Abstract
Background: Despite the extensive effort on gastric cancer (GC) research and its achievement over the last decades, GC continues to remain the third leading cause of cancer mortality in the world. Detection of key genes involved in gastric cancer progression and prognosis leads to efficient approach to treat cancer.
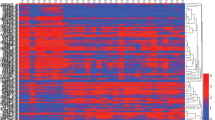
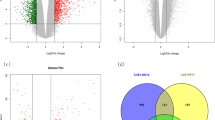
Methods: Two datasets (PRJNA506381 and PRJNA438844) from Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database were analysed using available bioinformatics tools and differently expressed genes (DEGs) were identified. The enrichment, protein–protein interaction (PPI) network and survival analysis were carried out to unaware the potential genes responsible for GC progression.
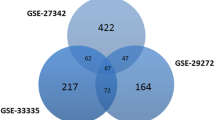
Results: Totally, 227 upregulated and 247 downregulated genes were obtained, out of that overlapping 45 DEGs were selected for further analysis. Protein digestion and absorption and gastric acid secretion were the most enriched pathways. The PPI network was constructed by GeneMANIA and visualized in Cytoscape having 55 nodes and 689 interactions. Subsequently, NetworkAnalyzer plugin in Cytoscape was used and found 13 hub genes (MT1X, MT1E, MT1H, MT1F, MT1G, MT2A, MT1M, MT1A, MT1B, ATP4A, MT1HL1, PGC and CA9) based on high degree of connectivity ≥30. Further, eight highly connecting genes (KCNE2, CPA2, GIF, DRD5, CTSE, CLIC6, CHIA and LIPF) from the highly enriched modules were selected. Also, the prognostic value of the key genes was checked using Kaplan–Meier plotter, in that MT1X, MT1H, MT1E, ATP4A, KCNE2, CPA2, DRD5, CLIC6 and CHIA were associated with survival in overall survival of GC.
Conclusion: These results reveal that 13 hub genes and 8 highly connecting genes might contribute a major role in GC progression. Further, study of CAP2 could be utilised as potential prognostic biomarker.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACRG :
-
Asian Cancer Research Group
- ATP4A :
-
ATPase H+/K+ transporting subunit alpha
- CA9 :
-
Carbonic anhydrase 9
- CBLIF :
-
Cobalamin binding intrinsic factor
- CHIA :
-
Chitinase acidic
- CLIC6 :
-
Chloride intracellular channel 6
- CNE-2:
-
CNE-2 enhancer upstream of SHOX
- CPA2 :
-
Carboxypeptidase A2
- CTSE :
-
Cathepsin E
- DEGs :
-
Differently expressed genes
- DRD5 :
-
Dopamine receptor D5
- GC :
-
Gastric cancer
- GO :
-
Gene ontology
- HTS :
-
High throughput sequencing
- KCNE2 :
-
Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily E member 2
- KEGG :
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- LIPF :
-
Lipase F, gastric type
- MCODE :
-
Molecular complex detection
- MT :
-
Metallothionein
- NCBI :
-
National Centre for Biotechnology Information
- NGS :
-
Next generation sequencing
- PGC :
-
Progastrics in (pepsinogen C)
- PPI :
-
Protein–protein interaction
- SRA :
-
Sequence read archive
References
National Cancer Institute and Editorial Content Team. https://www.cancer.gov/types/stomach/patient/stomach-treatment-pdq. Last Revised 4 Nov 2019
Ma J, Shen H, Kapesa L, Zeng S (2016) Lauren classification and individualized chemotherapy in gastric cancer. Oncol Lett 11:2959–2964
Sitarz R, Skierucha M, Mielko J, Offerhaus J, Maciejewski R, Polkowski W (2018) Gastric cancer: epidemiology, prevention, classification, and treatment. Cancer Manag Res 10:239–248
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68:394–424
Rawla P, Barsouk A (2019) Epidemiology of gastric cancer: global trends, risk factors and prevention. Gastroenterol Rev 14:26–38
Balakrishnan M, George R, Sharma A, Graham DY (2017) Changing trends in stomach cancer throughout the world. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 19:36
McLean MH, El-Omar EM (2014) Genetics of gastric cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 11:664–674
Necula L, Matei L, Dragu D, Neagu AI, Mambet C, Nedeianu S, Bleotu C, Diaconu CC, Chivu-Economescu M (2019) Recent advances in gastric cancer early diagnosis. World J Gastroenterol 25:2029–2044
