Abstract
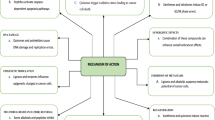
In the present scenario of the twenty-first century, the world is suffering from several alarming health issues that become life-threatening to millions of people. The evolution of multidrug-resistant microorganisms is such a significant problem. Besides that, the drastic rise in different types of cancer, diabetes, or neurodegenerative diseases has become a social disaster for us. For controlling such conditions, there is a continuous search for novel natural products that will be highly effective, specific, less toxic and have a minimal environmental impact. In this context, endophytes may be a better option for drug discovery and development. Endophytes are a promising source of novel bioactive compounds. To date, major reported endophytes are fungi. They are familiar because of their diversity and creative ability to produce secondary metabolites with various pharmaceutical properties like antimicrobial, anticancer, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and antitubercular potentials. Another uniqueness of fungi is that they release an array of active secondary metabolites outside their body, which can be easily accessible to the scientists for the downstream process of drug innovation. Therefore, they are seeking considerable attention from many scientists worldwide to fulfill the scarcity of expensive drugs. Antibacterial compounds from endophytic fungi block different enzymes involved in cell wall biosynthesis, causing impairment in nucleic acid metabolism, DNA repair, and protein synthesis. Anticancer compounds from endophytic fungi show a novel mode of action mainly by inhibiting microtubule depolymerization and polymerization; some impede topoisomerase I and II activity, cell proliferation by restraining cell cycle processes and inducing DNA damage, etc. Anti-inflammatory compounds block inflammatory processes by hindering COX-1, COX-2 activity, by lowering the level of various anti-inflammatory cytokines like IL6, IL8, TNF-α and by inhibiting pro-inflammatory signaling pathways. Thus endophytic fungi have emerged as a potent source of drugs for ameliorating various life-threatening diseases.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelhamid RA, Nafady AM, Abouelela ME, Konno H, El-Khayat ES (2020) Molecular simulation of polyketides isolated from the endophyte Phialophora verrucosa. Trends Phytochem Res 4(1):9–16
Aggarwal BB, Takada Y, Shishodia S, Gutierrez AM, Oommen OV, Ichikawa H, Baba Y, Kumar A (2004) Nuclear transcription factor NF-kappa B: role in biology and medicine. Indian J Exp Biol 42(4):341–353
Allison AC, Cacabelos R, Lombardi VRM, Álvarez XA, Vigo C (2001) Celastrol, a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory drug, as a possible treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 25(7):1341–1357. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0278-5846(01)00192-0
Aly AH, Debbab A, Kjer J, Proksch P (2010) Fungal endophytes from higher plants: a prolific source of phytochemicals and other bioactive natural products. Fungal Divers 41(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13225-010-0034-4
Anaya-Eugenio GD, Ali T, Rakotondraibe LH, Carcache de Blanco E (2019) Cytotoxic constituents from Penicillium concentricum, an endophytic fungus from Trichocolea tomentella. Anti-Cancer Drugs 30(4):323–329. https://doi.org/10.1097/cad.0000000000000759
Arai M, Yamamoto K, Namatame I, Tomoda H, Omura S (2003) New monordens produced by amidepsine-producing fungus Humicola sp. FO-2942. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 56(6):526–532. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.56.526
Arbuck SG, Christian MC, Fisherman JS, Cazenave LA, Sarosy G, Suffness M, Adams J, Canetta R, Cole KE, Friedman MA (1993) Clinical development of taxol. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr (15):11–24
Ariantari NP, Ancheeva E, Frank M, Stuhldreier F, Meier D, Gröner Y, Reimche I, Teusch N, Wesselborg S, Müller WEG, Kalscheuer R, Liu Z, Proksch P (2020) Didymellanosine, a new decahydrofluorene analogue, and ascolactone C from Didymella sp. IEA-3B.1, an endophyte of Terminalia catappa. RSC Adv 10(12):7232–7240. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA10685E
Ariefta NR, Kristiana P, Aboshi T, Murayama T, Tawaraya K, Koseki T, Kurisawa N, Kimura K-I, Shiono Y (2018) New isocoumarins, naphthoquinones, and a cleistanthane-type diterpene from Nectria pseudotrichia 120-1NP. Fitoterapia 127:356–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2018.03.012
Arunpanichlert J, Rukachaisirikul V, Phongpaichit S, Supaphon O, Sakayaroj J (2016) Xylariphilone: a new azaphilone derivative from the seagrass-derived fungus Xylariales sp. PSU-ES163. Nat Prod Res 30(1):46–51. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2015.1032282
Astuti P, Rollando R, Wahyuono S, Nurrochmad A, Garrido G (2020) Antimicrobial activities of isoprene compounds produced by an endophytic fungus isolated from the leaves of Coleus amboinicus Lour. J Pharm Pharmacogn Res 8:280–289
Auluck PK, Chan HYE, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VMY, Bonini NM (2002) Chaperone suppression of alpha-synuclein toxicity in a Drosophila model for Parkinson’s disease. Science 295(5556):865–868. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1067389
Bacon CE, White J (eds) (2000) Microbial endophytes. CRC Press, Boca Raton. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781482277302
Baeuerle PA, Baltimore DJS (1988) I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science 242(4878):540–546
Barnett CJ, Cullinan GJ, Gerzon K, Hoying RC, Jones WE, Newlon WM, Poore GA, Robison RL, Sweeney MJ (1978) Structure-activity relationships of dimeric Catharanthus alkaloids. 1. Deacetyl vinblastine amide (vindesine) sulfate. J Med Chem 21(1):88–96. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm00199a016
Beg AA, Baldwin AS (1993) The I kappa B proteins: multifunctional regulators of Rel/NF-kappa B transcription factors. Genes Dev 7(11):2064–2070
Berrington de Gonzalez A, Gilbert E, Curtis R, Inskip P, Kleinerman R, Morton L, Rajaraman P, Little MP (2013) Second solid cancers after radiation therapy: a systematic review of the epidemiologic studies of the radiation dose-response relationship. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 86(2):224–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.09.001
