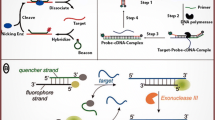
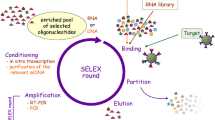
Abstract
Nucleic acid amplification methods are nucleic acid-assistant signal amplification strategies, which have been widely studied and applied for fundamental laboratory research, pharmacogenomics, gene diagnosis , and protein detection for many kinds of infectious diseases or cancers. Up to now, smart design and efficient applications of various nucleic acid molecule-based recycling amplification techniques have emerged as most promising tools, providing greatly enhanced sensitivity and selectivity for the targets in complicated biological samples, including blood, urine, saliva, tissues, and even living cells . Understanding the principles, characteristics, and dynamics of these amplification strategies is of great importance to their applications and research.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andras SC, Power JB, Cocking EC (2001) Strategies for signal amplification in nucleic acid detection. Mol Biotechnol 1:29–44
Banér J, Nilsson M, Mendel-Hartvig M et al (1998) Signal amplification of padlock probes by rolling circle replication. Nucleic Acids Res 26:5073–5078
Barany F (1991) Genetic disease detection and DNA amplification using cloned thermostable ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:189–193
Bi S, Yue S, Zhang SS (2017) Hybridization chain reaction: a versatile molecular tool for biosensing, bioimaging, and biomedicine. Chem Soc Rev 46:4281–4298
Blanco L, Bernad A, Lázaro JM et al (1989) Highly efficient DNA synthesis by the phage phi 29 DNA polymerase. Symmetrical mode of DNA replication. J Biol Chem 264:8935–8940
Breaker RR, Joyce GF (1994) A DNA enzyme that cleaves RNA. Chem Bio 4:223–229
Breaker RR, Joyce GF (1995) A DNA enzyme with Mg2+-dependent RNA phosphoesterase activity. Chem Bio 2:655–660
Cao W (2004) Recent developments in ligase-mediated amplification and detection. Trends Biotechnol 1:38–44
Chow WHA, McCloskey C, Tong YH et al (2008) Application of isothermal helicase-dependent amplification with a disposable detection device in a simple sensitive stool test for toxigenic Clostridium difficile. J Mol Diagn 10:452–458
Davis JD, Riley PK, Peters CW et al (1998) A comparison of ligase chain reaction to polymerase chain reaction in the detection of Chlamydia trachomatis endocervical infections. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol 2:257–260
Dirks RM, Pierce NA (2004) Triggered amplification by hybridization chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:15275–15278
Erlich HA, Gelfand D, Sninsky JJ (1991) Recent advances in the polymerase chain reaction. Science 252:1643–1651
Fire A, Xu SQ (1995) Biological sciences rolling replication of short DNA circles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:4641–4645
Gibbs RA (1991) Polymerase chain reaction techniques. Curr Opin Biotechnol 2:69–75
Goldmeyer J, Kong HM, Tang W (2007) Development of a novel one-tube isothermal reverse transcription thermophilic helicase-dependent amplification platform for rapid RNA detection. J Mol Diagn 5:9639–9644
Gong L, Zhao Z, Lv YF et al (2015) DNAzyme-based biosensors and nanodevices. Chem Commun 51:979–995
Guo Q, Yang X, Wang K, Tan W et al (2009) Sensitive fluorescence detection of nucleic acids based on isothermal circular strand-displacement polymerization reaction. Nucleic Acids Res 37:e20
Liu JW, Cao ZH, Lu Y (2009) Functional nucleic acid sensors. Chem Rev 109:1948–1998
Mahalanabis M, Do J, ALmuayad H (2010) An integrated disposable device for DNA extraction and helicase dependent amplification. Biomed Microdevices 12:353–359
Marshall RL, Laffler TG, Cerney MB et al (1994) Detection of HCV RNA by the asymmetric gap ligase chain reaction. PCR Methods Appl 2:80–84
Monis PT, Giglio S (2006) Nucleic acid amplification-based techniques for pathogen detection and identification. Infect Genet Evol 1:2–12
Mori Y, Notomi T (2009) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): a rapid, accurate, and cost-effective diagnostic method for infectious diseases. J Infect Chemother 15:62–69