Chao Wang JZ, Cai M, Zhu Z, Gu W, Yu Y, Zhang X (2015) DBGC: a database of human gastric cancer. PLoS One 10:e0142591
Katona BW, Rustgi AK (2017) Gastric cancer genomics: advances and future directions. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 3:211–217
Wong SS, Kim K-M, Ting JC, Yu K, Fu J, Liu S, Cristescu R, Nebozhyn M, Gong L, Yue YG, Wang J, Ronghua C, Loboda A, Hardwick J, Liu X, Dai H, Jin JG, Ye XS, Kang SY, Do IG, Park JO, Sohn TS, Reinhard C, Lee J, Kim S, Aggarwal A (2014) Genomic landscape and genetic heterogeneity in gastric adenocarcinoma revealed by whole-genome sequencing. Nat Commun 5:5477
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network (2014) Comprehensive molecular characterization of gastric adenocarcinoma. Nature 513:202–209
De Re V, Dolcetti R (2019) Genetic and epigenetic mechanisms in gastric cancer. In: Canzonieri V, Giordano A (eds) Gastric cancer in the precision medicine era: diagnosis and therapy. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 25–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04861-7_2
Puneet, Kazmi HR, Kumari S, Tiwari S, Khanna A, Narayan G (2018) Epigenetic mechanisms and events in gastric cancer-emerging novel biomarkers. Pathol Oncol Res 24:757–770
Liu X, Wu J, Zhang D, Bing Z, Tian J, Ni M, Zhang X, Meng Z, Liu S (2018) Identification of potential key genes associated with the pathogenesis and prognosis of gastric cancer based on integrated bioinformatics analysis. Front Genet 9:265
Leinonen R, Sugawara H, Shumway M (2010) The sequence read archive. Nucleic Acids Res 39:D19–D21
Team RC (2019) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Alboukadel Kassambara AK (2019) Quality control of sequencing data. CRAN
Kaisers W (2019) seqTools: analysis of nucleotide, sequence and quality content on fastq files. R package version 1.20.0
Liao Y, Smyth GK, Shi W (2019) The R package Rsubread is easier, faster, cheaper and better for alignment and quantification of RNA sequencing reads. Nucleic Acids Res 47:e47–e47
Lawrence M, Huber W, Pages H, Aboyoun P, Carlson M, Gentleman R, Morgan MT, Carey VJ (2013) Software for computing and annotating genomic ranges. PLoS Comput Biol 9:e1003118
Gene Ontology Consortium (2006) The Gene Ontology (GO) project in 2006. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D322–D326
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G (2000) Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat Genet 25:25–29
Kuleshov MV, Jones MR, Rouillard AD, Fernandez NF, Duan Q, Wang Z, Koplev S, Jenkins SL, Jagodnik KM, Lachmann A, McDermott MG, Monteiro CD, Gundersen GW, Ma’ayan A (2016) Enrichr: a comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res 44:W90–W97
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13:2498–2504
Franz M, Rodriguez H, Lopes C, Zuberi K, Montojo J, Bader GD, Morris Q (2018) GeneMANIA update 2018. Nucleic Acids Res 46:W60–W64
Nagy Á, Lánczky A, Menyhárt O, Győrffy B (2018) Validation of miRNA prognostic power in hepatocellular carcinoma using expression data of independent datasets. Sci Rep 8:9227
Kim N, Jung HC (2010) The role of serum pepsinogen in the detection of gastric cancer. Gut Liver 4:307–319
Si M, Lang J (2018) The roles of metallothioneins in carcinogenesis. J Hematol Oncol 11:107
Gomulkiewicz A, Podhorska-Okolow M, Szulc R, Smorag Z, Wojnar A, Zabel M, Dziegiel P (2010) Correlation between metallothionein (MT) expression and selected prognostic factors in ductal breast cancers. Folia Histochem Cytobiol 48:242–248
Cardoso SV, Barbosa HM, Candellori IM, Loyola AM, Aguiar MC (2002) Prognostic impact of metallothionein on oral squamous cell carcinoma. Virchows Arch 441:174–178
Hishikawa Y, Kohno H, Ueda S, Kimoto T, Dhar DK, Kubota H, Tachibana M, Koji T, Nagasue N (2001) Expression of metallothionein in colorectal cancers and synchronous liver metastases. Oncology 61:162–167
Hengstler JG, Pilch H, Schmidt M, Dahlenburg H, Sagemuller J, Schiffer I, Oesch F, Knapstein PG, Kaina B, Tanner B (2001) Metallothionein expression in ovarian cancer in relation to histopathological parameters and molecular markers of prognosis. Int J Cancer 95:121–127