Brandt GEL, Schmidt MD, Prisinzano TE, Blagg BSJ (2008) Gedunin, a Novel Hsp90 inhibitor: semisynthesis of derivatives and preliminary structure−activity relationships. J Med Chem 51(20):6495–6502. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm8007486
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Brown T, Tangen C, Fleming T, Macdonald J (1993) A phase II trial of taxol and granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) in patients with adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 12:200
Cai C, Chen Y, Zhong S, Ji B, Wang J, Bai X, Shi G (2014) Anti-inflammatory activity of N-butanol extract from Ipomoea stolonifera in vivo and in vitro. PLoS One 9(4):e95931. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0095931
Cai J, Zhou X-M, Yang X, Tang M-M, Liao Q-Y, Meng B-Z, Liao S, Chen G-Y (2020) Three new bioactive natural products from the fungus Talaromyces assiutensis JTY2. Bioorg Chem 94:103362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103362
Cao Y-M, Guo D-L, Jin M-Y, Tan L, Yang T-L, Deng F, Gu Y-C, Li X-H, Cao Z-X, Deng Y (2020) Two new nor-sesquiterpenoids from Fusarium tricinctum, an endophytic fungus isolated from Ligusticum chuanxiong. Nat Prod Res 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2020.1712385
Carelle N, Piotto E, Bellanger A, Germanaud J, Thuillier A, Khayat D (2002) Changing patient perceptions of the side effects of cancer chemotherapy. Cancer 95(1):155–163. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.10630
Carroll GC, Carroll FE (1978) Studies on the incidence of coniferous needle endophytes in the Pacific Northwest. Can J Bot 56(24):3034–3043. https://doi.org/10.1139/b78-367
Chakrabarti S, Jahandideh F, Wu J (2014) Food-derived bioactive peptides on inflammation and oxidative stress. Biomed Res Int 2014:608979
Chandra S (2012) Endophytic fungi: novel sources of anticancer lead molecules. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 95(1):47–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4128-7
Chattopadhyay S, Srivastava A, Bhojwani S, Bisaria VS (2002) Production of podophyllotoxin by plant cell cultures of Podophyllum hexandrum in bioreactor. J Biosci Bioeng 93:215–220. https://doi.org/10.1263/jbb.93.215
Chen Y, Wang B, Liu D, Li J, Xue Y, Sakata K, Zhu L-Q, Heldt S, Xu H, Liao F-F (2014) Hsp90 chaperone inhibitor 17-AAG attenuates A-induced synaptic toxicity and memory impairment. J Neurosci 34:2464–2470. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0151-13.2014
Chen S, Ding M, Liu W, Huang X, Liu Z, Lu Y, Liu H, She Z (2018) Anti-inflammatory meroterpenoids from the mangrove endophytic fungus Talaromyces amestolkiae YX1. Phytochemistry 146:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2017.11.011
Chen Y, Yang W, Zou G, Chen S, Pang J, She Z (2019) Bioactive polyketides from the mangrove endophytic fungi Phoma sp. SYSU-SK-7. Fitoterapia 139:104369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2019.104369
Chen H-L, Zhao W-T, Liu Q-P, Chen H-Y, Zhao W, Yang D-F, Yang X-L (2020a) (±)-Preisomide: a new alkaloid featuring a rare naturally occurring tetrahydro-2H-1,2-oxazin skeleton from an endophytic fungus Preussia isomera by using OSMAC strategy. Fitoterapia 141:104475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2020.104475
Chen L, Fan D-M, Tang J-W, An T, Xue L, Kong L-M, Puno P-T, Li Y (2020b) Discovery of isopenicin A, a meroterpenoid as a novel inhibitor of tubulin polymerization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.02.026
Chomcheon P, Wiyakrutta S, Sriubolmas N, Ngamrojanavanich N, Isarangkul D, Kittakoop P (2005) 3-Nitropropionic acid (3-NPA), a potent antimycobacterial agent from endophytic fungi: is 3-NPA in some plants produced by endophytes? J Nat Prod 68(7):1103–1105. https://doi.org/10.1021/np050036a
Chomcheon P, Sriubolmas N, Wiyakrutta S, Ngamrojanavanich N, Chaichit N, Mahidol C, Ruchirawat S, Kittakoop P (2006) Cyclopentenones, scaffolds for organic syntheses produced by the endophytic fungus mitosporic Dothideomycete sp. LRUB20. J Nat Prod 69(9):1351–1353. https://doi.org/10.1021/np060148h
Cleren C, Calingasan NY, Chen J, Beal MF (2005) Celastrol protects against MPTP- and 3-nitropropionic acid-induced neurotoxicity. J Neurochem 94(4):995–1004. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03253.x
Cragg G, Suffness M (1988) Metabolism of plant-derived anticancer agents. Pharmacol Ther 37(3):425–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/0163-7258(88)90006-x
Cui H, Liu Y, Li J, Huang X, Yan T, Cao W, Liu H, Long Y, She Z (2018) Diaporindenes A–D: four unusual 2,3-dihydro-1H-indene analogues with anti-inflammatory activities from the mangrove endophytic fungus Diaporthe sp. SYSU-HQ3. J Org Chem 83(19):11804–11813. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.8b01738
de Bary A (1866) Morphologie und physiologie der pilze, flechten und myxomyceten. Engelmann, Leipzig
de Medeiros AG, Savi DC, Mitra P, Shaaban KA, Jha AK, Thorson JS, Rohr J, Glienke C (2018) Bioprospecting of Diaporthe terebinthifolii LGMF907 for antimicrobial compounds. Folia Microbiol 63(4):499–505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-018-0587-2
Denning DW (2003) Echinocandin antifungal drugs. Lancet (London, England) 362(9390):1142–1151. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(03)14472-8
Deshmukh SK, Mishra PD, Kulkarni-Almeida A, Verekar S, Sahoo MR, Periyasamy G, Goswami H, Khanna A, Balakrishnan A, Vishwakarma R (2009) Anti-inflammatory and anticancer activity of ergoflavin isolated from an endophytic fungus. Chem Biodivers 6:784–789
Dreyfuss MM, Chapela IH (1994) Potential of fungi in the discovery of novel, low-molecular weight pharmaceuticals. Biotechnology 26:49–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-7506-9003-4.50009-5
Ebada SS, Ebrahim W (2020) A new antibacterial quinolone derivative from the endophytic fungus Aspergillus versicolor strain Eich.5.2.2. S Afr J Bot. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2019.12.004
Einzig AI, Gorowski E, Sasloff J, Wiernik PH (1991a) Phase II trial of taxol in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Investig 9(2):133–136. https://doi.org/10.3109/07357909109044223
Einzig AI, Wiernik PH, Schwartz EL (1991b) Taxol: a new agent active in melanoma and ovarian cancer. In: Muggia FM (ed) New drugs, concepts and results in cancer chemotherapy. Springer, Boston, MA, pp 89–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-3876-9_5