Mullis KB, Faloona FA (1987) Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerasecatalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol 155:335–350
Notomi T, Okayama H, Masubuchi H et al (2000) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 28:e63
Ramalingam N, San TC, Kai TJ et al (2009) Microfluidic devices harboring unsealed reactors for real-time isothermal helicase-dependent amplification. Microfluid Nanofluidics 7:325–336
Saiki RK, Scharf S, Faloona F et al (1985) Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science 230:1350–1354
Saiki RK, Gelfand DH, Stoffel S et al (1988) Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science 239:487–491
Shen W, Deng H, Gao Z (2012) Gold nanoparticle-enabled real-time ligation chain reaction for ultrasensitive detection of DNA. J Am Chem Soc 36:14678–14681
Shin GW, Chung B, Jung GY (2014) Multiplex ligase-based genotyping methods combined with CE. Electrophoresis 7:1004–1016
Srinivas N, Ouldridge TE, Šulc P et al (2013) On the biophysics and kinetics of toehold-mediated DNA strand displacement. Nucleic Acids Res 44:10641–10658
Tomita N, Mori Y, Kanda H et al (2008) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) of gene sequences and simple visual detection of products. Nat Protoc 3:877–882
Tong YH, Lemieux B, Kong HM (2011) Multiple strategies to improve sensitivity, speed and robustness of isothermal nucleic acid amplification for rapid pathogen detection. BMC Biotechnol 11:50
Vincent M, Xu Y, Kong H (2004) Helicase-dependent isothermal DNA amplification. EMBO Rep 5:795–800
Walker GT, Little MC, Nadeau JG et al (1992a) Isothermal in vitro amplification of DNA by a restriction enzyme/DNA polymerase system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:392–396
Walker GT, Fraiser MS, Schram JL et al (1992b) Strand displacement amplification—an isothermal, in vitro DNA amplification technique. Nucleic Acids Res 20:1691–1696
Willner I, Shlyahovsky B, Zayats M et al (2008) DNAzymes for sensing, nanobiotechnology and logic gate applications. Chem Soc Rev 37:1153–1165
Wu Z, Zhen Z, Jiang JH (2009) Terminal protection of small-molecule-linked DNA for sensitive electrochemical detection of protein binding via selective carbon nanotube assembly. J Am Chem Soc 131:12325–12332
Yin P, Choi HM, Calvert CR et al (2008) Programming bio-molecular self-assembly pathways. Nature 451:318–322
Zhang DY, Winfree E (2009) Control of DNA strand dis-placement kinetics using toehold exchange. J Am Chem Soc 131:17303–17314
Zhang DY, Turberfield AJ, Yurke B et al (2007) Engineering entropy-driven reactions and networks catalyzed by DNA. Science 318:1121–1125
Zhang Y, Park S, Liu K et al (2011) A surface topography assisted droplet manipulation platform for biomarker detection and pathogen identification. Lab Chip 11:398–406
Zhang X, Lowe SB, Gooding JJ (2014) Brief review of monitoring methods for loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). Biosens Bioelectron 61:491–499
Zhao YX, Chen F, Li Q et al (2015) Isothermal amplification of nucleic acids. Chem Rev 115:12491–12545
Zhou H, Zhang YY, Liu J et al (2013) Efficient quenching of electrochemiluminescence from K-doped graphene-CdS: Eu NCs by G-quadruplex-hemin and target recycling-assisted amplification for ultrasensitive DNA biosensing. Chem Commun 49:2246–2248
Zhou H, Liu J, Xu JJ et al (2018) Optical nano-biosensing interface via nucleic acid amplification strategy: construction and application. Chem Soc Rev 47:1996–2019
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Zhou, H. (2019). Nucleic Acid Amplification Strategies for Biosensing, Bioimaging, and Biomedicine. In: Zhang, S., Bi, S., Song, X. (eds) Nucleic Acid Amplification Strategies for Biosensing, Bioimaging and Biomedicine. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-7044-1_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-7044-1_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-13-7043-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-13-7044-1
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)