Abstract
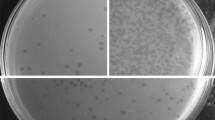
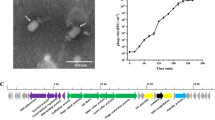
A virulent phage H6 infecting Lactobacillus brevis was isolated from the fermented Chinese cabbage samples, and its biological characteristics were determined. The electron microscope result showed that the phage had an icosahedra head of 93.3 nm in diameter and a long contractile tail about 166.6 nm in length, and it was classified as a lytic phage of Myoviridae in Caudovirales. The restriction enzymes analysis indicated that phage H6 was a dsDNA virus with a genome size of approximately 59.6–61.2 kb. The SDS-PAGE analysis displayed six protein bands with different amounts. As inferred from the one-step growth curve, the latent period of phage H6 was about 90 min and the burst size was about 40.4 pfu/infection center.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pederson CS, Albury MN (1969) The sauerkraut fermentation. New York State Agricultural Experiment Station Technical Bulletin 824. Geneva, New York
Lee JS, Heo GY, Lee JW, Oh YJ, Park JA, Park YH, Pyun YR, Ahn JS (2005) Analysis of kimchi microflora using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Int J Food Microbiol 102(2):143–150
Plengvidhya V, Breidt F Jr, Lu Z, Fleming HP (2007) DNA fingerprinting of lactic acid bacteria in sauerkraut fermentations. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(23):7697–7702
Medina E, Pérez-Díaz IM, Breidt F, Hayes J, Franco W, Butz N, Azcarate-Peril MA (2016) Bacterial ecology of fermented cucumber rising pH spoilage as determined by nonculture-based methods. J Food Sci 81(1):M121–M129
Chen YS, Wu HC, Lo HY, Lin WC, Hsu WH, Lin CW, Lin PY, Yanagida F (2012) Isolation and characterisation of lactic acid bacteria from jiang-gua (fermented cucumbers), a traditional fermented food in Taiwan. J Sci Food Agric 92(10):2069–2075
Lu Z, Breidt F, Plengvidhya V, Fleming HP (2003) Bacteriophage ecology in commercial sauerkraut fermentations. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:3192–3202
Yoon S-S, Barrangou-Poueys R, Breidt F, Klaenhammer TR, Fleming HP (2002) Isolation and characterization of bacteriophages from fermenting sauerkraut. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(2):973–976
Lu Z, Perez-Diaz IM, Hayes JS, Breidt F (2012) Bacteriophage ecology in a commercial cucumber fermentation. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(24):8571–8578
Kleooen HP, Holo H, Jeon SR, Nes IF, Yoon SS (2012) Novel Podoviridae family bacteriophage infecting Weissella cibaria isolated from Kimchi. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(20):7299–7308
Yan P, Chai Z, Xue W, Chang X, Kong D, Zhang H (2009) Lactic acid bacteria diversity in fermented cabbage estimated by culture-dependent and -independent. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 49(3):383–388
De Man JC, Rogosa M, Sharpe ME (1960) A medium for the cultivation of lactobacilli. J Appl Bacteriol 23(1):130–135
Gürtler V, Stanisich VA (1996) New approaches to typing and identification of bacteria using the 16S–23S rDNA spacer region. Microbiology 142(Pt 1):3–16
Jaomanjaka F, Ballestra P, Dols-lafargue M, Le Marrec C (2013) Expanding the diversity of oenococcal bacteriophages: insights into a novel group based on the integrase sequence. Int J Food 166(2):331–340
Nugent KM, Cole RM (1977) Characterization of group H streptococcal temperate bacteriophage phi 227. J Virol 21(3):1061–1073
Yang H, Liang L, Lin S, Jia S (2010) Isolation and characterization of a virulent bacteriophage of Acinetobacter baumannii. BMC Microbiol 10:131; PMID: 20426877; 1471-2180-10-131
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning. CSHL Press, New York
Chow JJ, Batt CA, Sinskey AJ (1988) Characterization of Lactobacillus bulgaricus bacteriophage ch2. Appl Environ Microbiol 54(5):1138–1142
Jung JY, Lee SH, Kim JM, Park MS, Bae JW, Hahn Y, Madsen EL, Jeon CO (2011) Metagenomic analysis of kimchi, a traditional Korean fermented food. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(7):2264–2274
Yoon S-S, Barrangou-Poueys R, Breidt F, Fleming HP (2007) Detection and characterization of a lytic Pediococcus bacteriophage from the fermenting cucumber brine. J Microbiol Biotechnol 17:262–270
Moineau S, Levesque C (2005) Control of bacteriophages in industrial fermentation. In: Kutte E, Sulakvelidze A (eds) Bacteriophage: biology and applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 286–296
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants 31370205 and 30970114).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Huang, K., Zhang, T., Yang, H. (2018). Isolation and Characterization of a Virulent Phage H6 Infecting Lactobacillus brevis from the Fermented Chinese Cabbage. In: Liu, H., Song, C., Ram, A. (eds) Advances in Applied Biotechnology. ICAB 2016. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 444. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-4801-2_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-4801-2_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-4800-5
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-4801-2
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)