El-Agamy DS, Ibrahim SRM, Ahmed N, Khoshhal S, Abo-Haded HM, Elkablawy MA, Aljuhani N, Mohamed GA (2019) Aspernolide F, as a new cardioprotective butyrolactone against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Int Immunopharmacol 72:429–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2019.04.045
El-Sayed E-S, Ahmed A, Abdelhakim H (2019) A novel source of the cardiac glycoside digoxin from the endophytic fungus Epicoccum nigrum: isolation, characterization, production enhancement by gamma irradiation mutagenesis and anticancer activity evaluation. J Appl Microbiol 128. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14510
Eming SA, Krieg T, Davidson JM (2007) Inflammation in wound repair: molecular and cellular mechanisms. J Investig Dermatol 127(3):514–525. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jid.5700701
Ettinger DS (1993) Taxol in the treatment of lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr (15):177–179
Feng L, Wang J, Liu S, Zhang X-J, Bi Q-R, Hu Y-Y, Wang Z, Tan N-H (2019) Colletopeptides A–D, anti-inflammatory cyclic tridepsipeptides from the plant endophytic fungus Colletotrichum sp. S8. J Nat Prod 82(6):1434–1441. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.8b00829
Fera MT, La Camera E, De Sarro A (2009) New triazoles and echinocandins: mode of action, in vitro activity and mechanisms of resistance. Expert Rev Anti-Infect Ther 7(8):981–998. https://doi.org/10.1586/eri.09.67
Filip P, Weber RW, Sterner O, Anke T (2003) Hormonemate, a new cytotoxic and apoptosis-inducing compound from the endophytic fungus Hormonema dematioides. I. Identification of the producing strain, and isolation and biological properties of hormonemate. Z Naturforschung C (J Biosci) 58(7–8):547–552. https://doi.org/10.1515/znc-2003-7-817
Forastiere AA, Neuberg D, Taylor SG, DeConti R, Adams G (1993) Phase II evaluation of taxol in advanced head and neck cancer: an Eastern Cooperative Oncology group trial. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr (15):181–184
Franck B, Baumann G, Ohnsorge U (1965) Ergochrome, eine ungewöhnlich vollständige gruppe dimerer farbstoffe aus claviceps purpurea. Tetrahedron Lett 6(25):2031–2037. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4039(00)90148-5
Gao N, Shang Z-C, Yu P, Luo J, Jian K-L, Kong L-Y, Yang M-H (2017) Alkaloids from the endophytic fungus Penicillium brefeldianum and their cytotoxic activities. Chin Chem Lett 28(6):1194–1199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2017.02.022
Gao Y, Wang L, Kalscheuer R, Liu Z, Proksch P (2020) Antifungal polyketide derivatives from the endophytic fungus Aplosporella javeedii. Bioorg Med Chem 28(10):115456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115456
Goutam J, Sharma G, Tiwari VK, Mishra A, Kharwar RN, Ramaraj V, Koch B (2017) Isolation and characterization of “terrein” an antimicrobial and antitumor compound from endophytic fungus Aspergillus terreus (JAS-2) associated from Achyranthus aspera Varanasi, India. Front Microbiol 8:1334. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01334
Guo B, Li H, Zhang L (1998) Isolation of an fungus producting vinbrastine. J Yunnan Univ Nat Sci Ed 20(3):214–215
Guo L, Niu S, Chen S, Liu L (2020) Diaporone A, a new antibacterial secondary metabolite from the plant endophytic fungus Diaporthe sp. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 73(2):116–119. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-019-0251-3
Haidle AM, Myers AG (2004) An enantioselective, modular, and general route to the cytochalasins: synthesis of L-696,474 and cytochalasin B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(33):12048. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0402111101
Hamaguchi T, Ono K, Yamada M (2010) Review: curcumin and Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurosci Ther 16(5):285–297. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-5949.2010.00147.x
Hilario F, Polinário G, de Amorim MR, de Sousa Batista V, do Nascimento Júnior NM, Araújo AR, Bauab TM, dos Santos LC (2020) Spirocyclic lactams and curvulinic acid derivatives from the endophytic fungus Curvularia lunata and their antibacterial and antifungal activities. Fitoterapia 141:104466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2019.104466
Holmes FA, Walters RS, Theriault RL, Forman AD, Newton LK, Raber MN, Buzdar AU, Frye DK, Hortobagyi GN (1991) Phase II trial of taxol, an active drug in the treatment of metastatic breast cancer. J Natl Cancer I 83(24):1797–1805. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/83.24.1797-a
Horn WS, Simmonds MSJ, Schwartz RE, Blaney WM (1995) Phomopsichalasin, a novel antimicrobial agent from an endophytic Phomopsis sp. Tetrahedron 51:3969–3978
Horwitz SB, Lothstein L, Manfredi JJ, Mellado W, Parness J, Roy SN, Schiff PB, Sorbara L, Zeheb R (1986) Taxol: mechanisms of action and resistance. Ann N Y Acad Sci 466:733–744. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb38455.x
Ibrahim SRM, Abdallah HM, Elkhayat ES, Al Musayeib NM, Asfour HZ, Zayed MF, Mohamed GA (2018) Fusaripeptide A: new antifungal and anti-malarial cyclodepsipeptide from the endophytic fungus Fusarium sp. J Asian Nat Prod Res 20(1):75–85. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286020.2017.1320989
Jennewein S, Rithner C, Williams R, Croteau R (2001) Taxol biosynthesis: taxane 13α-hydroxylase is a cytochrome P450-dependent monooxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:13595–13600. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.251539398
Kettering M, Weber D, Sterner O, Anke T (2004) Secondary metabolites from fungi—functions and applications. BIOspektrum 10:147–149
Kharwar RN, Mishra A, Gond SK, Stierle A, Stierle D (2011) Anticancer compounds derived from fungal endophytes: their importance and future challenges. Nat Prod Rep 28(7):1208–1228. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1np00008j
Khayat MT, Ibrahim SRM, Mohamed GA, Abdallah HM (2019) Anti-inflammatory metabolites from endophytic fungus Fusarium sp. Phytochem Lett 29:104–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2018.11.024
Kumar S, Nalli Y, Qadri M, Riyaz-Ul-Hassan S, Satti NK, Gupta V, Bhushan S, Ali A (2017) Isolation of three new metabolites and intervention of diazomethane led to separation of compound 1 & 2 from an endophytic fungus, Cryptosporiopsis sp. depicting cytotoxic activity. Med Chem Res 26(11):2900–2908. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-017-1989-4
