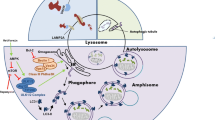
Abstract
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is one of the major kidney diseases associated with poor clinical outcomes both in short- and long-term, which caused by toxins, transient ischemia, and so on. Autophagy is a cellular stress response that plays important roles in the pathogenesis of various diseases, including kidney diseases. Autophagy is induced in proximal tubules during AKI. It has been demonstrated that autophagy plays a renoprotective role in AKI by pharmacological and genetic inhibitory studies. However, the role of autophagy in kidney recovery and repair from AKI remains unknown mostly. In many studies, a dynamic change of autophagy was important for tubular proliferation and repair in the recovery phase of AKI. Moreover, autophagy may not only promote renal fibrosis through inducing tubular atrophy and decomposition but also prevent it by mediating intracellular degradation of excessive collagen in terms of renal fibrosis. In further researches, we expect to clarify the regulation of autophagy in kidney injury and repair, and find out therapeutic drugs for treating AKI and preventing its progression to chronic kidney disease.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolisetty S, Traylor AM, Kim J, Joseph R, Ricart K, Landar A, Agarwal A (2010) Heme oxygenase-1 inhibits renal tubular macroautophagy in acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:1702–1712
Broz DK, Mello SS, Bieging KT, Jiang D, Dusek RL, Brady CA, Sidow A, Attardi LD (2013) Global genomic profiling reveals an extensive p53-regulated autophagy program contributing to key p53 responses. Genes Dev 27(9):1016–1031
Ding Y, Kim S, Lee SY, Koo JK, Wang Z, Choi ME (2014) Autophagy regulates TGF-beta expression and suppresses kidney fibrosis induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction. J Am Soc Nephrol 25:2835–2846
Harris RC, Cheng H (2016) Telomerase, autophagy and acute kidney injury. Nephron 134:145–148
Havasi A, Dong Z (2016) Autophagy and tubular cell death in the kidney. Semin Nephrol 36:174–188
Kim SM, Kim YG, Kim DJ, Park SH, Jeong KH, Lee YH, Lim SJ, Lee SH, Moon JY (2018) Inflammasome-independent role of NLRP3 mediates mitochondrial regulation in renal injury. Front Immunol 9:2563
Kimura T, Takabatake Y, Takahashi A, Kaimori JY, Matsui I, Namba T, Kitamura H, Niimura F, Matsusaka T, Soga T, Rakugi H, Isaka Y (2011) Autophagy protects the proximal tubule from degeneration and acute ischemic injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:902–913
Kume S, Uzu T, Horiike K, Chin-Kanasaki M, Isshiki K, Araki S, Sugimoto T, Haneda M, Kashiwagi A, Koya D (2010) Calorie restriction enhances cell adaptation to hypoxia through Sirt1-dependent mitochondrial autophagy in mouse aged kidney. J Clin Invest 120:1043–1055
Li J, Gui Y, Ren J, Liu X, Feng Y, Zeng Z, He W, Yang J, Dai C (2016) Metformin protects against cisplatin-induced tubular cell apoptosis and acute kidney injury via AMPKalpha-regulated autophagy induction. Sci Rep 6:23975
Molitoris BA (2014) Therapeutic translation in acute kidney injury: the epithelial/endothelial axis. J Clin Invest 124(6):2355–2363
Poluzzi C, Nastase MV, Zeng-Brouwers J, Roedig H, Hsieh LT, Michaelis JB, Buhl EM, Rezende F, Manavski Y, Bleich A, Boor P, Brandes RP, Pfeilschifter J, Stelzer EHK, Munch C, Dikic I, Brandts C, Iozzo RV, Wygrecka M, Schaefer L (2019) Biglycan evokes autophagy in macrophages via a novel CD44/Toll-like receptor 4 signaling axis in ischemia/reperfusion injury. Kidney Int 95:540–562
Tan X, Zhu H, Tao Q, Guo L, Jiang T, Xu L, Yang R, Wei X, Wu J, Li X, Zhang JS (2018) FGF10 protects against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating autophagy and inflammatory signaling. Front Genet 9:556
Xu Y, Ruan S, Wu X, Chen H, Zheng K, Fu B (2013) Autophagy and apoptosis in tubular cells following unilateral ureteral obstruction are associated with mitochondrial oxidative stress. Int J Mol Med 31:628–636
Yadav RK, Lee GH, Lee HY, Li B, Jung HE, Rashid HO, Choi MK, Yadav BK, Kim WH, Kim KW, Park BH, Kim W, Lee YC, Kim HR, Chae HJ (2015) TMBIM6 (transmembrane BAX inhibitor motif containing 6) enhances autophagy and reduces renal dysfunction in a cyclosporine A-induced nephrotoxicity model. Autophagy 11:1760–1774
Zeng Y, Li S, Wu J, Chen W, Sun H, Peng W, Yu X, Yang X (2014) Autophagy inhibitors promoted aristolochic acid I induced renal tubular epithelial cell apoptosis via mitochondrial pathway but alleviated nonapoptotic cell death in mouse acute aritolochic acid nephropathy model. Apoptosis 19:1215–1224
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Science Press and Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Cui, J., Bai, X., Chen, X. (2020). Autophagy and Acute Kidney Injury. In: Le, W. (eds) Autophagy: Biology and Diseases. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 1207. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-4272-5_34
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-4272-5_34
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-4271-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-4272-5
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)