Abstract
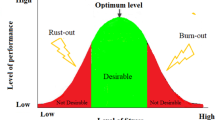
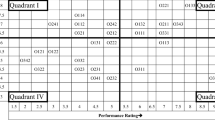
The current research focuses on the study of stress in software employees using multi-grade fuzzy (MGF) approach and importance-performance analysis (IPA). Stress is a common factor in most of the IT sector employees. A model for assessing the stress was developed by applying MGF. A software company has been selected as a model to perform employee stress assessment by applying MGF to obtain the stress index. The result of the application had indicated significant employee stress in the case study. The areas which need immediate attention to alleviate employee stress had been identified and suggested using the IPA analysis. The current framework developed would help to measure the stress in other software organizations and help them to provide attention to their weaker attributes to overcome employee stress.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mucci N, Giorgi G, Cupelli V, Gioffrè PA, Rosati MV, Tomei G, Breso-Esteve E, Arcangeli G (2015) Work-related stress assessment in a population of Italian workers. The stress questionnaire. Sci Total Environ 502:673–679
Palmer S, Cooper C, Thomas K (2004) A model of work stress. Counselling at work. Winter, 5, 25
Thayer JF, Verkuil B, Brosschotj JF, Kevin K, West A, Sterling C et al (2010) Effects of the physical work environment on physiological measures of stress. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehab 17(4):431–439
Williams S, Cooper CL (1998) Measuring occupational stress: development of the pressure management indicator. J Occup Health Psychol 3(4):306
Lambert VA, Lambert CE (2001) Literature review of role stress/strain on nurses: an international perspective. Nurs Health Sci 3(3):161–172
Kumar V, Kumar S (2014) Workplace spirituality as a moderator in relation between stress and health: an exploratory empirical assessment. Int Rev Psychiatry 26(3):344–351
Shukla A, Srivastava R (2016) Development of short questionnaire to measure an extended set of role expectation conflict, coworker support and work-life balance: the new job stress scale. Cogent Bus Manage 3(1):1
Chen JG, Jung HS, Peacock BJ (1994) A fuzzy sets modelling approach for ergonomic workload stress analysis. Int J Ind Ergon 13(3):189–216
Fahlen G, Peter R, Knutsson A (2004) The effort-reward imbalance model of psychosocial stress at the workplace—a comparison of ERI exposure assessment using two estimation methods. Work Stress 18(1):81–88
Nübling M, Stößel U, Hasselhorn HM, Michaelis M, Hofmann F (2006) Measuring psychological stress and strain at work—evaluation of the COPSOQ questionnaire in Germany. GMS Psycho-Soc Med 3
Padma V, Anand NN, Gurukul SS, Javid SSM, Prasad A, Arun S (2015) Health problems and stress in information technology and business process outsourcing employees. J Pharm Bioallied Sci 7(Suppl 1):S9
Vinodh S, Chintha SK (2011) Leanness assessment using multi-grade fuzzy approach. Int J Prod Res 49(2):431–445
Vinodh S (2011) Assessment of sustainability using multi-grade fuzzy approach. Clean Technol Environ Policy 13(3):509–515
Ganesh J, Suresh M (2016, Dec) Safety practice level assessment using multigrade fuzzy approach: a case of Indian manufacturing company. In: 2016 IEEE International conference on computational intelligence and computing research (ICCIC). IEEE, pp 1–5
Sridharan V, Suresh M (2016, Dec) Environmental sustainability assessment using multigrade fuzzy—a case of two Indian colleges. In: 2016 IEEE International conference on computational intelligence and computing research (ICCIC). IEEE, pp 1–4
Ormanovic S, Ciric A, Talovic M, Alic H, Jeleskovic E, Causevic D (2017) Importance-performance analysis: different approaches. Acta Kinesiol 11:58–66
Dickson D, Ford R, Deng WJ (2008) Fuzzy importance-performance analysis for determining critical service attributes. Int J Serv Ind Manage
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sreedharshini, S., Suresh, M., Lakshmi Priyadarsini, S. (2021). Workplace Stress Assessment of Software Employees Using Multi-grade Fuzzy and Importance Performance Analysis. In: Jeena Jacob, I., Kolandapalayam Shanmugam, S., Piramuthu, S., Falkowski-Gilski, P. (eds) Data Intelligence and Cognitive Informatics. Algorithms for Intelligent Systems. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-8530-2_35
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-8530-2_35
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-8529-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-8530-2
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)