Kusari S, Spiteller M (2011) Are we ready for industrial production of bioactive plant secondary metabolites utilizing endophytes? Nat Prod Rep 28(7):1203–1207. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1np00030f
Kusari S, Lamshöft M, Zühlke S, Spiteller M (2008) An endophytic fungus from Hypericum perforatum that produces hypericin. J Nat Prod 71:159–162. https://doi.org/10.1021/np070669k
Kusari S, Zühlke S, Spiteller M (2009) An endophytic fungus from Camptotheca acuminata that produces camptothecin and analogues. J Nat Prod 72(1):2–7. https://doi.org/10.1021/np800455b
Kusari S, Hertweck C, Spiteller M (2012) Chemical ecology of endophytic fungi: origins of secondary metabolites. Chem Biol 19(7):792–798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2012.06.004
Kwon HJ, Yoshida M, Nagaoka R, Obinata T, Beppu T, Horinouchi S (1997) Suppression of morphological transformation by radicicol is accompanied by enhanced gelsolin expression. Oncogene 15(21):2625–2631. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201443
Lee W-G, Kim W-S, Park S-G, Kim H, Hong J, Ko H, Kim Y-C (2012) Immunosuppressive effects of subglutinol derivatives. Chem Med Chem 7(2):218–222. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.201100409
Lee C, Kim S, Li W, Bang S, Lee H, Lee H-J, Noh E-Y, Park J-E, Bang WY, SHJTJoa S (2017) Bioactive secondary metabolites produced by an endophytic fungus Gaeumannomyces sp. JS0464 from a maritime halophyte Phragmites communis. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 70(6):737–742
Lei H, Lin X, Han L, Ma J, Ma Q, Zhong J, Sun T, Wang J, Huang X (2017) New metabolites and bioactive chlorinated benzophenone derivatives produced by a marine-derived fungus Pestalotiopsis heterocornis. Mar Drugs 15:69. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15030069
Li JY, Harper JK, Grant DM, Tombe BO, Bashyal B, Hess WM, Strobel GA (2001) Ambuic acid, a highly functionalized cyclohexenone with antifungal activity from Pestalotiopsis spp. and Monochaetia sp. Phytochemistry 56(5):463–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(00)00408-8
Li E, Tian R, Liu S, Chen X, Guo L, Che Y (2008) Pestalotheols A-D, bioactive metabolites from the plant endophytic fungus Pestalotiopsis theae. J Nat Prod 71(4):664–668. https://doi.org/10.1021/np700744t
Li CS, Yang BJ, Turkson J, Cao S (2017a) Anti-proliferative ambuic acid derivatives from Hawaiian endophytic fungus Pestalotiopsis sp. FT172. Phytochemistry 140:77–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2017.04.017
Li W, Lee C, Bang SH (2017b) Isochromans and related constituents from the endophytic fungus Annulohypoxylon truncatum of Zizania caduciflora and their anti-inflammatory effects. J Nat Prod 80(1):205–209. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00698
Li F, Guo W, Wu L, Zhu T, Gu Q, Li D, Che Q (2018) Saroclazines A-C, thio-diketopiperazines from mangrove-derived fungi Sarocladium kiliense HDN11-84. Arch Pharm Res 41(1):30–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-017-0961-7
Li W-Y, Liu Y, Lin Y-T, Liu Y-C, Guo K, Li X-N, Luo S-H, Li S-H (2020) Antibacterial harziane diterpenoids from a fungal symbiont Trichoderma atroviride isolated from Colquhounia coccinea var. mollis. Phytochemistry 170:112198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2019.112198
Liang H (2008) Sordarin, an antifungal agent with a unique mode of action. Beilstein J Org Chem 4:31. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjoc.4.31
Liao G, Wu P, Xue J, Liu L, Li H, Wei X (2018) Asperimides A–D, anti-inflammatory aromatic butenolides from a tropical endophytic fungus Aspergillus terreus. Fitoterapia 131:50–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2018.10.011
Lin PY, Simon SM, Koh WK, Folorunso O, Umbaugh CS, Pierce A (2013) Heat shock factor 1 over-expression protects against exposure of hydrophobic residues on mutant SOD1 and early mortality in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Mol Neurodegener 8:43. https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1326-8-43
Lin R, Kim H, Hong J, Li QJ (2014) Biological evaluation of subglutinol a as a novel immunosuppressive agent for inflammation intervention. ACS Med Chem Lett 5(5):485–490. https://doi.org/10.1021/ml4004809
Liu Y, Stuhldreier F, Kurtán T, Mándi A, Arumugam S, Lin W, Stork B, Wesselborg S, Weber H, Henrich B, Daletos G, Proksch P (2018a) Daldinone derivatives from the mangrove-derived endophytic fungus Annulohypoxylon sp. RSC Adv. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA27306H
Liu Z, Liu H, Chen Y, She Z (2018b) A new anti-inflammatory meroterpenoid from the fungus Aspergillus terreus H010. Nat Prod Res 32(22):2652–2656. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2017.1375924
Liu W, Chen S, Li J, Yang X, Yan C, Liu H (2019a) A new β-tetralonyl glucoside from the Santalum album derived endophytic fungus Colletotrichum sp. GDMU-1. Nat Prod Res 33(3):354–359. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2018.1452003
Liu X-B, Zheng N, Liang L-Q, Zhao D-M, Qin Y-Y, Li J, Yang R-Y (2019b) Secondary metabolites from the endophytic fungus Fusarium equiseti and their antibacterial activities. Chem Nat Compd 55(6):1141–1144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-019-02915-0
Liu Y, Ruan Q, Jiang S, Qu Y, Chen J, Zhao M, Yang B, Liu Y, Zhao Z, Cui H (2019c) Cytochalasins and polyketides from the fungus Diaporthe sp. GZU-1021 and their anti-inflammatory activity. Fitoterapia 137:104187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2019.104187
Luo X, Lin X, Tao H, Wang J, Li J, Yang B, Zhou X, Liu Y (2018) Isochromophilones A–F, cytotoxic chloroazaphilones from the marine mangrove endophytic fungus Diaporthe sp. SCSIO 41011. J Nat Prod 81(4):934–941. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.7b01053
Ma Y, Wu X, Xiu Z, Liu X, Huang B, Hu L, Liu J, Zhou Z, Tang X (2018) Cytochalasin H isolated from mangrove-derived endophytic fungus induces apoptosis and inhibits migration in lung cancer cells. Oncol Rep 39:2899–2905. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2018.6347
Majumder A, Jha S (2009) Biotechnological approaches for the production of potential anticancer leads podophyllotoxin and paclitaxel: an overview. J Biol Sci 1:46–69