Wulfing C, van Ahlen H, Eltze E, Piechota H, Hertle L, Schmid KW (2007) Metallothionein in bladder cancer: correlation of overexpression with poor outcome after chemotherapy. World J Urol 25:199–205
Tong M, Lu W, Liu H, Wu J, Jiang M, Wang X, Hao J, Fan D (2019) Evaluation of MT family isoforms as potential biomarker for predicting progression and prognosis in gastric cancer. Biomed Res Int 2019:1–15
Galizia G, Ferraraccio F, Lieto E, Orditura M, Castellano P, Imperatore V, La Manna G, Pinto M, Ciardiello F, La Mura A, De Vita F (2006) p27 downregulation and metallothionein overexpression in gastric cancer patients are associated with a poor survival rate. J Surg Oncol 93:241–252
Janssen AM, van Duijn W, Kubben FJ, Griffioen G, Lamers CB, van Krieken JH, van de Velde CJ, Verspaget HW (2002) Prognostic significance of metallothionein in human gastrointestinal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 8:1889–1896
Shen S, Jiang J, Yuan Y (2017) Pepsinogen C expression, regulation and its relationship with cancer. Cancer Cell Int 17:57
Melle C, Ernst G, Schimmel B, Bleul A, Kaufmann R, Hommann M, Richter KK, Daffner W, Settmacher U, Claussen U, von Eggeling F (2005) Characterization of pepsinogen C as a potential biomarker for gastric cancer using a histo-proteomic approach. J Proteome Res 4:1799–1804
Xu Q, Sun LP, Wang BG, Liu JW, Li P, He CY, Yuan Y (2013) The co-expression of functional gastric proteins in dynamic gastric diseases and its clinical significance. BMC Clin Pathol 13:21
Benej M, Pastorekova S, Pastorek J (2014) Carbonic anhydrase IX: regulation and role in cancer. Subcell Biochem 75:199–219
Chen J, Rocken C, Hoffmann J, Kruger S, Lendeckel U, Rocco A, Pastorekova S, Malfertheiner P, Ebert MP (2005) Expression of carbonic anhydrase 9 at the invasion front of gastric cancers. Gut 54:920–927
Abbott GW, Roepke TK (2016) KCNE2 and gastric cancer: bench to bedside. Oncotarget 7:17286–17287
Wu W, Juan WC, Liang CR, Yeoh KG, So J, Chung MC (2012) S100A9, GIF and AAT as potential combinatorial biomarkers in gastric cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Proteomics Clin Appl 6:152–162
Leng ZG, Lin SJ, Wu ZR, Guo YH, Cai L, Shang HB, Tang H, Xue YJ, Lou MQ, Zhao W, Le WD, Zhao WG, Zhang X, Wu ZB (2017) Activation of DRD5 (dopamine receptor D5) inhibits tumor growth by autophagic cell death. Autophagy 13:1404–1419
Konno-Shimizu M, Yamamichi N, Inada K, Kageyama-Yahara N, Shiogama K, Takahashi Y, Asada-Hirayama I, Yamamichi-Nishina M, Nakayama C, Ono S, Kodashima S, Fujishiro M, Tsutsumi Y, Ichinose M, Koike K (2013) Cathepsin E is a marker of gastric differentiation and signet-ring cell carcinoma of stomach: a novel suggestion on gastric tumorigenesis. PLoS One 8:e56766
Ossandon FJ, Villarroel C, Aguayo F, Santibanez E, Oue N, Yasui W, Corvalan AH (2008) In silico analysis of gastric carcinoma Serial Analysis of Gene Expression libraries reveals different profiles associated with ethnicity. Mol Cancer 7:22
Kong Y, Zheng Y, Jia Y, Li P, Wang Y (2016) Decreased LIPF expression is correlated with DGKA and predicts poor outcome of gastric cancer. Oncol Rep 36:1852–1860
Liu X, Chang X (2016) Identifying module biomarkers from gastric cancer by differential correlation network. Onco Targets Ther 9:5701–5711
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Sinnarasan, V.S.P., Paul, D., Naorem, L.D., Muthaiyan, M., Ampasala, D.R., Venkatesan, A. (2020). Identification of Potential Key Genes Involved in Progression of Gastric Cancer Using Bioinformatics Analysis. In: Nagaraju, G.P., Peela, S. (eds) Novel therapeutic approaches for gastrointestinal malignancies. Diagnostics and Therapeutic Advances in GI Malignancies. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-5471-1_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-5471-1_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-5470-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-5471-1
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)