Abstract
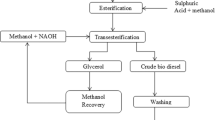
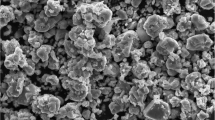
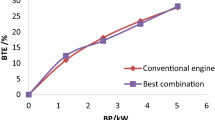
In the present research work, WCO biodiesel with iron oxide nanoparticle samples was considered for DI diesel engine, and its impacts on engine efficiency, combustion, and exhaust gas (emission) characteristics were studied. In this investigation the biodiesel is obtained from WCO by transesterification procedure. The experimental tests were conducted in a CI engine using WCO biodiesel with iron oxide nanoparticles. Engine trials were conducted for all the blends (B20WCOME and B20WCOMEINP75) and the obtained results were compared with diesel. All the tests regarding this work are carried out in a CI engine (diesel engine) at (1500 RPM) constant speed. The biofuel is obtained from WCO and commercially available iron oxide nanoparticles (INP) is used in the present experimental work. INP is added to biodiesel in proportions of 50, 75, and 100 ppm using an Ultrasonicator. The results obtained upon experimentation clearly show that the BTE increases marginally (14.285%) for iron oxide nanoparticles (for 75 ppm) blended WCOME while BSEC decreases (26%) when compared to other blends. The emission levels of oxides of nitrogen (4.87%), carbon oxide (16%), and unburnt hydrocarbons (10%) are marginally decreased as compared to diesel for 75 ppm concentration. From the present experimental work, the blending of iron oxide nanoparticles in WCOME produces most promising results in the CI engine performance with marginal drop in the harmful exhaust gases from CI engines.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramesha D, Prema Kumara K, Abhishek Jain C, Akash N, BabuReddy B, Kallappa R, Kammara M (2015) Experimental investigation on combustion, performance and emission characteristics of plastic oil and biodiesel as a substitute fuel in diesel engine. IRJET 02
Mani M, Nagarajan G, Sampath S (2013) Characteristic and effect of using waste plastic oil and diesel fuel blends in compression ignition engine. Energy 36:212–219
Ramesh DK, Dhananjaya Kumar JL, Hemanth Kumar SG, Namith V, Jambagi PB, Sharath S (2016) Study on effects of Alumina nanoparticles as additive with Poultry litter biodiesel on Performance, Combustion and Emission characteristic of Diesel engine. Mater Today Proc PMME EMT 338:2214–7853
Madheshiyaa AK, Vedrtnama A (2018) Energy-energy analysis of biodiesel fuels produced from waste cooking oil and mustard oil. Fuel 214:386–408
Avinash A, Sasikumar P, Murugesan A (2018) Understanding the interaction among the barriers of biodiesel production from waste cooking oil in India: an interpretive structural modeling approach. Renew Energy
Debbarma S, Misra RD (2017) Effects of iron nanoparticles blended biodiesel on the performance and emission characteristics of a diesel engine. J Energy Res Technol ASME 139
Seela CR, Ravi Sankar B, Kishore D, Babu MVS (2019) Experimental analysis on a DI diesel engine with cerium oxide added Mahua Methyl Ester blends. Int J Ambient Energy. https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2017.1360203
Ashok B, Nanthagopal K, Aravind M, Ajith J, Tamilarasu A (2017) Comparative analysis on the effect of zinc oxide and Ethanox as additives with biodiesel in CI engine. Energy (2017)
Jiaqiang E, Minhhieu P (2017) Effect of different technologies on combustion and emissions of the diesel engine fueled with biodiesel. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 80:620–647
Sadafb S, Iqbala J, Ullahd I (2018) Biodiesel production from waste cooking oil: an efficient technique to convert waste into biodiesel. Sustain Cities Soc 41:220–226
Musthafa MM, Kumar TA, Mohanraj T, Chandramouli R (2018) A comparative study on performance, combustion and emission characteristics of diesel engine fuelled by biodiesel blends with and without an additive. Fuel 225:343–348
Knoth G, Steidley KR (2018) The effect of metals and metal oxides on biodiesel oxidative stability from promotion to inhibition. Fuel Process Technol 177:75–80
Attia AMA, Hassaneen AE (2016) Influence of diesel fuel blended with biodiesel produced from waste cooking oil on diesel engine performance. Fuel 167:316–328
Hwang J, Bae C, Gupta T (2016) Application of waste cooking oil (WCO) biodiesel in a compression ignition engine. Fuel 176:20–31
Vairamuthu G, Sundarapandian S, Kailasanathan C, Thangagiri B (2015) Experimental investigation on the effects of cerium oxide nanoparticle on calophyllum inophyllum (Punnai) biodiesel blended with diesel fuel in di diesel engine modified by nozzle geometry. J Energy Inst 89(4):668–682
D Silvaa R, Binu KG, Thirumaleshwara B (2015) Performance and Emission characteristics of a C.I. Engine fuelled with diesel and TiO2 nanoparticles as fuel additive. Mater Today Proceed 2:728–3735
Man XJ, Cheung CS, Ning Z (2015) Effect of diesel engine operating conditions on the particulate size, nanostructure and oxidation properties when using wasting cooking oil biodiesel. Energy Procedia Energy 66:37–40
Cheung CS, Man XJ, Fong KW, Tsang OK (2015) Effect of waste cooking oil biodiesel on the emissions of a diesel engine. Energy Procedia Energy 66:93–96
Nanthagopal K, Ashok B, Tamilarasu A, Ajith J, Aravind M (2017) Influence on the effect of zinc oxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles as an additive with Calophyllum inophyllum methyl ester in a CI engine. Energy Convers Manage 146:8–19
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bharath, L., Ramesha, D.K. (2020). Performance, Combustion, and Emission Characteristics of Diesel Engine Fuelled with Waste Cooking Oil Biodiesel/Diesel Blends with Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. In: Narasimham, G., Babu, A., Reddy, S., Dhanasekaran, R. (eds) Recent Trends in Mechanical Engineering. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-1124-0_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-1124-0_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-1123-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-1124-0
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)