Maloney A, Workman P (2002) HSP90 as a new therapeutic target for cancer therapy: the story unfolds. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2(1):3–24. https://doi.org/10.1517/14712598.2.1.3
Mao Z, Xue M, Gu G, Wang W, Li D, Lai D, Zhou L (2020) Lophiostomin A–D: new 3,4-dihydroisocoumarin derivatives from the endophytic fungus Lophiostoma sp. Sigrf10. RSC Adv 10:6985–6991. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA00538J
Markman M (1991) Taxol: an important new drug in the management of epithelial ovarian cancer. Yale J Biol Med 64(6):583–590
Marron MT, Gunatilaka AAL (2007) Potential anticancer natural products from plant-associated fungi. In: Selected topics in the chemistry of natural products. World Scientific, Singapore, pp 471–502. https://doi.org/10.1142/9789812790781_0014
Martinez-Klimova E, Rodríguez-Peña K, Sánchez S (2017) Endophytes as sources of antibiotics. Biochem Pharmacol 134:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2016.10.010
Mawabo IK, Nkenfou C, Notedji A, Jouda JB, Lunga PK, Eke P, Fokou VT, Kuiate JR (2019) Antimicrobial activities of two secondary metabolites isolated from Aspergillus niger, endophytic fungus harbouring stems of Acanthus montanus. Biol Sci Pharm Res 7(1):7–15. https://doi.org/10.15739/ibspr.19.002
McGuire WP, Rowinsky EK, Rosenshein NB, Grumbine FC, Ettinger DS, Armstrong DK, Donehower RC (1989) Taxol: a unique antineoplastic agent with significant activity in advanced ovarian epithelial neoplasms. Ann Intern Med 111(4):273–279. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-111-4-273
Mendillo ML, Santagata S, Koeva M, Bell GW, Hu R, Tamimi RM, Fraenkel E, Ince TA, Whitesell L, Lindquist S (2012) HSF1 drives a transcriptional program distinct from heat shock to support highly malignant human cancers. Cell 150(3):549–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.06.031
Meng L, Gabai VL, Sherman MY (2010) Heat-shock transcription factor HSF1 has a critical role in human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-induced cellular transformation and tumorigenesis. Oncogene 29(37):5204–5213. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.277
Mirrington RN, Ritchie E, Shoppee CW, Sternhell S, Taylor WC (1966) Some metabolites of Nectria radicicola Gerlach & Nilsson (syn. Cylindrocarpon radicicola Wr.): the structure of radicicol (monorden). Aust J Chem 19(7):1265–1284
Misra S, Verma M, Mishra SK, Srivastava S, Lakshmi V, Misra-Bhattacharya S (2011) Gedunin and photogedunin of Xylocarpus granatum possess antifilarial activity against human lymphatic filarial parasite Brugia malayi in experimental rodent host. Parasitol Res 109(5):1351–1360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2380-x
Mittermeier R, Gil P, Hoffmann M, Pilgrim J, Brooks T, Mittermeier C, Lamoreux J, Fonseca G (2004) Hotspots revisited. Earth’s biologically richest and most endangered terrestrial ecoregions, vol 392. CEMEX, Mexico City
Mohamed GA, Ibrahim SRM, Asfour HZ (2020) Antimicrobial metabolites from the endophytic fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Phytochem Lett 35:152–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2019.12.003
Neckers L, Neckers K (2002) Heat-shock protein 90 inhibitors as novel cancer chemotherapeutic agents. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 7(2):277–288. https://doi.org/10.1517/14728214.7.2.277
Nisa H, Kamili AN, Nawchoo IA, Shafi S, Shameem N, Bandh SA (2015) Fungal endophytes as prolific source of phytochemicals and other bioactive natural products: a review. Microb Pathog 82:50–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2015.04.001
Noble HM, Langley D, Sidebottom PJ, Lane SJ, Fisher PJ (1991) An echinocandin from an endophytic Cryptosporiopsis sp. and Pezicula sp. in Pinus sylvestris and Fagus sylvatica. Mycol Res 95(12):1439–1440. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0953-7562(09)80401-2
Nozawa K, Nakajima S (2004) Isolation of radicicol from Penicillium luteo-aurantium, and meleagrin, a new metabolite from Penicillium meleagrinum. J Nat Prod 42:374–377. https://doi.org/10.1021/np50004a004
Nurgali K, Jagoe RT, Abalo R (2018) Editorial: Adverse effects of cancer chemotherapy: anything new to improve tolerance and reduce sequelae? Front Pharmacol 9:245–245. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00245
Pal S, Bhattacharjee A, Ali A, Mandal NC, Mandal SC, Pal M (2014) Chronic inflammation and cancer: potential chemoprevention through nuclear factor kappa B and p53 mutual antagonism. J Inflamm (London, England) 11:23. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-9255-11-23
Pan L, Chai HB, Kinghorn AD (2012) Discovery of new anticancer agents from higher plants. Front Biosci (Scholar edition) 4:142–156. https://doi.org/10.2741/257
Pan F, El-Kashef DH, Kalscheuer R, Müller WEG, Lee J, Feldbrügge M, Mándi A, Kurtán T, Liu Z, Wu W, Proksch P (2020) Cladosins L-O, new hybrid polyketides from the endophytic fungus Cladosporium sphaerospermum WBS017. Eur J Med Chem 191:112159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112159
Park MH, Hong JT (2016) Roles of NF-κB in cancer and inflammatory diseases and their therapeutic approaches. Cell 5(2):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells5020015
Parthasarathy R, Shanmuganathan R, Pugazhendhi A (2020) Vinblastine production by the endophytic fungus Curvularia verruculosa from the leaves of Catharanthus roseus and its in vitro cytotoxicity against HeLa cell line. Anal Biochem 593:113530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2019.113530
Patel B, Das S, Prakash R, Yasir M (2010) Natural bioactive compound with anticancer potential. Int J Res Pharm Biomed Sci 1:32–41. https://doi.org/10.5138/ijaps.2010.0976.1055.01003
Patil RH, Patil MP, Maheshwari VL (2016) Chapter 5—Bioactive secondary metabolites from endophytic fungi: a review of biotechnological production and their potential applications. In: Atta Ur R (ed) Studies in natural products chemistry, vol 49. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 189–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-63601-0.00005-3
Patjana T, Jantaharn P, Katrun P, Mongkolthanaruk W, Suwannasai N, Senawong T, Tontapha S, Amornkitbumrung V, McCloskey S (2019) Anti-inflammatory and cytotoxic agents from Xylaria sp. SWUF09-62 fungus. Nat Prod Res 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2019.1652292
