T.: Flow in perforated pipes: a comparison of models and experiments. SPE89036 (2006)
Wang, F.: Principle and Application of CFD Software for Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis. Tsinghua University Press, Beijing (2004)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank China University of Petroleum Beijing for the support during this research and permission to publish this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liu, Ss. (2021). Numerical Simulation Analysis on the Influence of Wall Inflow on Main Stream in Perforation Completion. In: Lin, J. (eds) Proceedings of the International Petroleum and Petrochemical Technology Conference 2020. IPPTC 2020. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-1123-0_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-1123-0_24
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-1122-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-1123-0
eBook Packages: EnergyEnergy (R0)