Patwardhan CA, Fauq A, Peterson LB, Miller C, Blagg BSJ, Chadli A (2013) Gedunin inactivates the co-chaperone p23 protein causing cancer cell death by apoptosis. J Biol Chem 288(10):7313–7325. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.427328
Pearce A, Haas M, Viney R, Pearson SA, Haywood P, Brown C, Ward R (2017) Incidence and severity of self-reported chemotherapy side effects in routine care: a prospective cohort study. PLoS One 12(10):e0184360. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0184360
Pérez-Bonilla M, González-Menéndez V, Pérez-Victoria I, de Pedro N, Martín J, Molero-Mesa J, Casares-Porcel M, González-Tejero MR, Vicente F, Genilloud O, Tormo JR, Reyes F (2017) Hormonemate derivatives from Dothiora sp., an endophytic fungus. J Nat Prod 80(4):845–853. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00680
Petrini O (1991) Fungal endophytes of tree leaves. In: Andrews JH, Hirano SS (eds) Microbial ecology of leaves. Springer, New York, pp 179–197
Prabha P, Suganya K, Murugan D, Alagusundaram P, Murugan M (2019) Purification, crystallization and anti-cancer activity evaluation of the compound Alternariol Methyl Ether (AME) from endophytic fungi Alternaria alternata. J Appl Microbiol 127. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14410
Puri S, Verma V, Amna T, Qazi G, Spiteller M (2006) An endophytic fungus from Nothapodytes foetida that produces camptothecin. J Nat Prod 68:1717–1719. https://doi.org/10.1021/np0502802
Qi C, Gao W, Wang J, Liu M, Zhang J, Chen C, Hu Z, Xue Y, Li D, Zhang Q, Lai Y, Zhou Q, Zhu H, Zhang Y (2018) Terrusnolides A-D, new butenolides with anti-inflammatory activities from an endophytic Aspergillus from Tripterygium wilfordii. Fitoterapia 130:134–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2018.08.021
Qiu L, Wang P, Liao G, Zeng Y, Cai C, Kong F, Guo Z, Proksch P, Dai H, Mei W (2018) New eudesmane-type sesquiterpenoids from the mangrove-derived endophytic fungus Penicillium sp. J-54. Mar Drugs 16(4):108. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16040108
Qu H-R, Yang W-W, Zhang X-Q, Lu Z-H, Deng Z-S, Guo Z-Y, Cao F, Zou K, Proksch P (2020) Antibacterial bisabolane sesquiterpenoids and isocoumarin derivatives from the endophytic fungus Phomopsis prunorum. Phytochem Lett 37:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2020.03.003
Rajuw S (2009) NSAIDs (including aspirin): allergic and pseudoallergic reactions. UpToDate Inc.
Ran X, Zhang G, Li S, Wang J (2017) Characterization and antitumor activity of camptothecin from endophytic fungus Fusarium solani isolated from Camptotheca acuminate. Afr Health Sci 17(2):566–574. https://doi.org/10.4314/ahs.v17i2.34
Rodriguez R, Redman R (2005) Balancing the generation and elimination of reactive oxygen species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(9):3175–3176. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0500367102
Rostom A, Dubé C, Lewin G, Tsertsvadze A, Barrowman N, Code C, Sampson M, Moher D (2007a) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors for primary prevention of colorectal cancer: a systematic review prepared for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann Intern Med 146(5):376–389. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-146-5-200703060-00010
Rostom A, Muir K, Dubé C, Jolicoeur E, Boucher M, Joyce J, Tugwell P, Wells GW (2007b) Gastrointestinal safety of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors: a Cochrane Collaboration systematic review. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 5(7):818–828, 828.e811–815; quiz 768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2007.03.011
Roth SH (2012) Coming to terms with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug gastropathy. Drugs 72(7):873–879. https://doi.org/10.2165/11633740-000000000-00000
Roth BJ, Yeap BY, Wilding G, Kasimis B, McLeod D, Loehrer PJ (1993) Taxol in advanced, hormone-refractory carcinoma of the prostate. A phase II trial of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Cancer 72(8):2457–2460. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(19931015)72:8<2457::aid-cncr2820720825>3.0.co;2-z
Ruan B-H, Yu Z-F, Yang X-Q, Yang Y-B, Hu M, Zhang Z-X, Zhou Q-Y, Zhou H, Ding Z-T (2018) New bioactive compounds from aquatic endophyte Chaetomium globosum. Nat Prod Res 32(9):1050–1055. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2017.1378210
Safe S, Taylor A (1972) Sporidesmins. Part XIII. Ovine III-thrift in Nova Scotia. Part III. The characterisation of chetomin a toxic metabolite of Chaetomium cochliodes and Chaetomium globosum. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans I 4:472–479. https://doi.org/10.1039/P19720000472
Schiff PB, Fant J, Auster LA, Horwitz SB (1978) Effects of taxol on cell growth and in vitro microtubule assembly. J Cell Biochem Suppl 2(Suppl):328
Schulz B, Boyle C, Draeger S, Römmert A-K, Krohn K (2002) Endophytic fungi: a source of novel biologically active secondary metabolites* *Paper presented at the British Mycological Society symposium on Fungal Bioactive Compounds, held at the University of Wales Swansea on 22–27 April 2001. Mycol Res 106(9):996–1004. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0953756202006342
Schulz B, Haas S, Junker C, Andrée-Busch N, Schobert M (2015) Fungal endophytes are involved in multiple balanced antagonisms. Curr Sci 109:39–45
Senthil Kumar V, Kumaresan S, Tamizh MM, Hairul Islam MI, Thirugnanasambantham K (2019) Anticancer potential of NF-κB targeting apoptotic molecule “flavipin” isolated from endophytic Chaetomium globosum. Phytomedicine 61:152830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2019.152830
Sharma N, Kushwaha M, Arora D, Jain S, Singamaneni V, Sharma S, Shankar R, Bhushan S, Gupta P, Jaglan S (2018) New cytochalasin from Rosellinia sanctae-cruciana, an endophytic fungus of Albizia lebbeck. J Appl Microbiol 125. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13764
Singh BK, Vatsa N, Nelson VK, Kumar V, Kumar SS, Mandal SC, Pal M, Jana NR (2018) Azadiradione restores protein quality control and ameliorates the disease pathogenesis in a mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 55(8):6337–6346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0853-3
Song R-Y, Liu Y, Liu R-H, Wang X-B, Li T-X, Kong L-Y, Yang M-H (2017) Benzophenone derivatives from the plant endophytic fungus, Pestalotiopsis sp. Phytochem Lett 22:189–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2017.10.006
Staniek A, Woerdenbag HJ, Kayser O (2008) Endophytes: exploiting biodiversity for the improvement of natural product-based drug discovery. J Plant Interact 3(2):75–93. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429140801886293
Stierle AA, Stierle DB (2015) Bioactive secondary metabolites produced by the fungal endophytes of conifers. Nat Prod Commun 10(10):1671–1682
Stierle A, Strobel G, Stierle D (1993) Taxol and taxane production by Taxomyces andreanae, an endophytic fungus of Pacific yew. Science 260(5105):214–216. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.8097061
Stierle A, Strobel G, Stierle D, Grothaus P, Bignami G (1995) The search for a taxol-producing microorganism among the endophytic fungi of the Pacific Yew, Taxus brevifolia. J Nat Prod 58:1315–1324. https://doi.org/10.1021/np50123a002
Strobel G, Daisy B (2003) Bioprospecting for microbial endophytes and their natural products. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 67(4):491–502. https://doi.org/10.1128/mmbr.67.4.491-502.2003
Strobel G, Daisy B, Castillo U, Harper J (2004) Natural products from endophytic microorganisms. J Nat Prod 67(2):257–268. https://doi.org/10.1021/np030397v
Suresh G, Kokila D, Suresh TC, Kumaran S, Velmurugan P, Vedhanayakisri KA, Sivakumar S, Ravi AV (2020) Mycosynthesis of anticancer drug taxol by Aspergillus oryzae, an endophyte of Tarenna asiatica, characterization, and its activity against a human lung cancer cell line. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 24:101525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101525
Tanaka A, Christensen MJ, Takemoto D, Park P, Scott B (2006) Reactive oxygen species play a role in regulating a fungus-perennial ryegrass mutualistic interaction. Plant Cell 18(4):1052–1066. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.105.039263
Tang J-W, Kong L-M, Zu W-Y, Hu K, Li X-N, Yan B-C, Wang W-G, Sun H-D, Li Y, Puno P-T (2019) Isopenicins A–C: two types of antitumor meroterpenoids from the plant endophytic fungus Penicillium sp. sh18. Org Lett 21(3):771–775. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.8b04020
Tantapakul C, Promgool T, Kanokmedhakul K, Soytong K, Song J, Hadsadee S, Jungsuttiwong S, Kanokmedhakul S (2020) Bioactive xanthoquinodins and epipolythiodioxopiperazines from Chaetomium globosum 7s-1, an endophytic fungus isolated from Rhapis cochinchinensis (Lour.) Mart. Nat Prod Res 34(4):494–502. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2018.1489392
Tawfike AF, Romli M, Clements C, Abbott G, Young L, Schumacher M, Diederich M, Farag M, Edrada-Ebel R (2019) Isolation of anticancer and anti-trypanosome secondary metabolites from the endophytic fungus Aspergillus flocculus via bioactivity guided isolation and MS based metabolomics. J Chromatogr B 1106–1107:71–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.12.032
Teiten MH, Reuter S, Schmucker S, Dicato M, Diederich M (2009) Induction of heat shock response by curcumin in human leukemia cells. Cancer Lett 279(2):145–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2009.01.031
Tenguria R, Khan F, Kalam S (2011) Endophytes—mines of pharmacological therapeutics. World J Sci Technol 1:127–149
Turbyville TJ, Wijeratne EM, Whitesell L, Gunatilaka AA (2005) The anticancer activity of the fungal metabolite terrecyclic acid A is associated with modulation of multiple cellular stress response pathways. Mol Cancer Ther 4(10):1569–1576. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.mct-05-0050
Turbyville TJ, Wijeratne EM, Liu MX, Burns AM, Seliga CJ, Luevano LA, David CL, Faeth SH, Whitesell L, Gunatilaka AA (2006) Search for Hsp90 inhibitors with potential anticancer activity: isolation and SAR studies of radicicol and monocillin I from two plant-associated fungi of the Sonoran desert. J Nat Prod 69(2):178–184. https://doi.org/10.1021/np058095b
Ukwatta KM, Lawrence JL, Wijayarathne CD (2019) Antimicrobial, anti-cancer, anti-filarial and anti-inflammatory activities of Cowabenzophenone A extracted from the endophytic fungus Aspergillus terreus isolated from a mangrove plant Bruguiera gymnorrhyza. Mycology 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/21501203.2019.1707722
Verma SC, Ladha JK, Tripathi AK (2001) Evaluation of plant growth promoting and colonization ability of endophytic diazotrophs from deep water rice. J Biotechnol 91(2–3):127–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-1656(01)00333-9
Verma VC, Gond SK, Kumar A, Mishra A, Kharwar RN, Gange AC (2009) Endophytic actinomycetes from Azadirachta indica A. Juss.: isolation, diversity, and anti-microbial activity. Microb Ecol 57(4):749–756. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-008-9450-3
Viziteu E, Grandmougin C, Goldschmidt H, Seckinger A, Hose D, Klein B, Moreaux J (2016) Chetomin, targeting HIF-1p300 complex, exhibits antitumour activity in multiple myeloma. Br J Cancer 114:519–523. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2016.20
Wagenaar MM, Corwin J, Strobel G, Clardy J (2000) Three new cytochalasins produced by an endophytic fungus in the genus Rhinocladiella. J Nat Prod 63(12):1692–1695. https://doi.org/10.1021/np0002942
Wani MC, Taylor HL, Wall ME, Coggon P, McPhail AT (1971) Plant antitumor agents. VI. The isolation and structure of taxol, a novel antileukemic and antitumor agent from Taxus brevifolia. J Am Chem Soc 93(9):2325–2327. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00738a045
Weber D, Sterner O, Anke T, Gorzalczancy S, Martino V, Acevedo C (2004) Phomol, a new antiinflammatory metabolite from an endophyte of the medicinal plant Erythrina crista-galli. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 57(9):559–563. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.57.559
Wen J, You KR, Lee SY, Song CH, Kim DG (2002) Oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis. The anticancer effect of the sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide. J Biol Chem 277(41):38954–38964. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M203842200
Wen Y, Lv Y, Hao J, Chen H, Huang Y, Liu C, Huang H, Ma Y, Yang X (2019) Two new compounds of Penicillium polonicum, an endophytic fungus from Camptotheca acuminata Decne. Nat Prod Res 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2019.1569003
Westerheide SD, Bosman JD, Mbadugha BN, Kawahara TL, Matsumoto G, Kim S, Gu W, Devlin JP, Silverman RB, Morimoto RI (2004) Celastrols as inducers of the heat shock response and cytoprotection. J Biol Chem 279(53):56053–56060. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M409267200
Whitesell L, Lindquist SL (2005) HSP90 and the chaperoning of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 5(10):761–772. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1716
Wilson D (1995) Endophyte: the evolution of a term, and clarification of its use and definition. Oikos 73(2):274–276. https://doi.org/10.2307/3545919
Wu Y, Chen S (2019) Cytotoxic isocoumarin derivatives from the mangrove endophytic fungus Aspergillus sp. HN15-5D. Arch Pharm Res 42(4):326–331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-018-1019-1
Xiao J, Hu JY, Sun HD, Zhao X, Zhong WT, Duan DZ, Wang L, Wang XL (2018) Sinopestalotiollides A-D, cytotoxic diphenyl ether derivatives from plant endophytic fungus Pestalotiopsis palmarum. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 28(3):515–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2017.11.044
Xu K, Zhang X, Chen JW, Shen Y, Jiang N, Tan RX, Jiao RH, Ge HM (2019) Anti-inflammatory diterpenoids from an endophytic fungus Phomopsis sp. S12. Tetrahedron Lett 60(38):151045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2019.151045
Yan C, Liu W, Li J, Deng Y, Chen S, Liu H (2018) Bioactive terpenoids from Santalum album derived endophytic fungus Fusarium sp. YD-2. RSC Adv 8:14823–14828. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA02430H
Yang ZQ, Geng X, Solit D, Pratilas CA, Rosen N, Danishefsky SJ (2004) New efficient synthesis of resorcinylic macrolides via ynolides: establishment of cycloproparadicicol as synthetically feasible preclinical anticancer agent based on Hsp90 as the target. J Am Chem Soc 126(25):7881–7889. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0484348
Yang Y-H, Yang D-S, Li G-H, Pu X-J, Mo M-H, Zhao P-J (2019) Antibacterial diketopiperazines from an endophytic fungus Bionectria sp. Y1085. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 72(10):752–758. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-019-0209-5
Yu Y, Hamza A, Zhang T, Gu M, Zou P, Newman B, Li Y, Gunatilaka AAL, Zhan C-G, Sun D (2010) Withaferin A targets heat shock protein 90 in pancreatic cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol 79(4):542–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2009.09.017
Yu F-X, Chen Y, Yang Y-H, Li G-H, Zhao P-J (2018) A new epipolythiodioxopiperazine with antibacterial and cytotoxic activities from the endophytic fungus Chaetomium sp. M336. Nat Prod Res 32(6):689–694. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2017.1338285
Yu S, Zhu YX, Peng C, Li J (2019) Two new sterol derivatives isolated from the endophytic fungus Aspergillus tubingensis YP-2. Nat Prod Res 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2019.1696793
Zhang L, Guo B, Li H, Zeng S, Shao H, Gu S, Wei R (2000) Preliminary study on the isolation of endophytic fungus of Catharanthus roseus and its fermentation to produce products of therapeutic value. Chin Trad Herbal Drugs (Zhong Cao Yao) 31(11):805–807
Zhang H, Chung D, Yang Y-C, Neely L, Tsurumoto S, Fan J, Zhang L, Biamonte M, Brekken J, Lundgren K, Burrows F (2006) Identification of new biomarkers for clinical trials of Hsp90 inhibitors. Mol Cancer Ther 5:1256–1264. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-05-0537
Zhang T, Hamza A, Cao X, Wang B, Yu S, Zhan CG, Sun D (2008) A novel Hsp90 inhibitor to disrupt Hsp90/Cdc37 complex against pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 7(1):162–170. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.mct-07-0484
Zhang X, Timmermann B, Samadi AK, Cohen MS (2012) Withaferin a induces proteasome-dependent degradation of breast cancer susceptibility gene 1 and heat shock factor 1 proteins in breast cancer cells. ISRN Biochem 2012:707586. https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/707586
Zhang Q, Luan R, Li H, Liu Y, Liu P, Wang L, Li D, Wang M, Zou Q, Liu H, Matsuzaki K, Zhao F (2018) Anti-inflammatory action of ambuic acid, a natural product isolated from the solid culture of Pestalotiopsis neglecta, through blocking ERK/JNK mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med 16(2):1538–1546. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2018.6294
Zhang P, Jia C, Deng Y, Chen S, Chen B, Yan S, Li J, Liu L (2019) Anti-inflammatory prenylbenzaldehyde derivatives isolated from Eurotium cristatum. Phytochemistry 158:120–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2018.11.017
Zhao JL, Zhang M, Liu JM, Tan Z, Chen RD, Xie KB, Dai JG (2017) Bioactive steroids and sorbicillinoids isolated from the endophytic fungus Trichoderma sp. Xy24. J Asian Nat Prod Res 19(10):1028–1035. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286020.2017.1285908
Zhao M, Yuan LY, Guo DL, Ye Y, Da-Wa ZM, Wang XL, Ma FW, Chen L, Gu YC, Ding LS, Zhou Y (2018) Bioactive halogenated dihydroisocoumarins produced by the endophytic fungus Lachnum palmae isolated from Przewalskia tangutica. Phytochemistry 148:97–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2018.01.018
Zheng CJ, Liao HX, Mei RQ, Huang GL, Yang LJ, Zhou XM, Shao TM, Chen GY, Wang CY (2019) Two new benzophenones and one new natural amide alkaloid isolated from a mangrove-derived Fungus Penicillium citrinum. Nat Prod Res 33(8):1127–1134. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2018.1460832
Zhou L, Zhao J, Xu L, Huang Y, Ma Z, Wang J, Jiang W (2009) Antimicrobial compounds produced by plant endophytic fungi, pp 91–119
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to Dr. Surendra Kumar Gond for providing some important references and reviewing the MS carefully. SG thanks CSIR for a Research Fellowship (ad-hoc).
Declaration: All authors declare they have no conflicts of interest. This article does not contain any studies with animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Samanta, S., Ghosh, S., Mandal, N.C. (2021). Endophytic Fungi: A Source of Novel Pharmaceutical Compounds. In: Patil, R.H., Maheshwari, V.L. (eds) Endophytes. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-9371-0_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-9371-0_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-9370-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-9371-0
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)